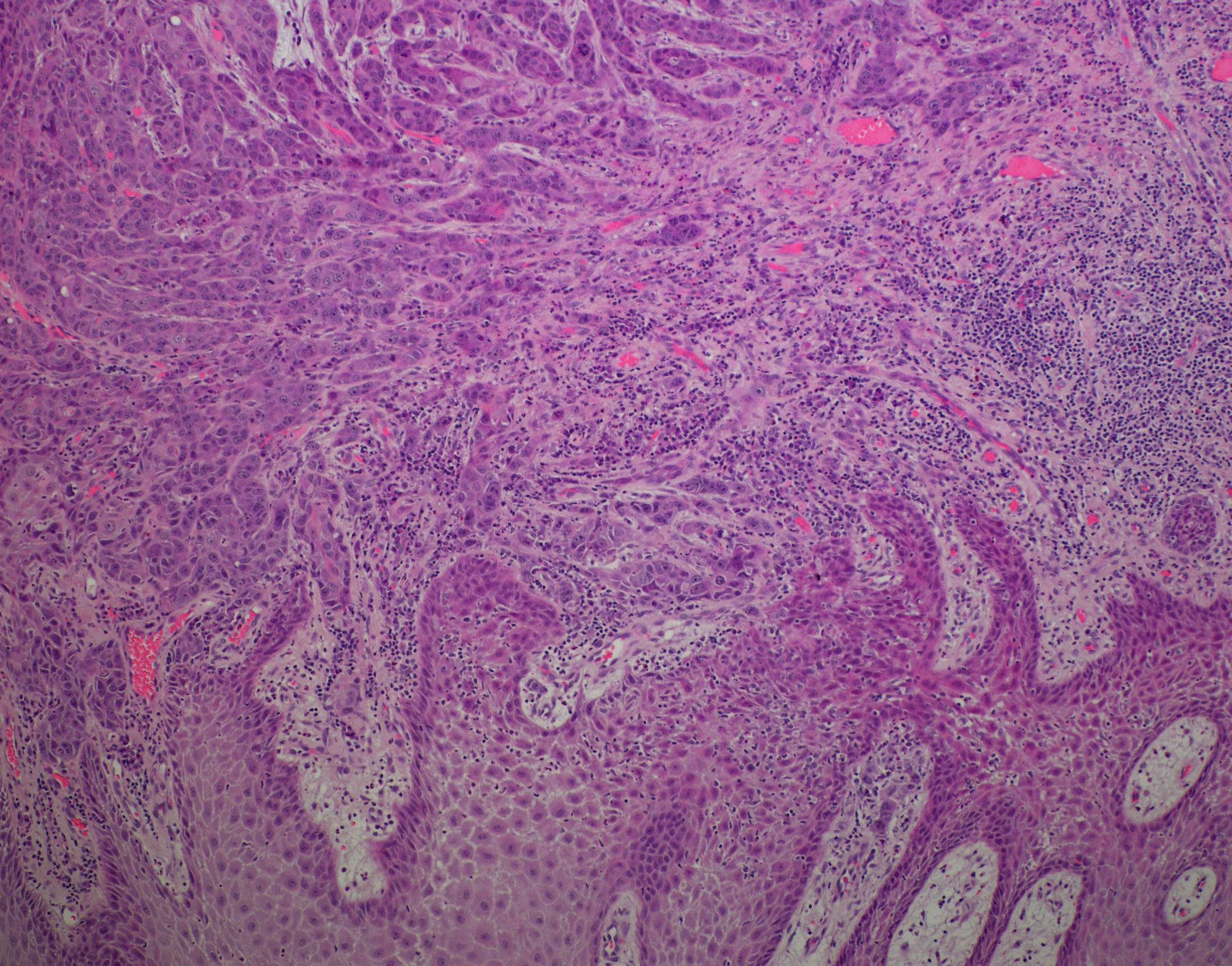
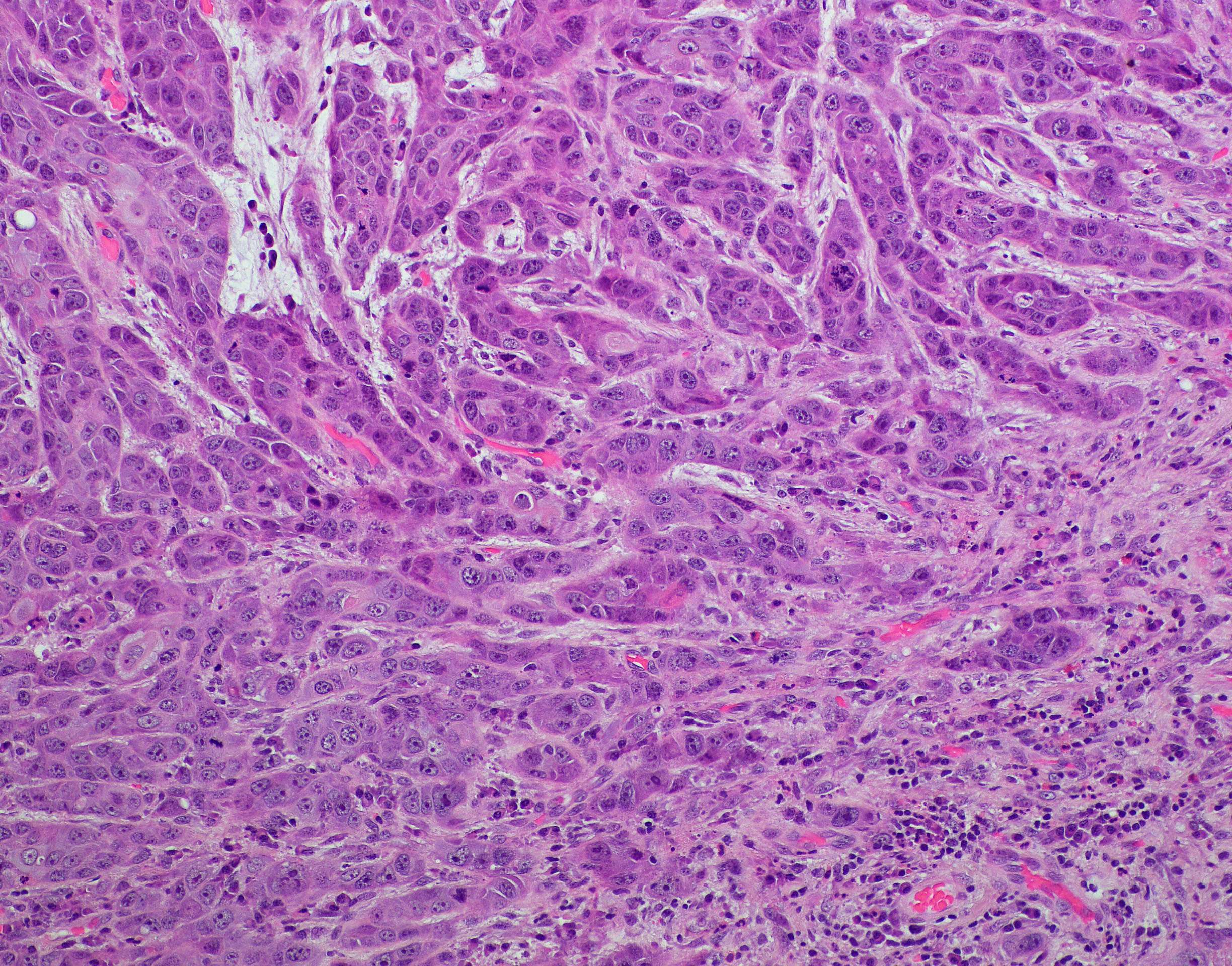
Invasive Moderately Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma - Infiltrating moderately differentiated keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma. The 2 main types are squamous cell cancer and. Biopsy report of buccal mucosa: Report of biopsy reads (in part):invasive ductal carcinoma with 'focal squamous differentiation' does this mean in fact there are squamous cells pres? Your type of oesophageal cancer depends on the type of cell that it starts in. Untreated, it will kill you. Oesophageal cancer can start anywhere in the oesophagus.
Report of biopsy reads (in part):invasive ductal carcinoma with 'focal squamous differentiation' does this mean in fact there are squamous cells pres? Oesophageal cancer can start anywhere in the oesophagus. Your type of oesophageal cancer depends on the type of cell that it starts in. Biopsy report of buccal mucosa: The 2 main types are squamous cell cancer and. Untreated, it will kill you. Infiltrating moderately differentiated keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma.
Your type of oesophageal cancer depends on the type of cell that it starts in. Biopsy report of buccal mucosa: The 2 main types are squamous cell cancer and. Report of biopsy reads (in part):invasive ductal carcinoma with 'focal squamous differentiation' does this mean in fact there are squamous cells pres? Oesophageal cancer can start anywhere in the oesophagus. Infiltrating moderately differentiated keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma. Untreated, it will kill you.
sland of moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, with
The 2 main types are squamous cell cancer and. Biopsy report of buccal mucosa: Oesophageal cancer can start anywhere in the oesophagus. Report of biopsy reads (in part):invasive ductal carcinoma with 'focal squamous differentiation' does this mean in fact there are squamous cells pres? Untreated, it will kill you.
14 Squamous cell carcinoma. Moderately differentiated (nonkeratinizing
Report of biopsy reads (in part):invasive ductal carcinoma with 'focal squamous differentiation' does this mean in fact there are squamous cells pres? Oesophageal cancer can start anywhere in the oesophagus. Your type of oesophageal cancer depends on the type of cell that it starts in. Biopsy report of buccal mucosa: Untreated, it will kill you.
Biopsy of the mass revealed invasive, moderately differentiated
Infiltrating moderately differentiated keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma. Biopsy report of buccal mucosa: Untreated, it will kill you. Your type of oesophageal cancer depends on the type of cell that it starts in. Report of biopsy reads (in part):invasive ductal carcinoma with 'focal squamous differentiation' does this mean in fact there are squamous cells pres?
Moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma of the floor of oral
Biopsy report of buccal mucosa: Oesophageal cancer can start anywhere in the oesophagus. Infiltrating moderately differentiated keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma. The 2 main types are squamous cell cancer and. Report of biopsy reads (in part):invasive ductal carcinoma with 'focal squamous differentiation' does this mean in fact there are squamous cells pres?
What Is Invasive Moderately Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Untreated, it will kill you. Infiltrating moderately differentiated keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma. Biopsy report of buccal mucosa: Report of biopsy reads (in part):invasive ductal carcinoma with 'focal squamous differentiation' does this mean in fact there are squamous cells pres? Your type of oesophageal cancer depends on the type of cell that it starts in.
(A) Invasive moderately differentiated keratinizing squamous cell
Report of biopsy reads (in part):invasive ductal carcinoma with 'focal squamous differentiation' does this mean in fact there are squamous cells pres? Infiltrating moderately differentiated keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma. The 2 main types are squamous cell cancer and. Biopsy report of buccal mucosa: Your type of oesophageal cancer depends on the type of cell that it starts in.
Moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma of the floor of oral
Biopsy report of buccal mucosa: Infiltrating moderately differentiated keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma. Oesophageal cancer can start anywhere in the oesophagus. Your type of oesophageal cancer depends on the type of cell that it starts in. The 2 main types are squamous cell cancer and.
Conventional squamous cell carcinoma, moderately differentiated
Your type of oesophageal cancer depends on the type of cell that it starts in. Untreated, it will kill you. Biopsy report of buccal mucosa: Report of biopsy reads (in part):invasive ductal carcinoma with 'focal squamous differentiation' does this mean in fact there are squamous cells pres? Infiltrating moderately differentiated keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma.
Section from lung showing a moderately differentiated invasive squamous
Infiltrating moderately differentiated keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma. Untreated, it will kill you. Your type of oesophageal cancer depends on the type of cell that it starts in. Oesophageal cancer can start anywhere in the oesophagus. Report of biopsy reads (in part):invasive ductal carcinoma with 'focal squamous differentiation' does this mean in fact there are squamous cells pres?
Conventional squamous cell carcinoma, moderately differentiated
Biopsy report of buccal mucosa: Report of biopsy reads (in part):invasive ductal carcinoma with 'focal squamous differentiation' does this mean in fact there are squamous cells pres? The 2 main types are squamous cell cancer and. Untreated, it will kill you. Infiltrating moderately differentiated keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma.
The 2 Main Types Are Squamous Cell Cancer And.
Report of biopsy reads (in part):invasive ductal carcinoma with 'focal squamous differentiation' does this mean in fact there are squamous cells pres? Oesophageal cancer can start anywhere in the oesophagus. Your type of oesophageal cancer depends on the type of cell that it starts in. Biopsy report of buccal mucosa:
Untreated, It Will Kill You.
Infiltrating moderately differentiated keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma.