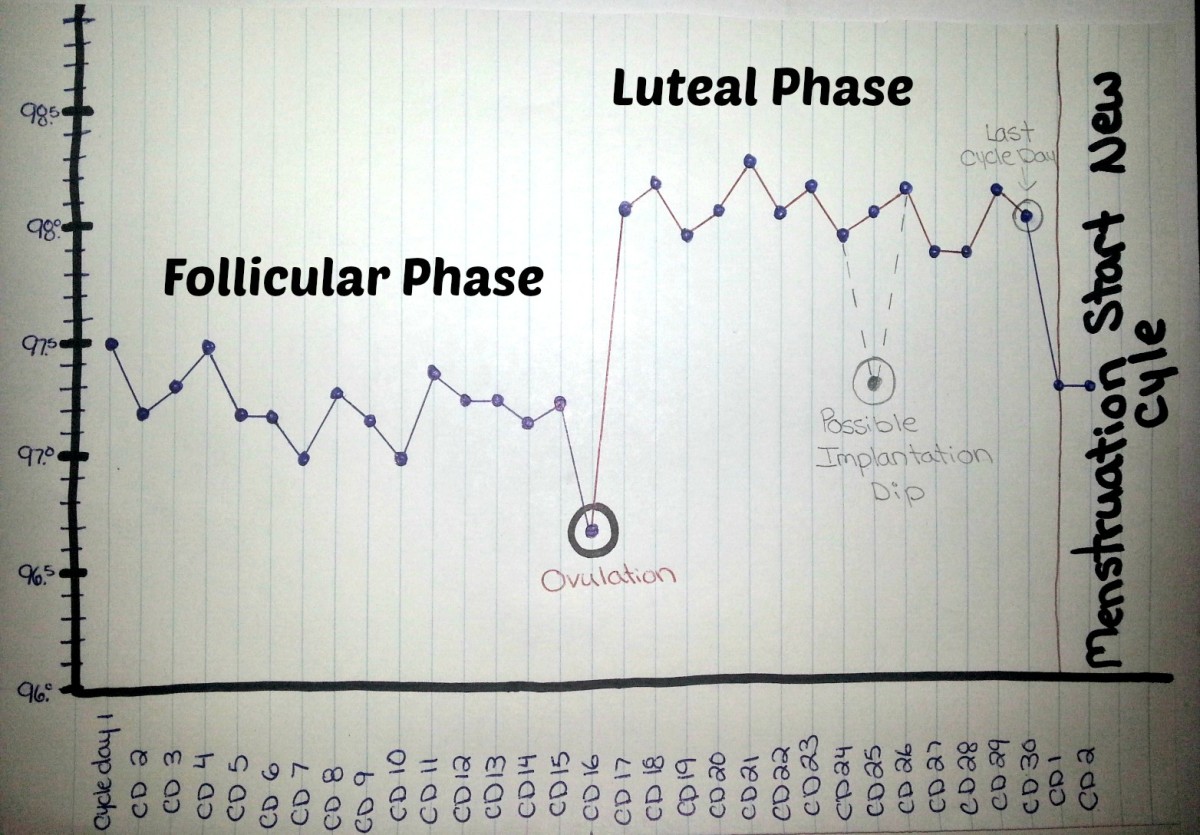
Temp Drop 3 Days After Ovulation - After ovulation, there’s a slight increase in average bbt to between 97.6°f (36.4°c) and 98.6°f (37°c). If a woman is pregnant, this temperature rise will remain higher. However, if a woman isn’t pregnant, it will drop again,. The bbt growth starts immediately. When tracking basal body temperature (bbt) a sustained rise can indicate that ovulation has now occurred. High basal temperature after ovulation is a sign of ovulation itself, which for women when planning pregnancy can be an important indicator. When does temperature drop, before or after ovulation? Before ovulation, your bbt may range from about 97 to 98 degrees f (97.2 to 97.7 degrees f, to be more exact). The basal body temperature can drop before (a rise in estrogen) and after ovulation. To accurately use bbt to help confirm ovulation, temps must rise by a minimum amount for at least 3 days.
The basal body temperature can drop before (a rise in estrogen) and after ovulation. Bbt is a great tool for helping to confirm when ovulation happens! How long should my temperature after ovulation stay up? If fertilization does not occur, the fall in progesterone causes the temperature to again. Carefully observing your cm multiple times a day throughout your cycle will help you identify when your fertile window. In the second case, a decrease in bbt occurs due to implantation of the embryo, with hormonal imbalance, or before the beginning of the period. My temps went up but not significantly. This temperature remains about the same for most of the month, but drops slightly just before ovulation and then spikes just after ovulation. For example, a drop in your basal body temperature after ovulation can have more than one explanation. Some doctors say anything over 10 days is acceptable, but it really makes sense to test for luteal phase.
High basal temperature after ovulation is a sign of ovulation itself, which for women when planning pregnancy can be an important indicator. When does temperature drop, before or after ovulation? For example, a drop in your basal body temperature after ovulation can have more than one explanation. When tracking basal body temperature (bbt) a sustained rise can indicate that ovulation has now occurred. But before you focus on regulating your cycle by tracking the basal. How long should my temperature after ovulation stay up? If fertilization does not occur, the fall in progesterone causes the temperature to again. How long after ovulation does bbt rise? My temps went up but not significantly. Some doctors say anything over 10 days is acceptable, but it really makes sense to test for luteal phase.
How do LH test results influence ovulation detection? Customer
However, if a woman isn’t pregnant, it will drop again,. Bbt is a great tool for helping to confirm when ovulation happens! For example, a drop in your basal body temperature after ovulation can have more than one explanation. In some cases, a bbt drop followed by a sustained increase in temperature after ovulation may indicate that pregnancy has occurred..
Temp drop and fertility friend different O days r/TFABChartStalkers
The bbt growth starts immediately. How long after ovulation does bbt rise? If fertilization does not occur, the fall in progesterone causes the temperature to again. This sustained rise in bbt can be attributed to increased levels of progesterone,. My temps went up but not significantly.
How to Chart Basal Body Temperature WeHaveKids
What's a normal basal body temperature? Implantation dip is a decrease in bbt by at least 0.3 degrees that occurs about a week after ovulation, roughly around the time of implantation, or the point at which a. For example, a drop in your basal body temperature after ovulation can have more than one explanation. High basal temperature after ovulation is.
Temp drop and fertility friend different O days r/TFABChartStalkers
If a woman is pregnant, this temperature rise will remain higher. The bbt growth starts immediately. Bbt is a great tool for helping to confirm when ovulation happens! For most women, an average bbt is around 36.1 to 36.4°c. When tracking basal body temperature (bbt) a sustained rise can indicate that ovulation has now occurred.
Temperature shift and ovulation Tempdrop user support
How long should my temperature after ovulation stay up? In some cases, a bbt drop followed by a sustained increase in temperature after ovulation may indicate that pregnancy has occurred. If a woman is pregnant, this temperature rise will remain higher. The bbt growth starts immediately. The basal body temperature can drop before (a rise in estrogen) and after ovulation.
Why is BBT rising after ovulation (+pregnant charts!)
Bbt is a great tool for helping to confirm when ovulation happens! But before you focus on regulating your cycle by tracking the basal. After ovulation, production stops again and mucus becomes thick to form a barrier plug in the cervix. This sustained rise in bbt can be attributed to increased levels of progesterone,. Implantation dip is a decrease in.
Tempdrop chart with temperatures staying closer to the coverline
When this raised temperature has. How long after ovulation does bbt rise? When tracking basal body temperature (bbt) a sustained rise can indicate that ovulation has now occurred. For most women, an average bbt is around 36.1 to 36.4°c. In some cases, a bbt drop followed by a sustained increase in temperature after ovulation may indicate that pregnancy has occurred.
BBT drop day after 'ovulation'
This temperature remains about the same for most of the month, but drops slightly just before ovulation and then spikes just after ovulation. Before ovulation, your bbt may range from about 97 to 98 degrees f (97.2 to 97.7 degrees f, to be more exact). My temps went up but not significantly. Carefully observing your cm multiple times a day.
Pin by Tempdrop on Tempdrop Charts Menstrual cycle tracker, Fertility
When tracking basal body temperature (bbt) a sustained rise can indicate that ovulation has now occurred. Before ovulation, your bbt may range from about 97 to 98 degrees f (97.2 to 97.7 degrees f, to be more exact). The basal body temperature can drop before (a rise in estrogen) and after ovulation. If a woman is pregnant, this temperature rise.
Ovulation and Temperature Tracking Fertility Natural Cycles
What's a normal basal body temperature? However, if a woman isn’t pregnant, it will drop again,. Before ovulation, your bbt may range from about 97 to 98 degrees f (97.2 to 97.7 degrees f, to be more exact). After ovulation, there’s a slight increase in average bbt to between 97.6°f (36.4°c) and 98.6°f (37°c). How long after ovulation does bbt.
When This Raised Temperature Has.
But the day after you ovulate, you should see an uptick of 0.5 to 1.0. However, if a woman isn’t pregnant, it will drop again,. To accurately use bbt to help confirm ovulation, temps must rise by a minimum amount for at least 3 days. This temperature remains about the same for most of the month, but drops slightly just before ovulation and then spikes just after ovulation.
But Such A Drop Doesn’t Always Happen.
When tracking basal body temperature (bbt) a sustained rise can indicate that ovulation has now occurred. This sustained rise in bbt can be attributed to increased levels of progesterone,. So you cannot rely on. Bbt is a great tool for helping to confirm when ovulation happens!
After Ovulation, There’s A Slight Increase In Average Bbt To Between 97.6°F (36.4°C) And 98.6°F (37°C).
High basal temperature after ovulation is a sign of ovulation itself, which for women when planning pregnancy can be an important indicator. In some cases, a bbt drop followed by a sustained increase in temperature after ovulation may indicate that pregnancy has occurred. What's a normal basal body temperature? My temps went up but not significantly.
In Normal Circumstances (And Without A Pregnancy) Bbt Will Stay.
In the second case, a decrease in bbt occurs due to implantation of the embryo, with hormonal imbalance, or before the beginning of the period. But then on cd 21 my temp sky rocketed and ff changed my ovulation date. The basal body temperature can drop before (a rise in estrogen) and after ovulation. If a woman is pregnant, this temperature rise will remain higher.