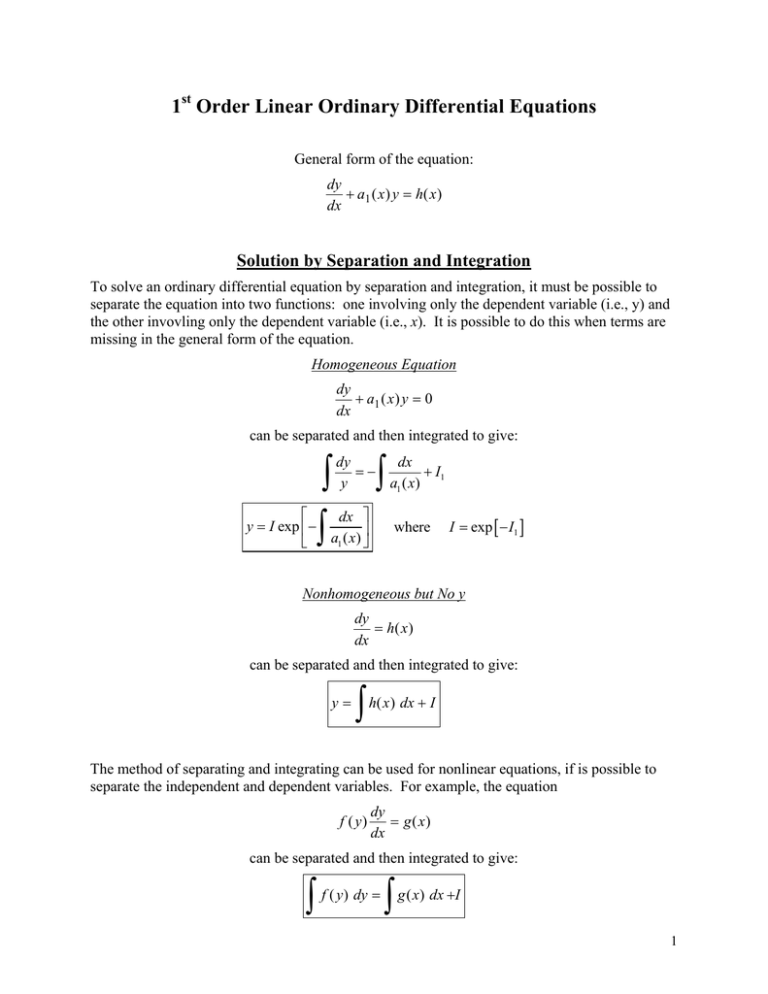
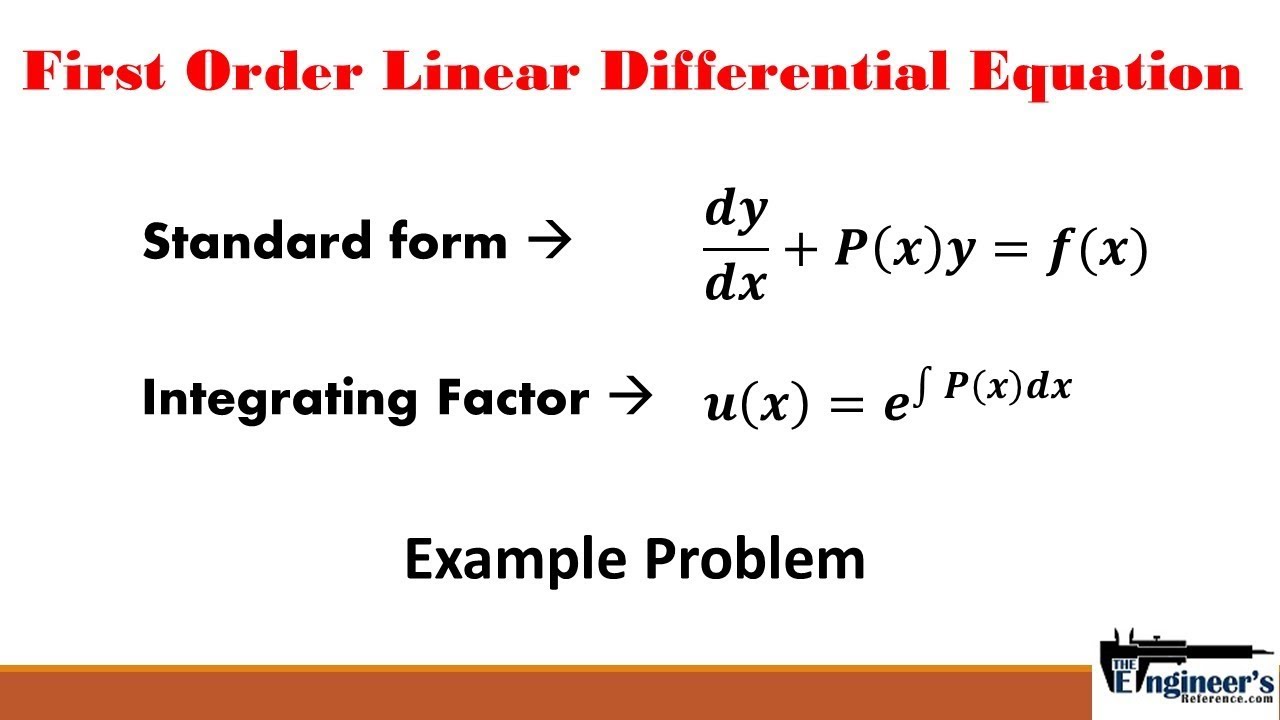
What Is A Linear Ordinary Differential Equation - A linear differential equation is a differential equation that is defined by a linear polynomial in the unknown function and its derivatives, that is. The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or. Differential equation, ordinary) that is linear in the unknown function of one independent variable. What is a linear differential equation? State the definition of a linear differential equation. Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations. An ordinary differential equation (cf. If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of y, then they.
An ordinary differential equation (cf. A linear differential equation is a differential equation that is defined by a linear polynomial in the unknown function and its derivatives, that is. The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or. Differential equation, ordinary) that is linear in the unknown function of one independent variable. Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations. What is a linear differential equation? If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of y, then they. State the definition of a linear differential equation.
Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations. An ordinary differential equation (cf. What is a linear differential equation? State the definition of a linear differential equation. If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of y, then they. Differential equation, ordinary) that is linear in the unknown function of one independent variable. The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or. A linear differential equation is a differential equation that is defined by a linear polynomial in the unknown function and its derivatives, that is.
1 Order Linear Ordinary Differential Equations
The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or. A linear differential equation is a differential equation that is defined by a linear polynomial in the unknown function and its derivatives, that is. What is a linear differential equation? State the definition of a linear differential equation. If.
Linear Equation Examples Tessshebaylo
State the definition of a linear differential equation. What is a linear differential equation? Differential equation, ordinary) that is linear in the unknown function of one independent variable. An ordinary differential equation (cf. The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or.
Linear Differential Equation denis
If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of y, then they. What is a linear differential equation? The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or. Differential equation, ordinary) that is linear in the unknown function of one independent variable. An ordinary.
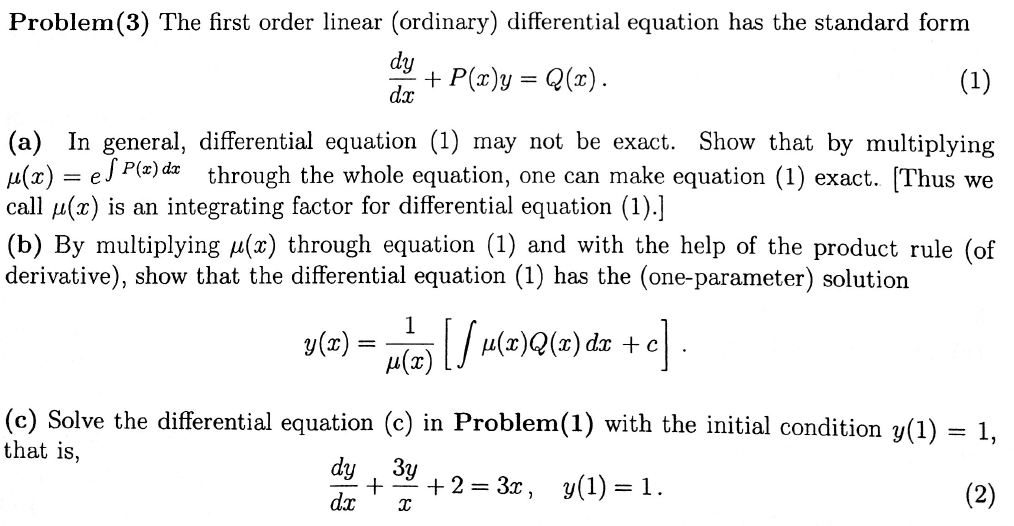
Solved The first order linear (ordinary) differential
The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or. A linear differential equation is a differential equation that is defined by a linear polynomial in the unknown function and its derivatives, that is. Differential equation, ordinary) that is linear in the unknown function of one independent variable. If.
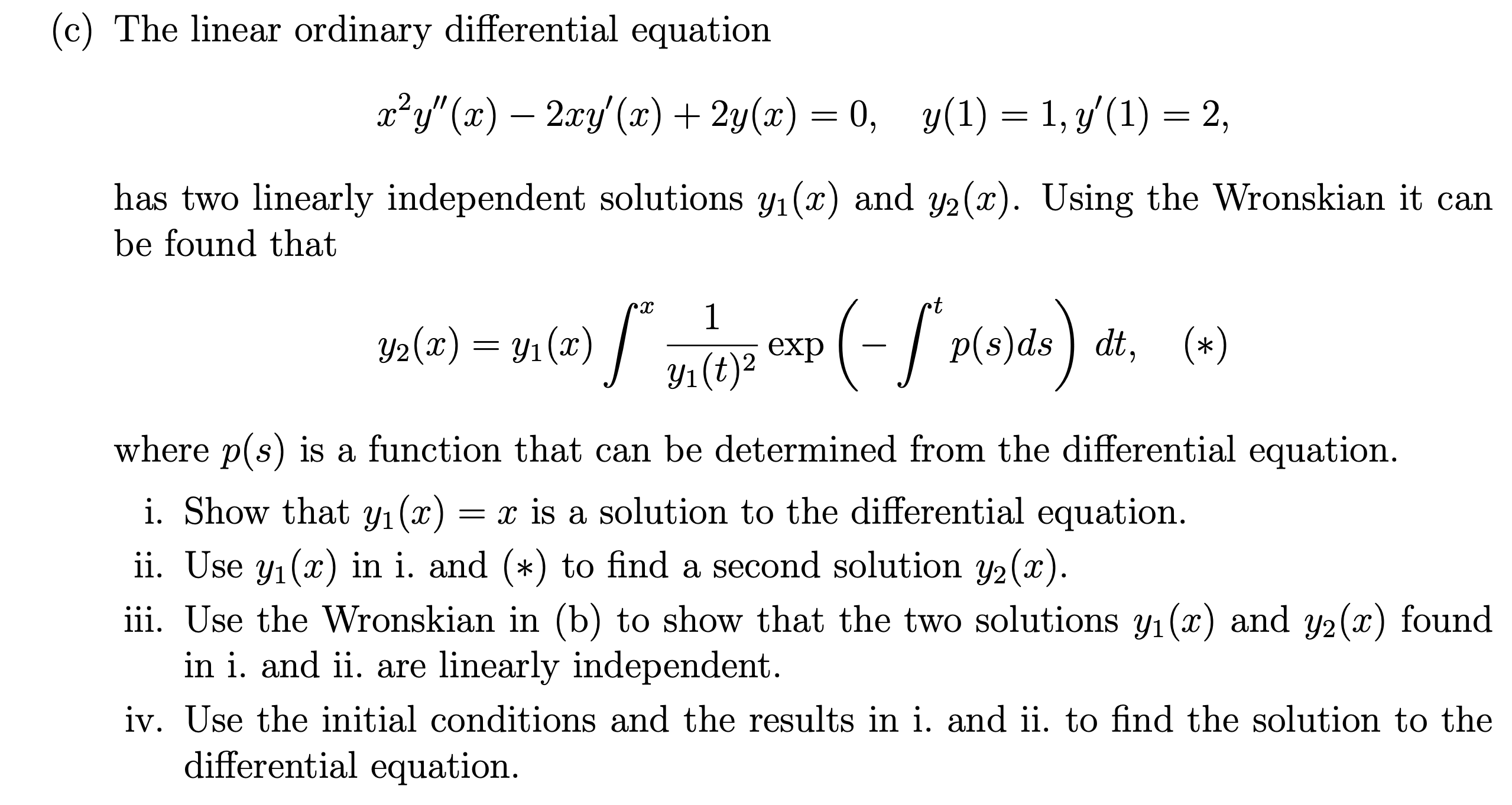
Solved (c) The linear ordinary differential
What is a linear differential equation? An ordinary differential equation (cf. Differential equation, ordinary) that is linear in the unknown function of one independent variable. Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations. If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of y, then they.
Solved A differential equation is given. Classify it as an
Differential equation, ordinary) that is linear in the unknown function of one independent variable. A linear differential equation is a differential equation that is defined by a linear polynomial in the unknown function and its derivatives, that is. The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or. Explain.
Differential Equations (Definition, Types, Order, Degree, Examples)
If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of y, then they. Differential equation, ordinary) that is linear in the unknown function of one independent variable. An ordinary differential equation (cf. Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations. What is a linear differential equation?
What makes a differential equation, linear or Mathematics
Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations. The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or. State the definition of a linear differential equation. A linear differential equation is a differential equation that is defined by a linear polynomial in the unknown function and.
Solved Determine if the equations are (linear or
An ordinary differential equation (cf. Differential equation, ordinary) that is linear in the unknown function of one independent variable. State the definition of a linear differential equation. A linear differential equation is a differential equation that is defined by a linear polynomial in the unknown function and its derivatives, that is. Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple.
Linear Differential Equation denis
State the definition of a linear differential equation. A linear differential equation is a differential equation that is defined by a linear polynomial in the unknown function and its derivatives, that is. The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or. If differential equations can be written as.
What Is A Linear Differential Equation?
An ordinary differential equation (cf. Differential equation, ordinary) that is linear in the unknown function of one independent variable. Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations. If differential equations can be written as the linear combinations of the derivatives of y, then they.
State The Definition Of A Linear Differential Equation.
The linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or. A linear differential equation is a differential equation that is defined by a linear polynomial in the unknown function and its derivatives, that is.