Parabolic Partial Differential Equation - If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). After reading this chapter, you should be able to: In this section we discuss a classical approach based on the regularity and decay properties of. If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave).
If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). After reading this chapter, you should be able to: In this section we discuss a classical approach based on the regularity and decay properties of. If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave).
If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). After reading this chapter, you should be able to: In this section we discuss a classical approach based on the regularity and decay properties of. If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave).
Solved I want parabolic partial differential equation
If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). In this section we discuss a classical approach based on the regularity and decay properties of. If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave). After reading this chapter, you should be able to:
How to solve Parabolic partial differential equation Mathematica
If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave). After reading this chapter, you should be able to: If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). In this section we discuss a classical approach based on the regularity and decay properties of.
Parabolic Partial Differential Equation PDF Partial Differential
If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave). If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). In this section we discuss a classical approach based on the regularity and decay properties of. After reading this chapter, you should be able to:
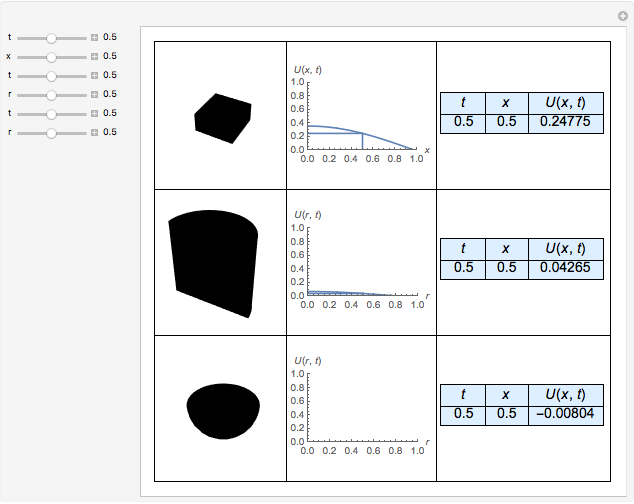
A Parabolic Partial Differential Equation in Three Different Geometries
After reading this chapter, you should be able to: If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave). If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). In this section we discuss a classical approach based on the regularity and decay properties of.
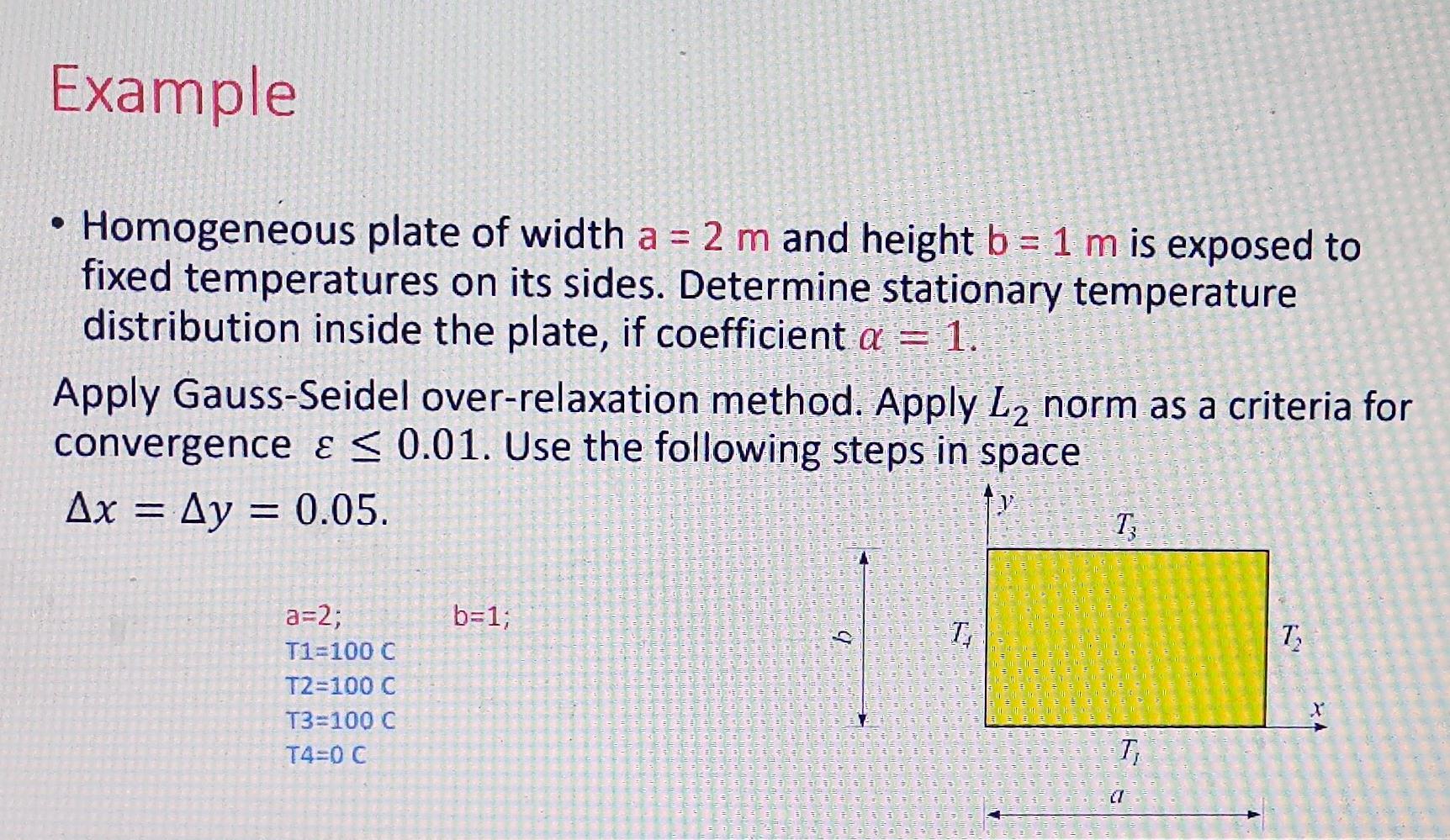
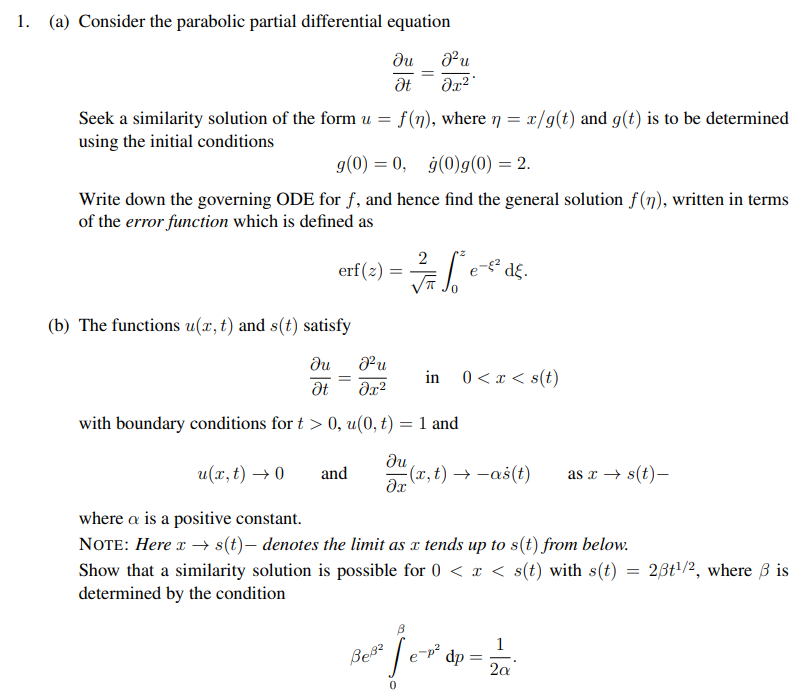
Solved 1. (a) Consider the parabolic partial differential
In this section we discuss a classical approach based on the regularity and decay properties of. After reading this chapter, you should be able to: If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave).
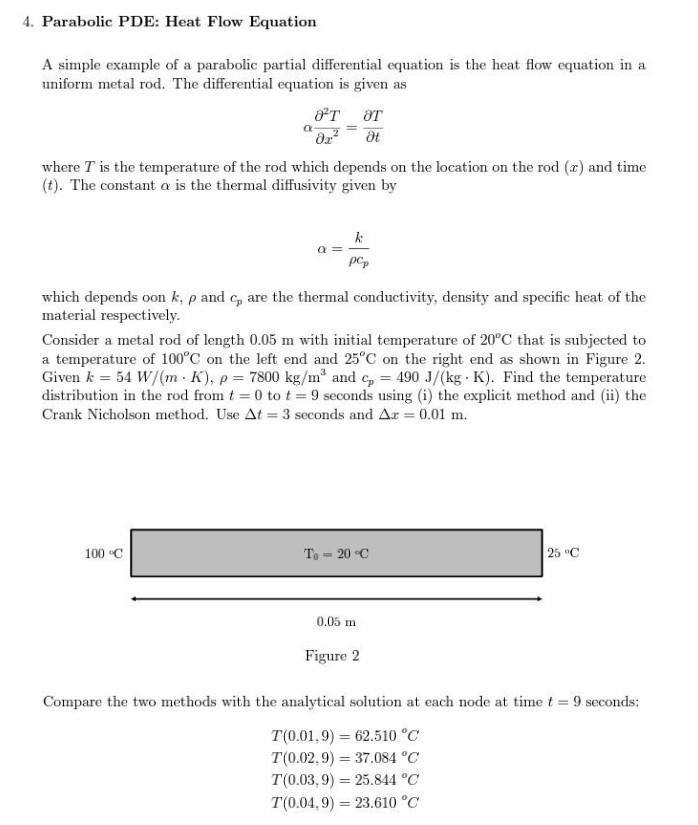
Solved 4. Parabolic PDE Heat Flow Equation A simple example
If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave). After reading this chapter, you should be able to: In this section we discuss a classical approach based on the regularity and decay properties of.
Solved The Heat Diffusion Equation Is A Parabolic Partial...
If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave). If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). In this section we discuss a classical approach based on the regularity and decay properties of. After reading this chapter, you should be able to:
(a) Consider the parabolic partial differential
After reading this chapter, you should be able to: If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave). In this section we discuss a classical approach based on the regularity and decay properties of. If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat).
Lecture 5 Parabolic Partial Differential Equation PDF Partial
After reading this chapter, you should be able to: If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). In this section we discuss a classical approach based on the regularity and decay properties of. If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave).
discrete mathematics How do I discretize a parabolic partial
After reading this chapter, you should be able to: If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave). In this section we discuss a classical approach based on the regularity and decay properties of. If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat).
If B2 4Ac = 0, Then The Pde Is Parabolic (Heat).
In this section we discuss a classical approach based on the regularity and decay properties of. After reading this chapter, you should be able to: If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave).