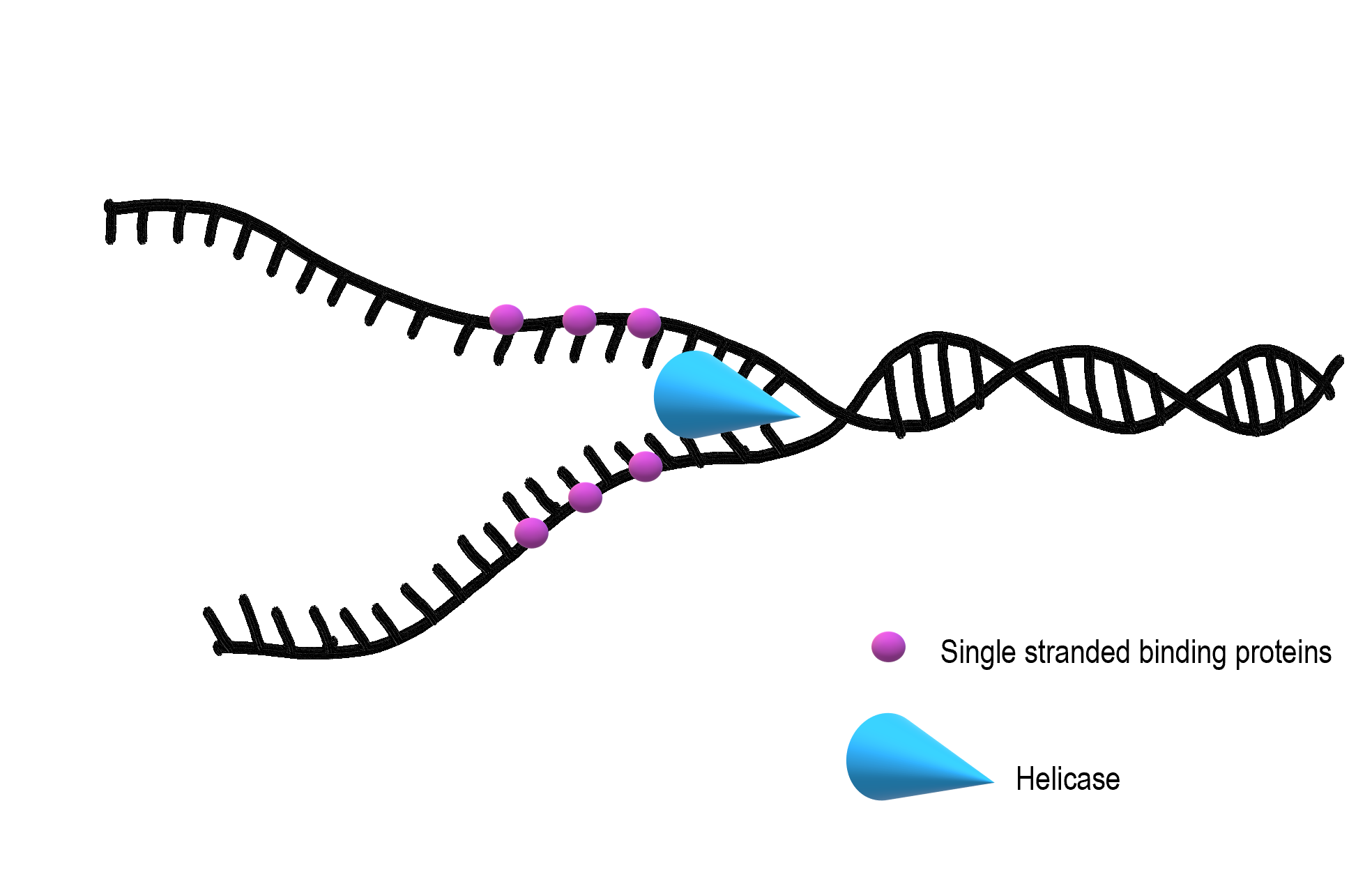
How Does Alkylation Prevent Dna Replication - As a background to exploring repair mechanisms. The alkylation adducts can cause mutations or block essential biological processes such as dna replication leading to cell death (figure 3). Fortunately, cells are protected by several dna repair mechanisms. Dna alkyltransferases are responsible for removing alkylation damage from dna. Cells use a vast number of dna. Alkylation can cause dna to form abnormal structures or create bulky adducts, which hinder the normal process of dna unwinding and. 57 rows dna alkylation damage, prevalent within cells, can have detrimental cellular effects if left unrepaired. Dna structural change caused by alkylation blocks replication of new dna (interstrand crosslink formation disrupts dna separation).
Dna structural change caused by alkylation blocks replication of new dna (interstrand crosslink formation disrupts dna separation). 57 rows dna alkylation damage, prevalent within cells, can have detrimental cellular effects if left unrepaired. The alkylation adducts can cause mutations or block essential biological processes such as dna replication leading to cell death (figure 3). As a background to exploring repair mechanisms. Dna alkyltransferases are responsible for removing alkylation damage from dna. Alkylation can cause dna to form abnormal structures or create bulky adducts, which hinder the normal process of dna unwinding and. Fortunately, cells are protected by several dna repair mechanisms. Cells use a vast number of dna.
Cells use a vast number of dna. The alkylation adducts can cause mutations or block essential biological processes such as dna replication leading to cell death (figure 3). Dna alkyltransferases are responsible for removing alkylation damage from dna. Dna structural change caused by alkylation blocks replication of new dna (interstrand crosslink formation disrupts dna separation). Alkylation can cause dna to form abnormal structures or create bulky adducts, which hinder the normal process of dna unwinding and. Fortunately, cells are protected by several dna repair mechanisms. As a background to exploring repair mechanisms. 57 rows dna alkylation damage, prevalent within cells, can have detrimental cellular effects if left unrepaired.
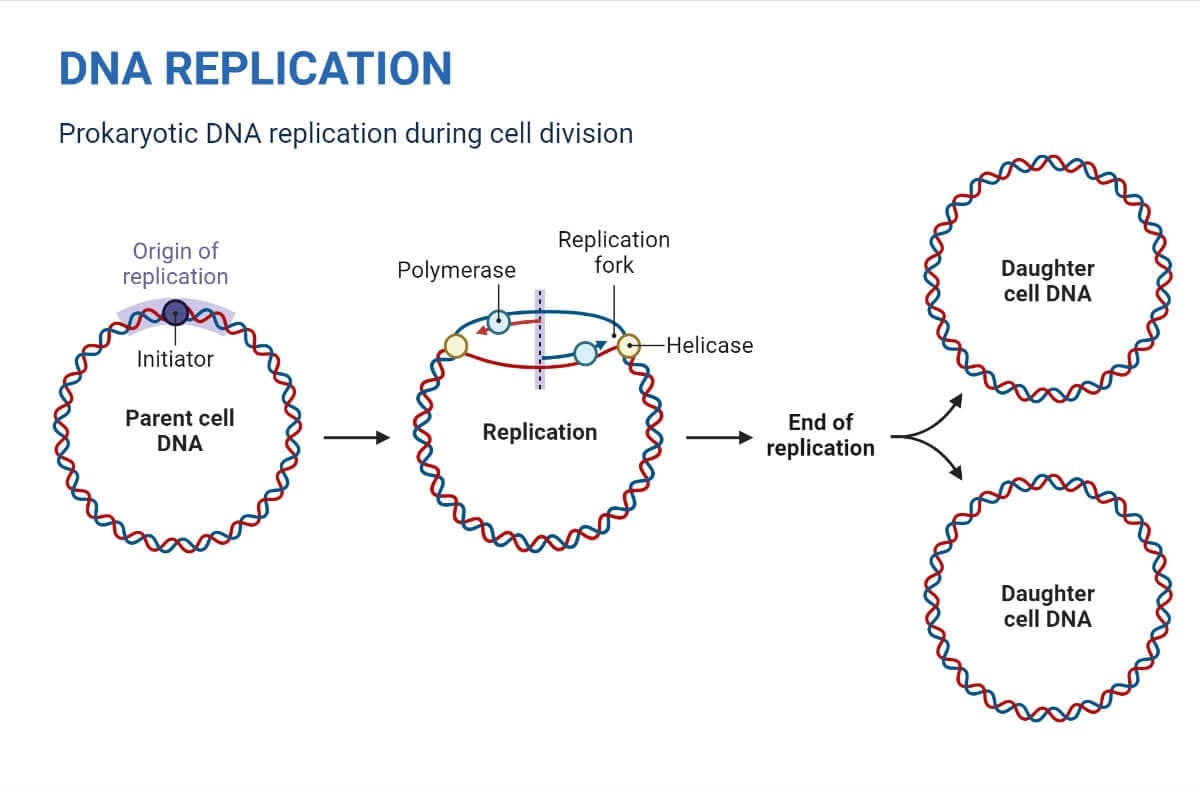
5.4 DNA Replication Human Biology
As a background to exploring repair mechanisms. Alkylation can cause dna to form abnormal structures or create bulky adducts, which hinder the normal process of dna unwinding and. 57 rows dna alkylation damage, prevalent within cells, can have detrimental cellular effects if left unrepaired. Cells use a vast number of dna. Dna structural change caused by alkylation blocks replication of.
Semiconservative DNA Replication in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
As a background to exploring repair mechanisms. 57 rows dna alkylation damage, prevalent within cells, can have detrimental cellular effects if left unrepaired. Cells use a vast number of dna. Dna structural change caused by alkylation blocks replication of new dna (interstrand crosslink formation disrupts dna separation). Alkylation can cause dna to form abnormal structures or create bulky adducts, which.
Site Map
The alkylation adducts can cause mutations or block essential biological processes such as dna replication leading to cell death (figure 3). 57 rows dna alkylation damage, prevalent within cells, can have detrimental cellular effects if left unrepaired. Dna alkyltransferases are responsible for removing alkylation damage from dna. Cells use a vast number of dna. Dna structural change caused by alkylation.
DNA Alkylation Semantic Scholar
Dna structural change caused by alkylation blocks replication of new dna (interstrand crosslink formation disrupts dna separation). Cells use a vast number of dna. Fortunately, cells are protected by several dna repair mechanisms. Alkylation can cause dna to form abnormal structures or create bulky adducts, which hinder the normal process of dna unwinding and. Dna alkyltransferases are responsible for removing.
How does semiconservative replication help prevent mutations during
Cells use a vast number of dna. 57 rows dna alkylation damage, prevalent within cells, can have detrimental cellular effects if left unrepaired. As a background to exploring repair mechanisms. Alkylation can cause dna to form abnormal structures or create bulky adducts, which hinder the normal process of dna unwinding and. Dna alkyltransferases are responsible for removing alkylation damage from.
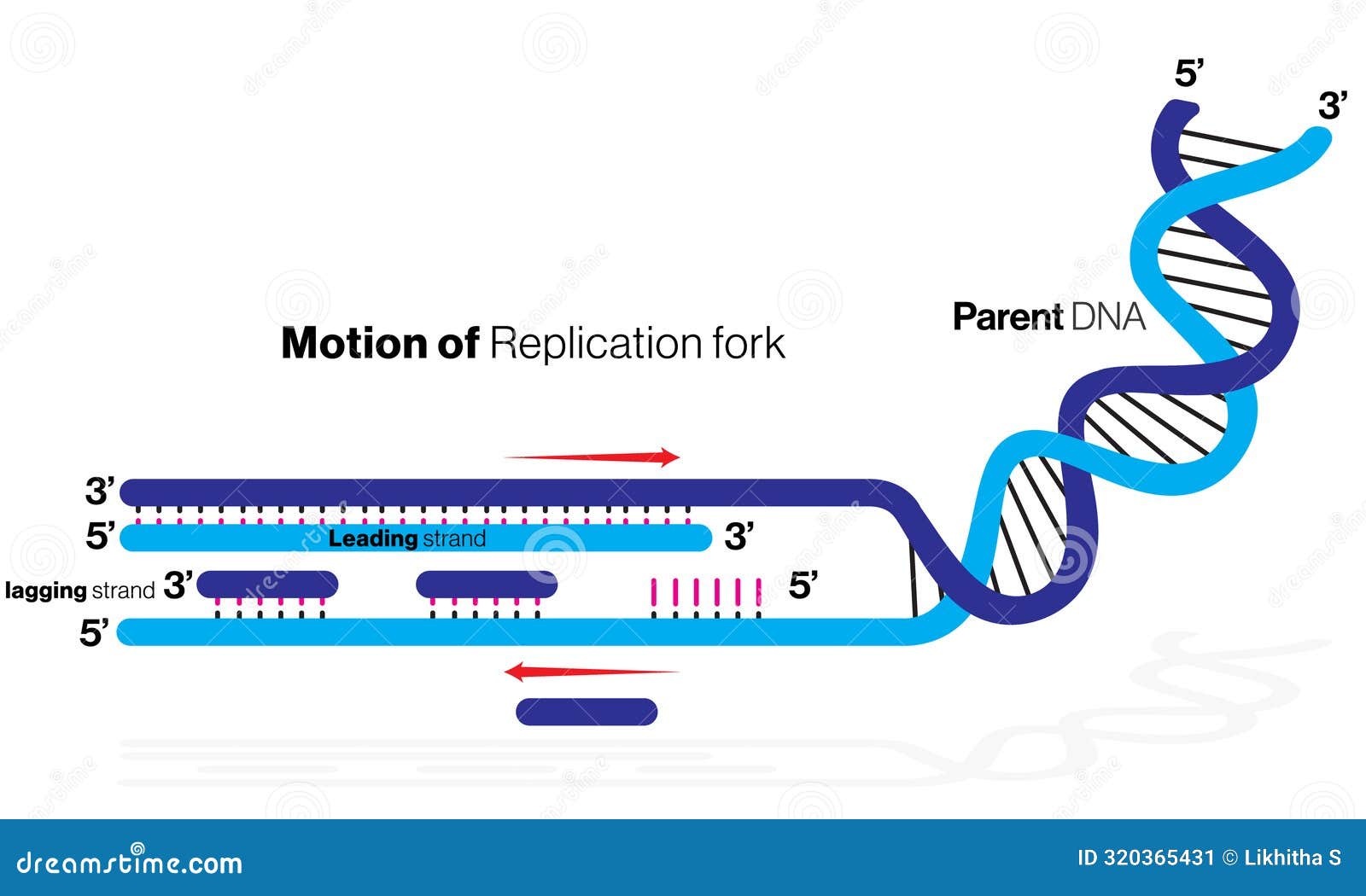
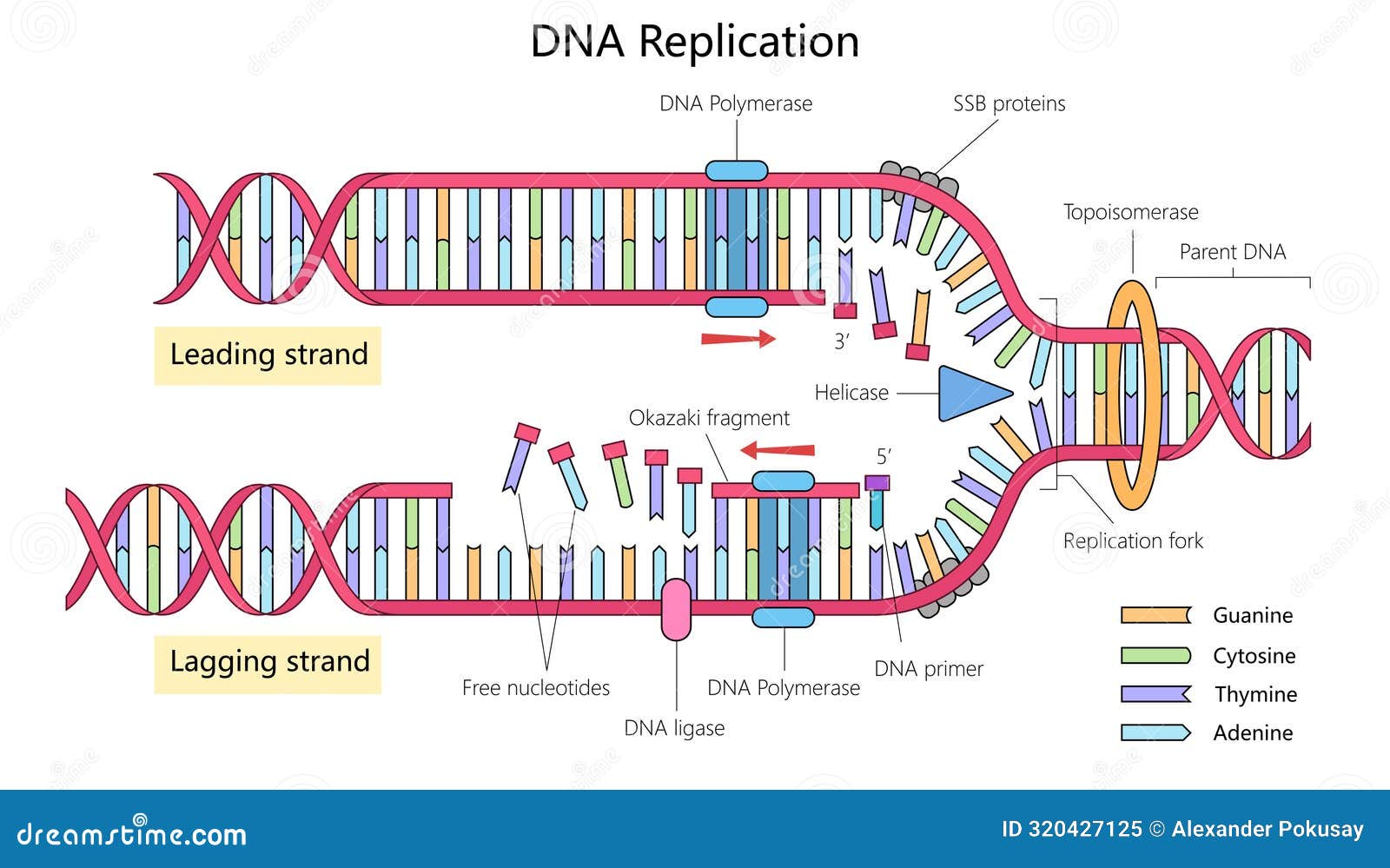
DNA Replication Process. Vector Illustration 318851774
Dna structural change caused by alkylation blocks replication of new dna (interstrand crosslink formation disrupts dna separation). 57 rows dna alkylation damage, prevalent within cells, can have detrimental cellular effects if left unrepaired. The alkylation adducts can cause mutations or block essential biological processes such as dna replication leading to cell death (figure 3). As a background to exploring repair.
Schematic representation of alkylation (interstrand crosslinks and
57 rows dna alkylation damage, prevalent within cells, can have detrimental cellular effects if left unrepaired. Dna alkyltransferases are responsible for removing alkylation damage from dna. Alkylation can cause dna to form abnormal structures or create bulky adducts, which hinder the normal process of dna unwinding and. The alkylation adducts can cause mutations or block essential biological processes such as.
Dna Replication Biology Quizizz Riset
Fortunately, cells are protected by several dna repair mechanisms. Dna alkyltransferases are responsible for removing alkylation damage from dna. Alkylation can cause dna to form abnormal structures or create bulky adducts, which hinder the normal process of dna unwinding and. The alkylation adducts can cause mutations or block essential biological processes such as dna replication leading to cell death (figure.
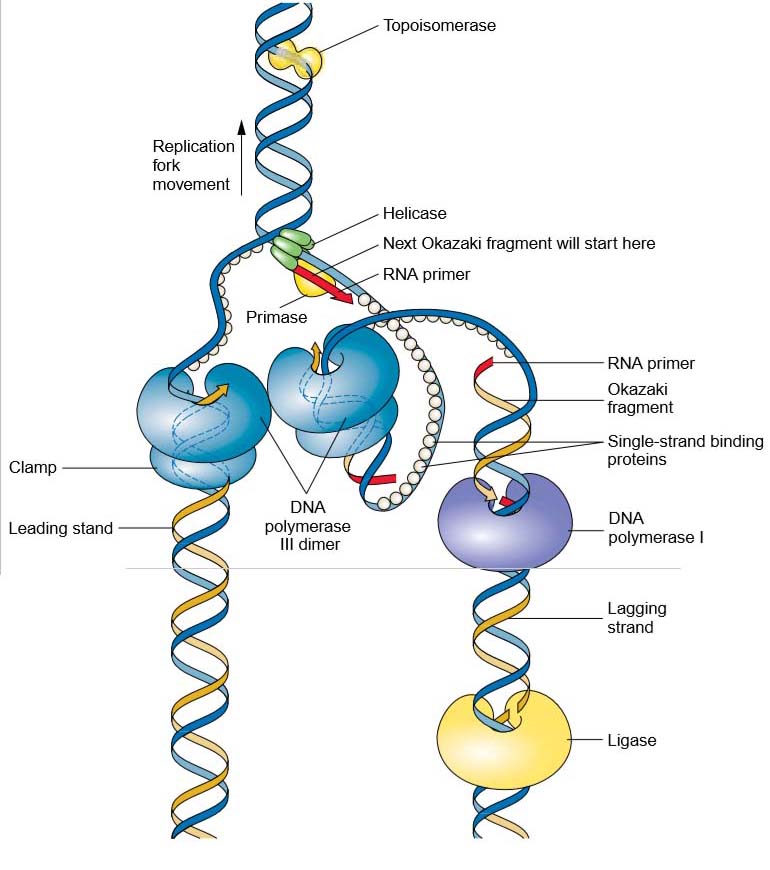
Replication Of Dna
Dna alkyltransferases are responsible for removing alkylation damage from dna. Cells use a vast number of dna. As a background to exploring repair mechanisms. Fortunately, cells are protected by several dna repair mechanisms. Alkylation can cause dna to form abnormal structures or create bulky adducts, which hinder the normal process of dna unwinding and.
DNA Replication Process. Vector Illustration 318851774
Cells use a vast number of dna. Fortunately, cells are protected by several dna repair mechanisms. The alkylation adducts can cause mutations or block essential biological processes such as dna replication leading to cell death (figure 3). Dna alkyltransferases are responsible for removing alkylation damage from dna. Alkylation can cause dna to form abnormal structures or create bulky adducts, which.
57 Rows Dna Alkylation Damage, Prevalent Within Cells, Can Have Detrimental Cellular Effects If Left Unrepaired.
Dna alkyltransferases are responsible for removing alkylation damage from dna. Alkylation can cause dna to form abnormal structures or create bulky adducts, which hinder the normal process of dna unwinding and. Fortunately, cells are protected by several dna repair mechanisms. Cells use a vast number of dna.
As A Background To Exploring Repair Mechanisms.
The alkylation adducts can cause mutations or block essential biological processes such as dna replication leading to cell death (figure 3). Dna structural change caused by alkylation blocks replication of new dna (interstrand crosslink formation disrupts dna separation).