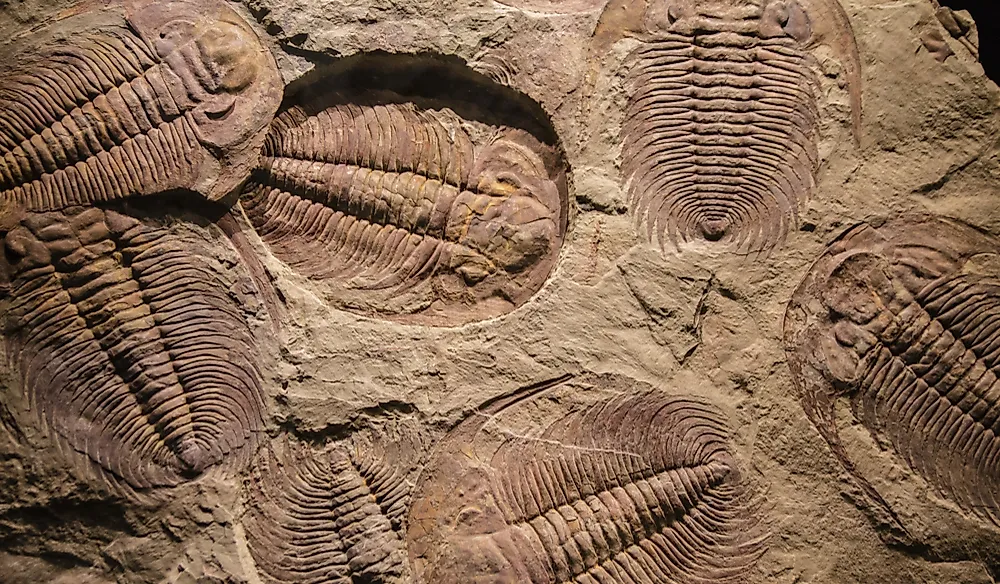
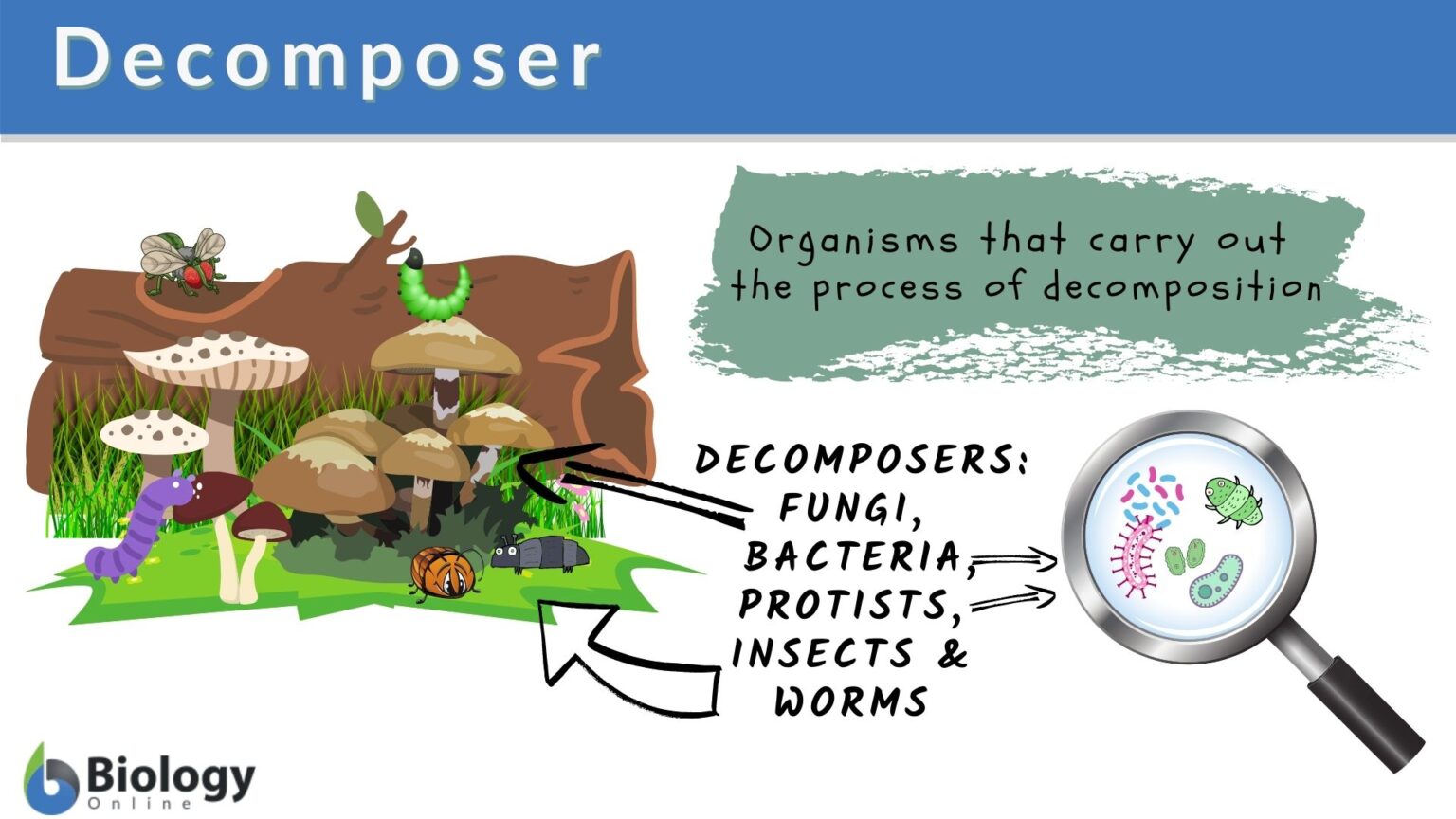
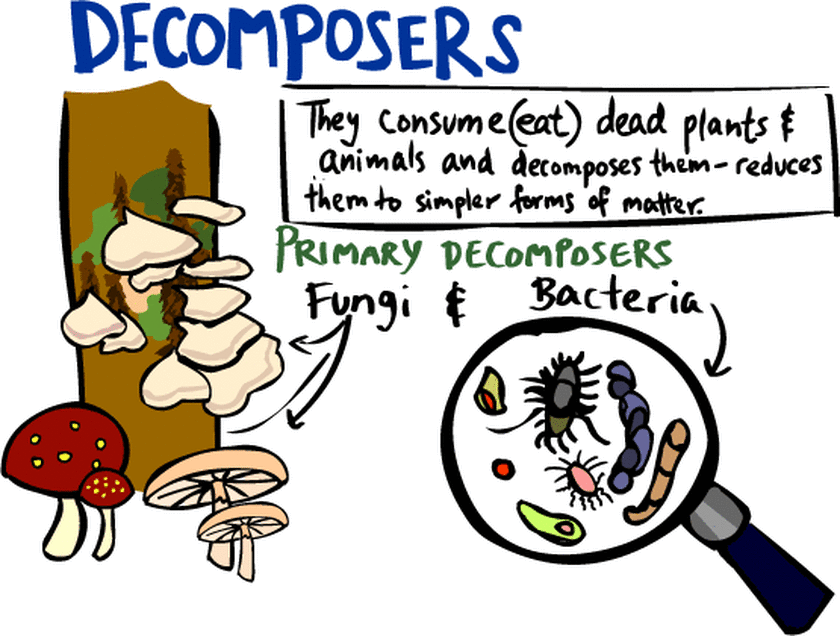
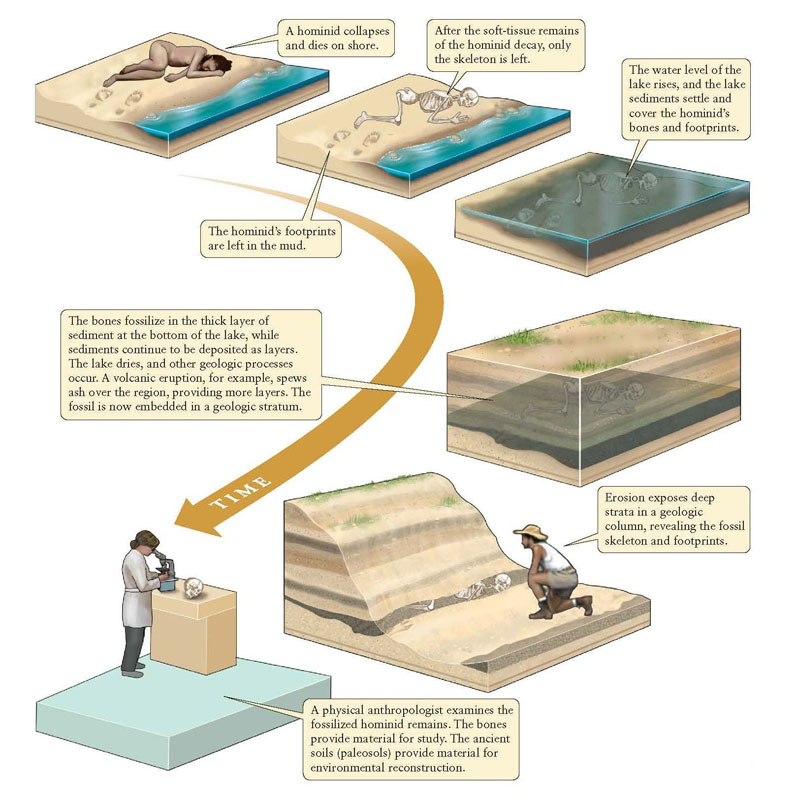
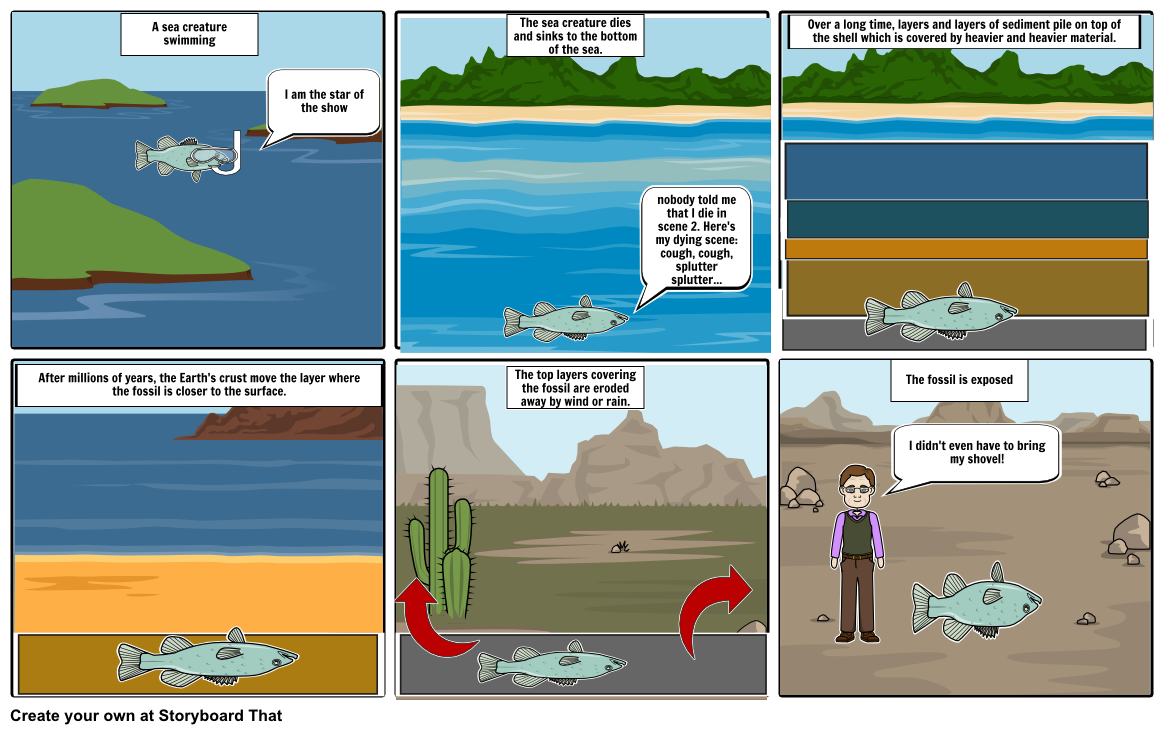
How Does A Decomposer Prevent Fossils From Being Formed - Identify the major agents of biological and mechanical destruction that would prevent the crab from becoming a fossil. The minerals that make up bones and shells and other hard parts are usually highly resistant to biological decay and physical weathering: Do you think an organism that gets buried quickly or slow will be more likely to form a fossil? Rapid burial protects an organism from biotic factors such as scavengers and decomposers, and from abiotic factors such as sun and wind,. How does a decomposer prevent. While decomposers typically prevent fossilization, certain conditions can help circumvent their effects:
Do you think an organism that gets buried quickly or slow will be more likely to form a fossil? The minerals that make up bones and shells and other hard parts are usually highly resistant to biological decay and physical weathering: How does a decomposer prevent. Rapid burial protects an organism from biotic factors such as scavengers and decomposers, and from abiotic factors such as sun and wind,. Identify the major agents of biological and mechanical destruction that would prevent the crab from becoming a fossil. While decomposers typically prevent fossilization, certain conditions can help circumvent their effects:
Identify the major agents of biological and mechanical destruction that would prevent the crab from becoming a fossil. Do you think an organism that gets buried quickly or slow will be more likely to form a fossil? How does a decomposer prevent. While decomposers typically prevent fossilization, certain conditions can help circumvent their effects: Rapid burial protects an organism from biotic factors such as scavengers and decomposers, and from abiotic factors such as sun and wind,. The minerals that make up bones and shells and other hard parts are usually highly resistant to biological decay and physical weathering:
Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
The minerals that make up bones and shells and other hard parts are usually highly resistant to biological decay and physical weathering: How does a decomposer prevent. Identify the major agents of biological and mechanical destruction that would prevent the crab from becoming a fossil. Rapid burial protects an organism from biotic factors such as scavengers and decomposers, and from.
What Does Mean in Science? Exploring the Role of
The minerals that make up bones and shells and other hard parts are usually highly resistant to biological decay and physical weathering: How does a decomposer prevent. Identify the major agents of biological and mechanical destruction that would prevent the crab from becoming a fossil. Rapid burial protects an organism from biotic factors such as scavengers and decomposers, and from.
How Are Fossils Formed? WorldAtlas
Do you think an organism that gets buried quickly or slow will be more likely to form a fossil? How does a decomposer prevent. The minerals that make up bones and shells and other hard parts are usually highly resistant to biological decay and physical weathering: While decomposers typically prevent fossilization, certain conditions can help circumvent their effects: Rapid burial.
Definition, Structure , Types & Functions
The minerals that make up bones and shells and other hard parts are usually highly resistant to biological decay and physical weathering: While decomposers typically prevent fossilization, certain conditions can help circumvent their effects: Rapid burial protects an organism from biotic factors such as scavengers and decomposers, and from abiotic factors such as sun and wind,. Identify the major agents.
Biology Simple
While decomposers typically prevent fossilization, certain conditions can help circumvent their effects: Identify the major agents of biological and mechanical destruction that would prevent the crab from becoming a fossil. Do you think an organism that gets buried quickly or slow will be more likely to form a fossil? The minerals that make up bones and shells and other hard.
biology Britannica
Rapid burial protects an organism from biotic factors such as scavengers and decomposers, and from abiotic factors such as sun and wind,. The minerals that make up bones and shells and other hard parts are usually highly resistant to biological decay and physical weathering: Do you think an organism that gets buried quickly or slow will be more likely to.
What Does Mean in Science? Exploring the Role of
While decomposers typically prevent fossilization, certain conditions can help circumvent their effects: Do you think an organism that gets buried quickly or slow will be more likely to form a fossil? Identify the major agents of biological and mechanical destruction that would prevent the crab from becoming a fossil. Rapid burial protects an organism from biotic factors such as scavengers.
How are fossils formed?
Identify the major agents of biological and mechanical destruction that would prevent the crab from becoming a fossil. Do you think an organism that gets buried quickly or slow will be more likely to form a fossil? How does a decomposer prevent. While decomposers typically prevent fossilization, certain conditions can help circumvent their effects: The minerals that make up bones.
How fossils are formed Storyboard by sarapark
The minerals that make up bones and shells and other hard parts are usually highly resistant to biological decay and physical weathering: Rapid burial protects an organism from biotic factors such as scavengers and decomposers, and from abiotic factors such as sun and wind,. While decomposers typically prevent fossilization, certain conditions can help circumvent their effects: Identify the major agents.
How Fossils are Formed? Facts and Other Information
The minerals that make up bones and shells and other hard parts are usually highly resistant to biological decay and physical weathering: Rapid burial protects an organism from biotic factors such as scavengers and decomposers, and from abiotic factors such as sun and wind,. Identify the major agents of biological and mechanical destruction that would prevent the crab from becoming.
Do You Think An Organism That Gets Buried Quickly Or Slow Will Be More Likely To Form A Fossil?
While decomposers typically prevent fossilization, certain conditions can help circumvent their effects: How does a decomposer prevent. The minerals that make up bones and shells and other hard parts are usually highly resistant to biological decay and physical weathering: Identify the major agents of biological and mechanical destruction that would prevent the crab from becoming a fossil.