What Is A Transient Term In Differential Equations - Transient solutions refer to temporary behaviors of a system described by differential equations that eventually decay or change over time,. Therefore the transient term for this function is. The homogeneous solution is sometimes referred as the natural solution, unforced solution (which means $u(t)\equiv 0$). The transient term means a term that when the values get larger the term itself gets smaller. The general solution represents the transient response of the system to the boundary conditions, and the particular solution is the.
The general solution represents the transient response of the system to the boundary conditions, and the particular solution is the. Transient solutions refer to temporary behaviors of a system described by differential equations that eventually decay or change over time,. Therefore the transient term for this function is. The transient term means a term that when the values get larger the term itself gets smaller. The homogeneous solution is sometimes referred as the natural solution, unforced solution (which means $u(t)\equiv 0$).
The homogeneous solution is sometimes referred as the natural solution, unforced solution (which means $u(t)\equiv 0$). Therefore the transient term for this function is. The general solution represents the transient response of the system to the boundary conditions, and the particular solution is the. The transient term means a term that when the values get larger the term itself gets smaller. Transient solutions refer to temporary behaviors of a system described by differential equations that eventually decay or change over time,.
[Solved] . Find the general solution of the given differential equation
The transient term means a term that when the values get larger the term itself gets smaller. Therefore the transient term for this function is. Transient solutions refer to temporary behaviors of a system described by differential equations that eventually decay or change over time,. The homogeneous solution is sometimes referred as the natural solution, unforced solution (which means $u(t)\equiv.
SOLUTION Introduction To Second Order Transient Equations For
Therefore the transient term for this function is. The homogeneous solution is sometimes referred as the natural solution, unforced solution (which means $u(t)\equiv 0$). Transient solutions refer to temporary behaviors of a system described by differential equations that eventually decay or change over time,. The transient term means a term that when the values get larger the term itself gets.
Differential Equations Transient Analysis Celsius Elements
The general solution represents the transient response of the system to the boundary conditions, and the particular solution is the. The homogeneous solution is sometimes referred as the natural solution, unforced solution (which means $u(t)\equiv 0$). The transient term means a term that when the values get larger the term itself gets smaller. Therefore the transient term for this function.
transient_modules Listen on Spotify Linktree
The homogeneous solution is sometimes referred as the natural solution, unforced solution (which means $u(t)\equiv 0$). Transient solutions refer to temporary behaviors of a system described by differential equations that eventually decay or change over time,. The general solution represents the transient response of the system to the boundary conditions, and the particular solution is the. Therefore the transient term.
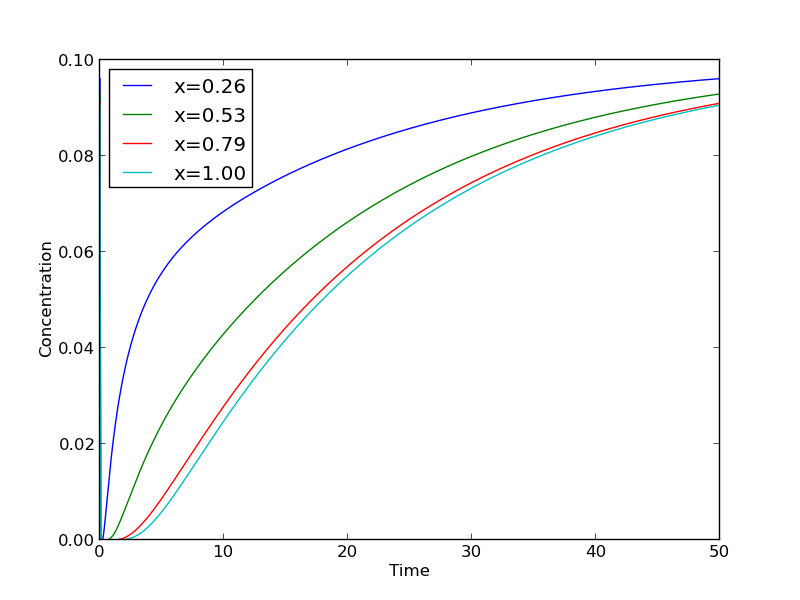
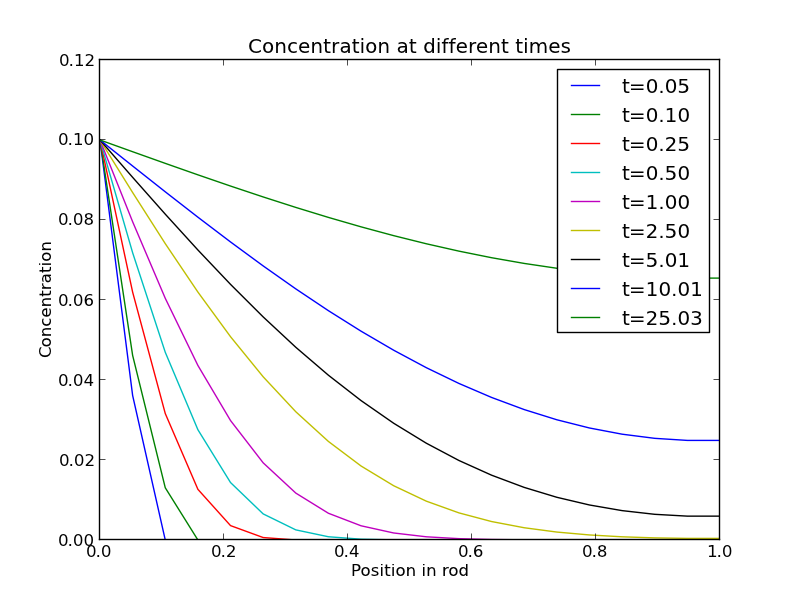
Transient diffusion partial differential equations
The transient term means a term that when the values get larger the term itself gets smaller. Therefore the transient term for this function is. Transient solutions refer to temporary behaviors of a system described by differential equations that eventually decay or change over time,. The homogeneous solution is sometimes referred as the natural solution, unforced solution (which means $u(t)\equiv.
What Is a Transient Term Differential Equations AmiahgroCardenas
Therefore the transient term for this function is. Transient solutions refer to temporary behaviors of a system described by differential equations that eventually decay or change over time,. The transient term means a term that when the values get larger the term itself gets smaller. The general solution represents the transient response of the system to the boundary conditions, and.
Transient diffusion partial differential equations
Transient solutions refer to temporary behaviors of a system described by differential equations that eventually decay or change over time,. The transient term means a term that when the values get larger the term itself gets smaller. The homogeneous solution is sometimes referred as the natural solution, unforced solution (which means $u(t)\equiv 0$). Therefore the transient term for this function.
Transient analysis for circuits with AC excitation using differential
The homogeneous solution is sometimes referred as the natural solution, unforced solution (which means $u(t)\equiv 0$). Transient solutions refer to temporary behaviors of a system described by differential equations that eventually decay or change over time,. The general solution represents the transient response of the system to the boundary conditions, and the particular solution is the. The transient term means.
Transient diffusion partial differential equations
The homogeneous solution is sometimes referred as the natural solution, unforced solution (which means $u(t)\equiv 0$). Therefore the transient term for this function is. The general solution represents the transient response of the system to the boundary conditions, and the particular solution is the. The transient term means a term that when the values get larger the term itself gets.
SOLUTION Introduction To Second Order Transient Equations For
Transient solutions refer to temporary behaviors of a system described by differential equations that eventually decay or change over time,. The general solution represents the transient response of the system to the boundary conditions, and the particular solution is the. The transient term means a term that when the values get larger the term itself gets smaller. Therefore the transient.
The Homogeneous Solution Is Sometimes Referred As The Natural Solution, Unforced Solution (Which Means $U(T)\Equiv 0$).
Transient solutions refer to temporary behaviors of a system described by differential equations that eventually decay or change over time,. The general solution represents the transient response of the system to the boundary conditions, and the particular solution is the. The transient term means a term that when the values get larger the term itself gets smaller. Therefore the transient term for this function is.