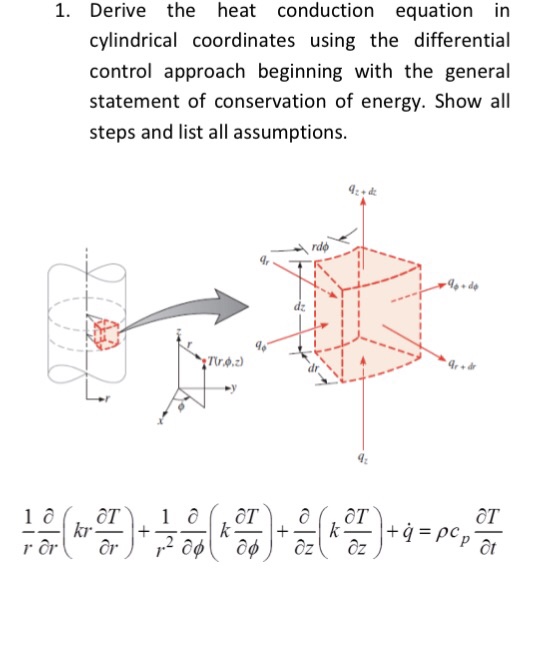
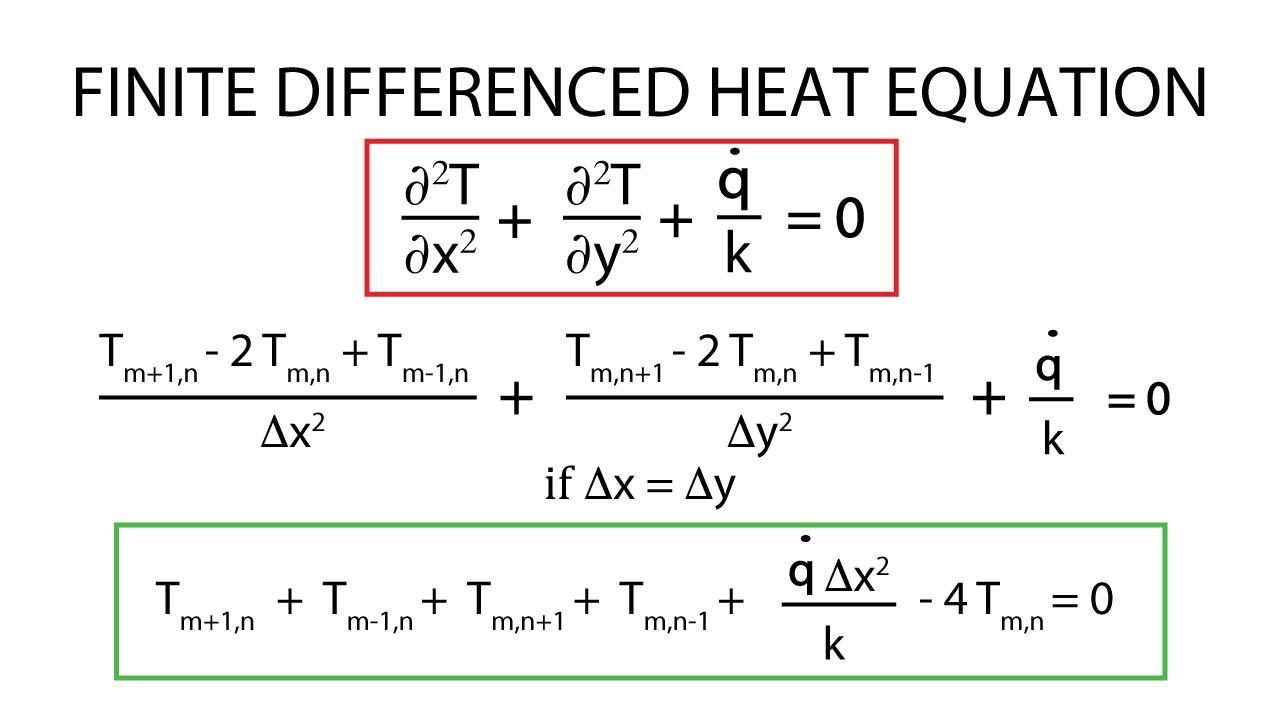
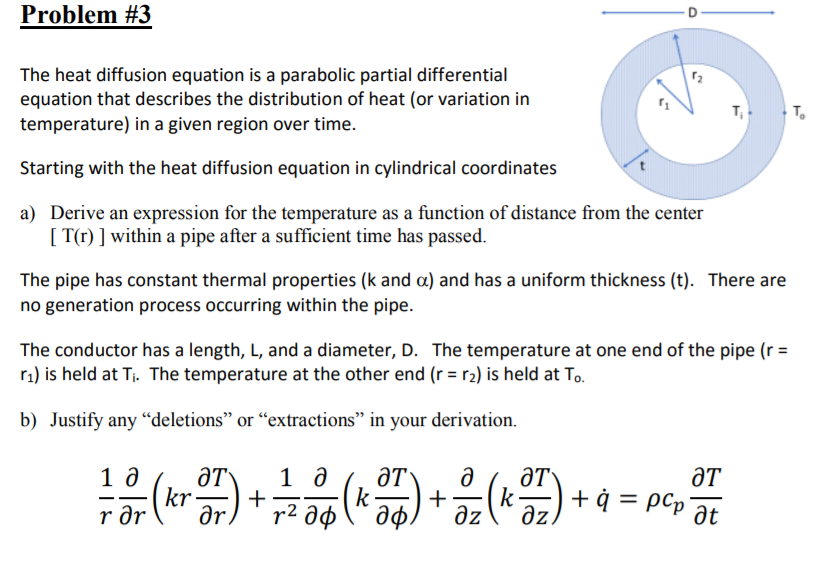
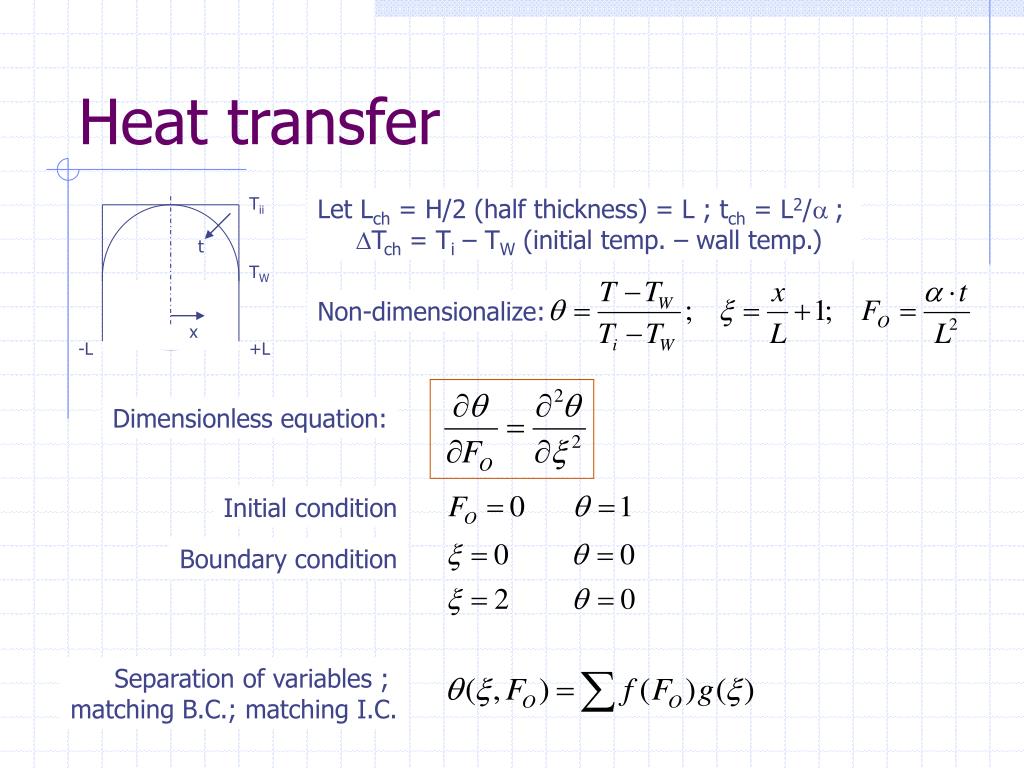
Heat Transfer Differential Equation - This equation involves the second derivative of temperature with respect to a spatial dimension (i.e., x) and the first derivative of. It is formulated considering a small volume element within the. In this section we will do a partial derivation of the heat equation that can be solved to give the temperature in a one dimensional. The heat equation describes how heat diffuses through a medium over time. A partial di erential equation (pde) for a function of more than one variable is a an equation involving a function of two or more variables and its.
It is formulated considering a small volume element within the. This equation involves the second derivative of temperature with respect to a spatial dimension (i.e., x) and the first derivative of. The heat equation describes how heat diffuses through a medium over time. A partial di erential equation (pde) for a function of more than one variable is a an equation involving a function of two or more variables and its. In this section we will do a partial derivation of the heat equation that can be solved to give the temperature in a one dimensional.
The heat equation describes how heat diffuses through a medium over time. In this section we will do a partial derivation of the heat equation that can be solved to give the temperature in a one dimensional. It is formulated considering a small volume element within the. A partial di erential equation (pde) for a function of more than one variable is a an equation involving a function of two or more variables and its. This equation involves the second derivative of temperature with respect to a spatial dimension (i.e., x) and the first derivative of.
Heat Conduction Equation In Cylindrical Coordinate System Tessshebaylo
The heat equation describes how heat diffuses through a medium over time. It is formulated considering a small volume element within the. A partial di erential equation (pde) for a function of more than one variable is a an equation involving a function of two or more variables and its. This equation involves the second derivative of temperature with respect.
Derivation Of Heat Transfer Equation In Cylindrical Coordinates
The heat equation describes how heat diffuses through a medium over time. In this section we will do a partial derivation of the heat equation that can be solved to give the temperature in a one dimensional. This equation involves the second derivative of temperature with respect to a spatial dimension (i.e., x) and the first derivative of. A partial.
Heat Transfer Equation Free Worksheets Printable
In this section we will do a partial derivation of the heat equation that can be solved to give the temperature in a one dimensional. It is formulated considering a small volume element within the. A partial di erential equation (pde) for a function of more than one variable is a an equation involving a function of two or more.
Heat Transfer Cylinder Equation Tessshebaylo
In this section we will do a partial derivation of the heat equation that can be solved to give the temperature in a one dimensional. A partial di erential equation (pde) for a function of more than one variable is a an equation involving a function of two or more variables and its. The heat equation describes how heat diffuses.
Solved The heat diffusion equation is a parabolic partial
This equation involves the second derivative of temperature with respect to a spatial dimension (i.e., x) and the first derivative of. In this section we will do a partial derivation of the heat equation that can be solved to give the temperature in a one dimensional. The heat equation describes how heat diffuses through a medium over time. It is.
Heat Transfer Heat Transfer Q Equation
This equation involves the second derivative of temperature with respect to a spatial dimension (i.e., x) and the first derivative of. It is formulated considering a small volume element within the. In this section we will do a partial derivation of the heat equation that can be solved to give the temperature in a one dimensional. The heat equation describes.
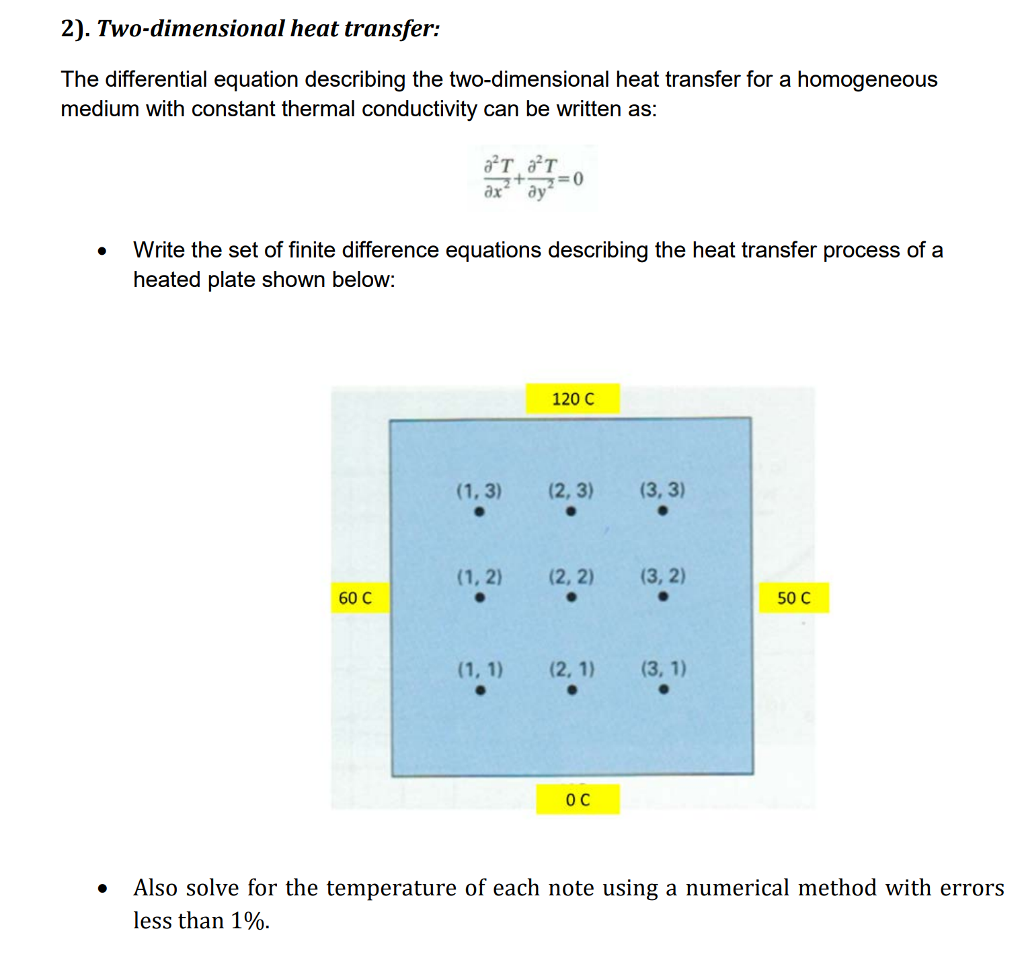
Solved 2). Twodimensional heat transfer The differential
A partial di erential equation (pde) for a function of more than one variable is a an equation involving a function of two or more variables and its. The heat equation describes how heat diffuses through a medium over time. It is formulated considering a small volume element within the. This equation involves the second derivative of temperature with respect.
Heat Transfer Equation For Solid Cylinder Tessshebaylo
The heat equation describes how heat diffuses through a medium over time. A partial di erential equation (pde) for a function of more than one variable is a an equation involving a function of two or more variables and its. It is formulated considering a small volume element within the. This equation involves the second derivative of temperature with respect.
Heat Conduction Equation Derivation Tessshebaylo
It is formulated considering a small volume element within the. A partial di erential equation (pde) for a function of more than one variable is a an equation involving a function of two or more variables and its. In this section we will do a partial derivation of the heat equation that can be solved to give the temperature in.
(PDF) Differential Equations of Heat Transfer DOKUMEN.TIPS
It is formulated considering a small volume element within the. The heat equation describes how heat diffuses through a medium over time. In this section we will do a partial derivation of the heat equation that can be solved to give the temperature in a one dimensional. This equation involves the second derivative of temperature with respect to a spatial.
It Is Formulated Considering A Small Volume Element Within The.
In this section we will do a partial derivation of the heat equation that can be solved to give the temperature in a one dimensional. The heat equation describes how heat diffuses through a medium over time. A partial di erential equation (pde) for a function of more than one variable is a an equation involving a function of two or more variables and its. This equation involves the second derivative of temperature with respect to a spatial dimension (i.e., x) and the first derivative of.