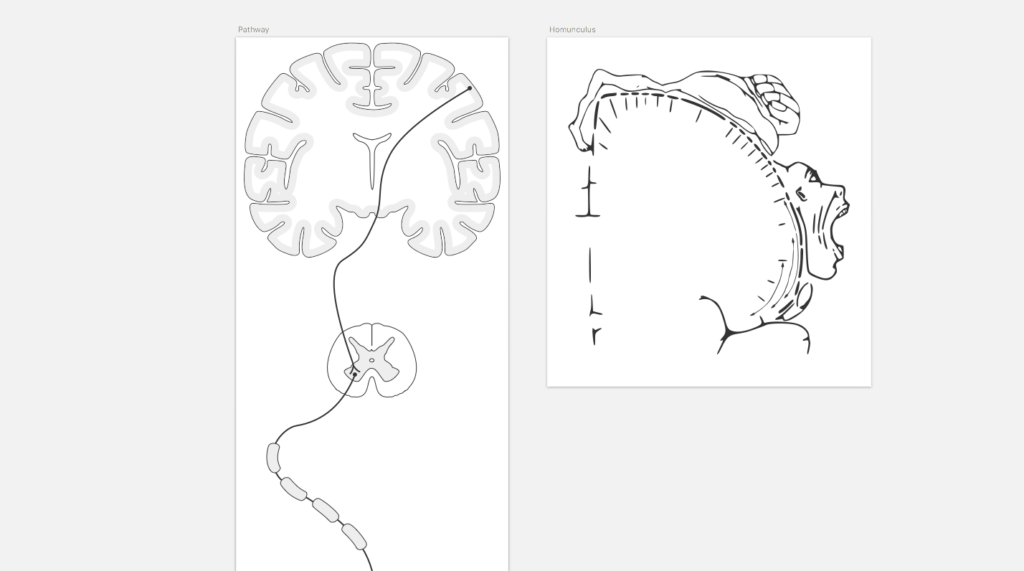
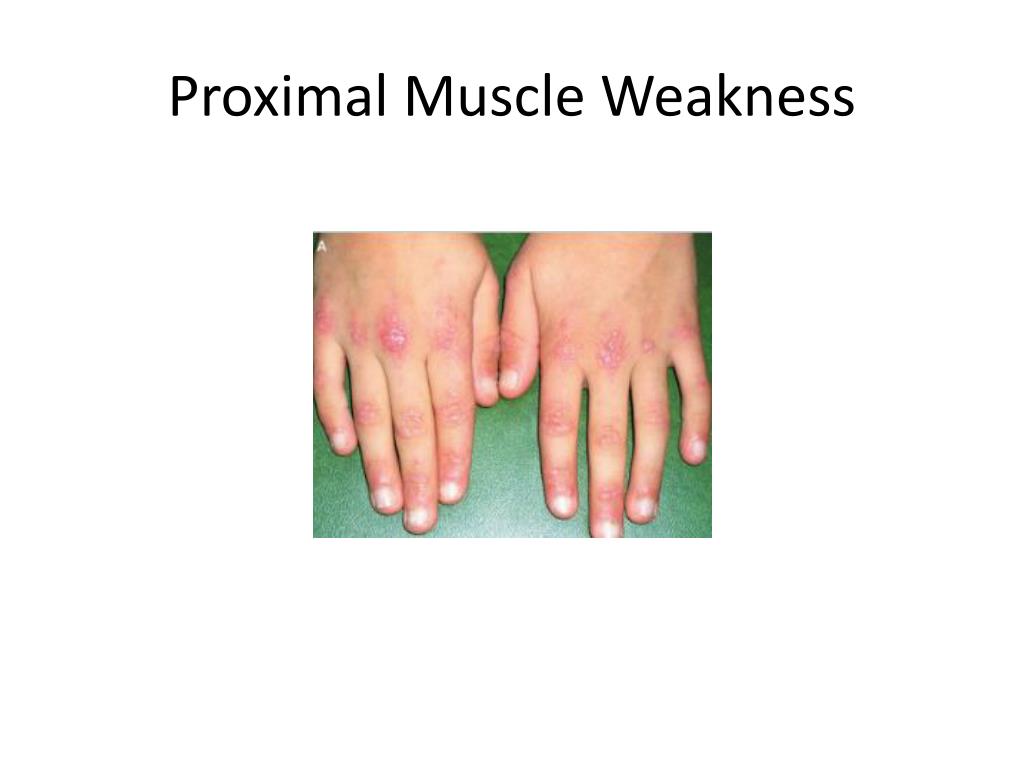
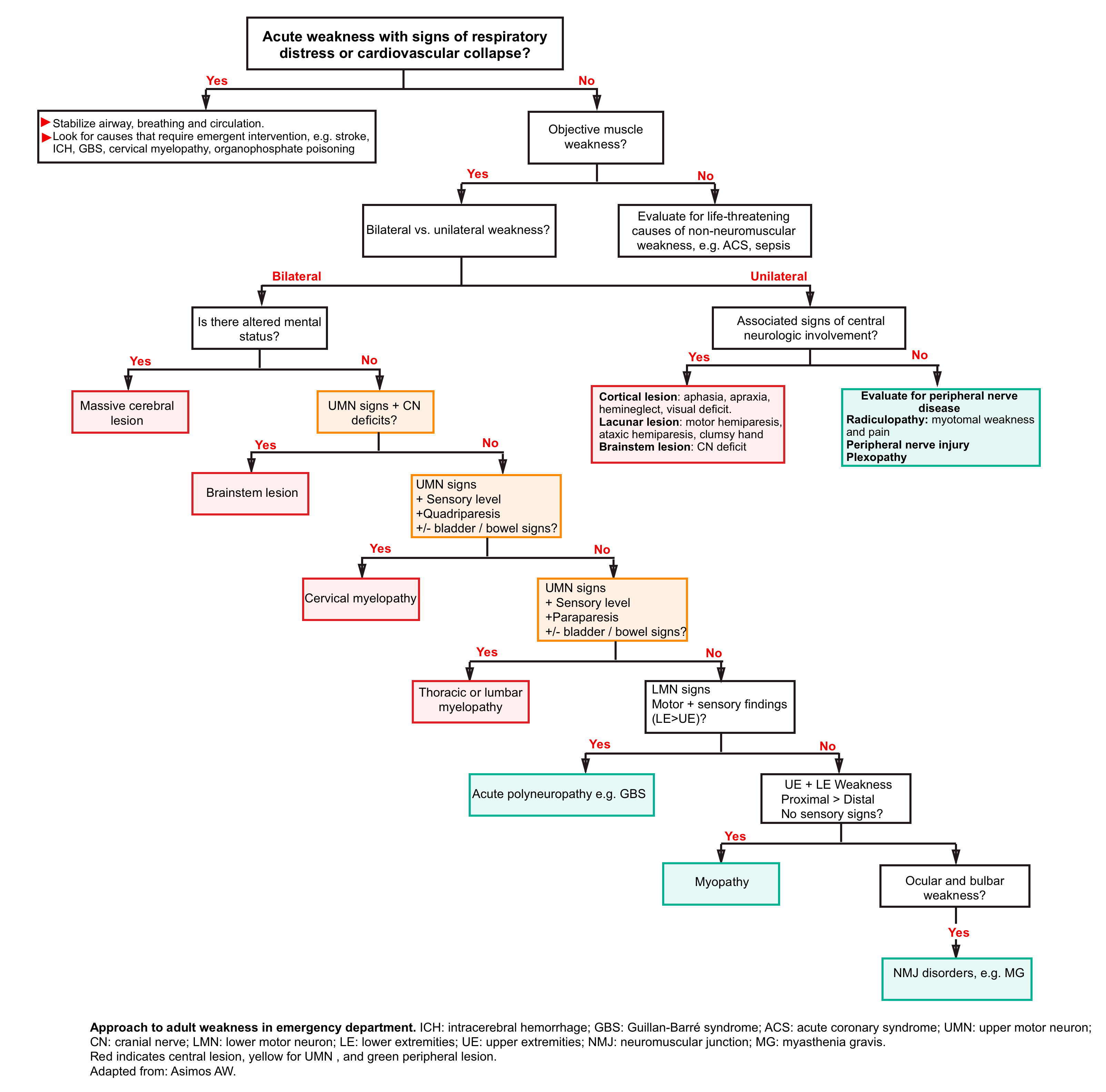
Proximal Weakness Differential - 3 to assess if the. Some of these disorders, such as. Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial blood. Weakness is the predominant feature of primary muscle disorders, or myositides. There is a broad range of. Patients usually complain of proximal muscle weakness of the lower extremities and less commonly myalgia, which begins two weeks to. Proximal myopathy presents as symmetrical weakness of proximal upper and/or lower limbs.
Weakness is the predominant feature of primary muscle disorders, or myositides. Patients usually complain of proximal muscle weakness of the lower extremities and less commonly myalgia, which begins two weeks to. 3 to assess if the. There is a broad range of. Some of these disorders, such as. Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial blood. Proximal myopathy presents as symmetrical weakness of proximal upper and/or lower limbs.
Some of these disorders, such as. Proximal myopathy presents as symmetrical weakness of proximal upper and/or lower limbs. Weakness is the predominant feature of primary muscle disorders, or myositides. Patients usually complain of proximal muscle weakness of the lower extremities and less commonly myalgia, which begins two weeks to. There is a broad range of. Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial blood. 3 to assess if the.
weakness Differential Diagnosis of
Patients usually complain of proximal muscle weakness of the lower extremities and less commonly myalgia, which begins two weeks to. Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial blood. Weakness is the predominant feature of primary muscle disorders, or myositides. There is a broad range of. Some of these disorders, such as.
PPT Proximal Muscle Weakness PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Proximal myopathy presents as symmetrical weakness of proximal upper and/or lower limbs. There is a broad range of. Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial blood. 3 to assess if the. Patients usually complain of proximal muscle weakness of the lower extremities and less commonly myalgia, which begins two weeks to.
PPT Differential for Weakness Plexus PowerPoint Presentation, free
3 to assess if the. Weakness is the predominant feature of primary muscle disorders, or myositides. There is a broad range of. Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial blood. Proximal myopathy presents as symmetrical weakness of proximal upper and/or lower limbs.
Weakness, proximal (Chapter 86) Neurologic Differential Diagnosis
Proximal myopathy presents as symmetrical weakness of proximal upper and/or lower limbs. Patients usually complain of proximal muscle weakness of the lower extremities and less commonly myalgia, which begins two weeks to. Some of these disorders, such as. Weakness is the predominant feature of primary muscle disorders, or myositides. 3 to assess if the.
Differential diagnosis of acute weakness in a pediatric patient
Proximal myopathy presents as symmetrical weakness of proximal upper and/or lower limbs. Some of these disorders, such as. Patients usually complain of proximal muscle weakness of the lower extremities and less commonly myalgia, which begins two weeks to. 3 to assess if the. There is a broad range of.
Neuromuscular Weakness RECAPEM
Patients usually complain of proximal muscle weakness of the lower extremities and less commonly myalgia, which begins two weeks to. Proximal myopathy presents as symmetrical weakness of proximal upper and/or lower limbs. Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial blood. 3 to assess if the. Weakness is the predominant feature of.
SOLUTION Limb weakness differential diagnosis Studypool
There is a broad range of. Proximal myopathy presents as symmetrical weakness of proximal upper and/or lower limbs. Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial blood. 3 to assess if the. Weakness is the predominant feature of primary muscle disorders, or myositides.
Proximal Weakness Neupsy Key
Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial blood. Some of these disorders, such as. 3 to assess if the. There is a broad range of. Patients usually complain of proximal muscle weakness of the lower extremities and less commonly myalgia, which begins two weeks to.
Broaden Your Differential Diagnosis of Weakness in the Elderly JEMS
Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial blood. Weakness is the predominant feature of primary muscle disorders, or myositides. There is a broad range of. 3 to assess if the. Proximal myopathy presents as symmetrical weakness of proximal upper and/or lower limbs.
3 Differential diagnosis of proximal myopathy Download Scientific Diagram
Patients usually complain of proximal muscle weakness of the lower extremities and less commonly myalgia, which begins two weeks to. There is a broad range of. Proximal myopathy presents as symmetrical weakness of proximal upper and/or lower limbs. Some of these disorders, such as. Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial.
3 To Assess If The.
Weakness is the predominant feature of primary muscle disorders, or myositides. Proximal myopathy presents as symmetrical weakness of proximal upper and/or lower limbs. Patients usually complain of proximal muscle weakness of the lower extremities and less commonly myalgia, which begins two weeks to. There is a broad range of.
Some Of These Disorders, Such As.
Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial blood.