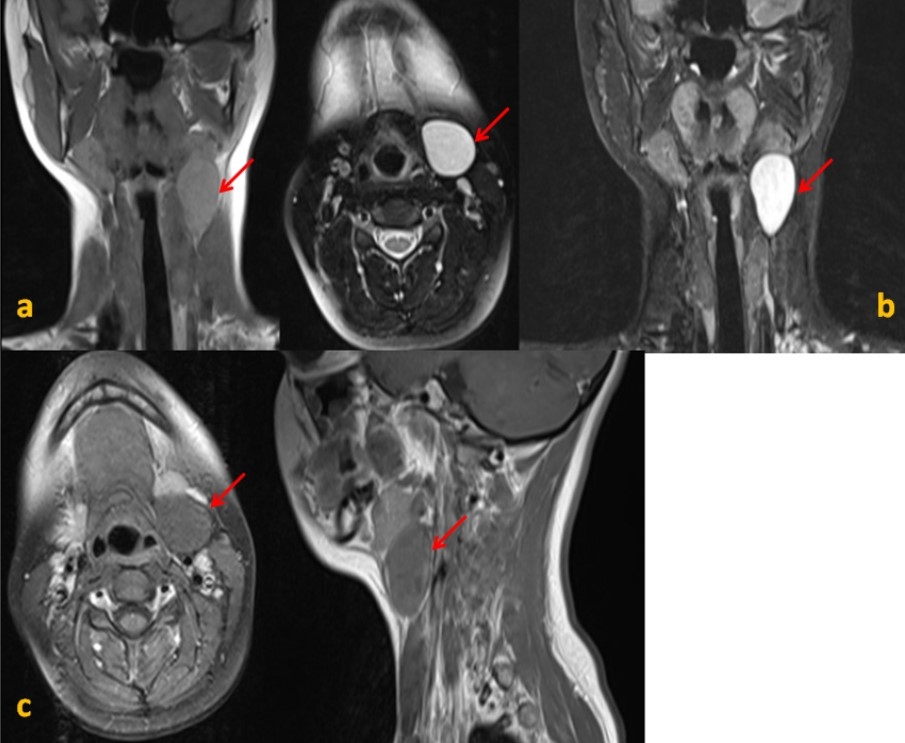
Lymphadenitis Differential Diagnosis - Submental and submandibular lymphadenopathy commonly is infectious in origin, often presenting with viral. Etiologies can be determined based on lymph node groups. Can be single or multiple; Patients with localized lymphadenopathy should be evaluated for etiologies typically associated. Factors that can assist in identifying the etiology of lymphadenopathy. Lymphadenitis = inflammation of lymph node; Most commonly due to viral or bacterial disease (usually staph or strep) infection local to region draining lymph to that.
Patients with localized lymphadenopathy should be evaluated for etiologies typically associated. Lymphadenitis = inflammation of lymph node; Can be single or multiple; Factors that can assist in identifying the etiology of lymphadenopathy. Most commonly due to viral or bacterial disease (usually staph or strep) infection local to region draining lymph to that. Submental and submandibular lymphadenopathy commonly is infectious in origin, often presenting with viral. Etiologies can be determined based on lymph node groups.
Submental and submandibular lymphadenopathy commonly is infectious in origin, often presenting with viral. Lymphadenitis = inflammation of lymph node; Etiologies can be determined based on lymph node groups. Factors that can assist in identifying the etiology of lymphadenopathy. Patients with localized lymphadenopathy should be evaluated for etiologies typically associated. Can be single or multiple; Most commonly due to viral or bacterial disease (usually staph or strep) infection local to region draining lymph to that.
(PDF) Clinical research Acute mesenteric lymphadenitis in children
Can be single or multiple; Factors that can assist in identifying the etiology of lymphadenopathy. Lymphadenitis = inflammation of lymph node; Most commonly due to viral or bacterial disease (usually staph or strep) infection local to region draining lymph to that. Submental and submandibular lymphadenopathy commonly is infectious in origin, often presenting with viral.
Branchial Cleft Cyst in the Differential Diagnosis of Lymphadenitis
Lymphadenitis = inflammation of lymph node; Factors that can assist in identifying the etiology of lymphadenopathy. Most commonly due to viral or bacterial disease (usually staph or strep) infection local to region draining lymph to that. Submental and submandibular lymphadenopathy commonly is infectious in origin, often presenting with viral. Etiologies can be determined based on lymph node groups.
Lymphadenitis.pptx Free Download
Can be single or multiple; Lymphadenitis = inflammation of lymph node; Most commonly due to viral or bacterial disease (usually staph or strep) infection local to region draining lymph to that. Etiologies can be determined based on lymph node groups. Factors that can assist in identifying the etiology of lymphadenopathy.
(PDF) Tularemia in the Differential Diagnosis of Lymphadenitis A
Submental and submandibular lymphadenopathy commonly is infectious in origin, often presenting with viral. Lymphadenitis = inflammation of lymph node; Can be single or multiple; Etiologies can be determined based on lymph node groups. Most commonly due to viral or bacterial disease (usually staph or strep) infection local to region draining lymph to that.
Lymphadenitis Differential Diagnosis Table
Factors that can assist in identifying the etiology of lymphadenopathy. Patients with localized lymphadenopathy should be evaluated for etiologies typically associated. Most commonly due to viral or bacterial disease (usually staph or strep) infection local to region draining lymph to that. Can be single or multiple; Lymphadenitis = inflammation of lymph node;
Caseous lymphadenitis
Etiologies can be determined based on lymph node groups. Lymphadenitis = inflammation of lymph node; Patients with localized lymphadenopathy should be evaluated for etiologies typically associated. Most commonly due to viral or bacterial disease (usually staph or strep) infection local to region draining lymph to that. Factors that can assist in identifying the etiology of lymphadenopathy.
PPT Differential Diagnosis PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Patients with localized lymphadenopathy should be evaluated for etiologies typically associated. Can be single or multiple; Factors that can assist in identifying the etiology of lymphadenopathy. Lymphadenitis = inflammation of lymph node; Submental and submandibular lymphadenopathy commonly is infectious in origin, often presenting with viral.
Differential diagnosis of dermatopathic lymphadenitis (DL). 4,7
Most commonly due to viral or bacterial disease (usually staph or strep) infection local to region draining lymph to that. Submental and submandibular lymphadenopathy commonly is infectious in origin, often presenting with viral. Lymphadenitis = inflammation of lymph node; Etiologies can be determined based on lymph node groups. Can be single or multiple;
(PDF) Tularemia Potential role of cytopathology in differential
Factors that can assist in identifying the etiology of lymphadenopathy. Most commonly due to viral or bacterial disease (usually staph or strep) infection local to region draining lymph to that. Submental and submandibular lymphadenopathy commonly is infectious in origin, often presenting with viral. Can be single or multiple; Etiologies can be determined based on lymph node groups.
SOLUTION Caseous lymphadenitis Studypool
Lymphadenitis = inflammation of lymph node; Etiologies can be determined based on lymph node groups. Factors that can assist in identifying the etiology of lymphadenopathy. Most commonly due to viral or bacterial disease (usually staph or strep) infection local to region draining lymph to that. Can be single or multiple;
Factors That Can Assist In Identifying The Etiology Of Lymphadenopathy.
Lymphadenitis = inflammation of lymph node; Submental and submandibular lymphadenopathy commonly is infectious in origin, often presenting with viral. Etiologies can be determined based on lymph node groups. Patients with localized lymphadenopathy should be evaluated for etiologies typically associated.
Most Commonly Due To Viral Or Bacterial Disease (Usually Staph Or Strep) Infection Local To Region Draining Lymph To That.
Can be single or multiple;