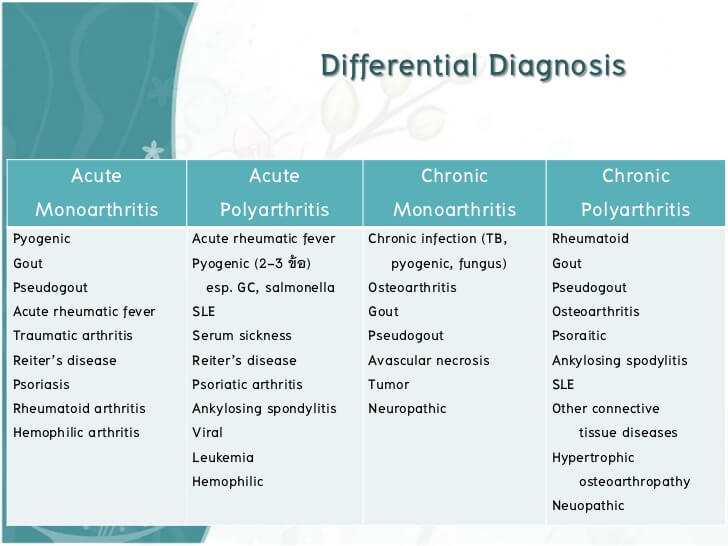
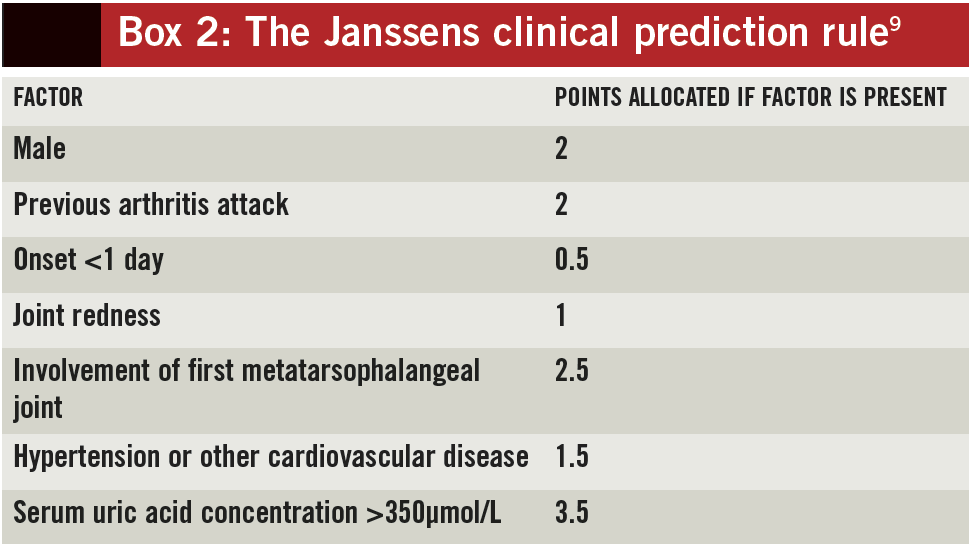
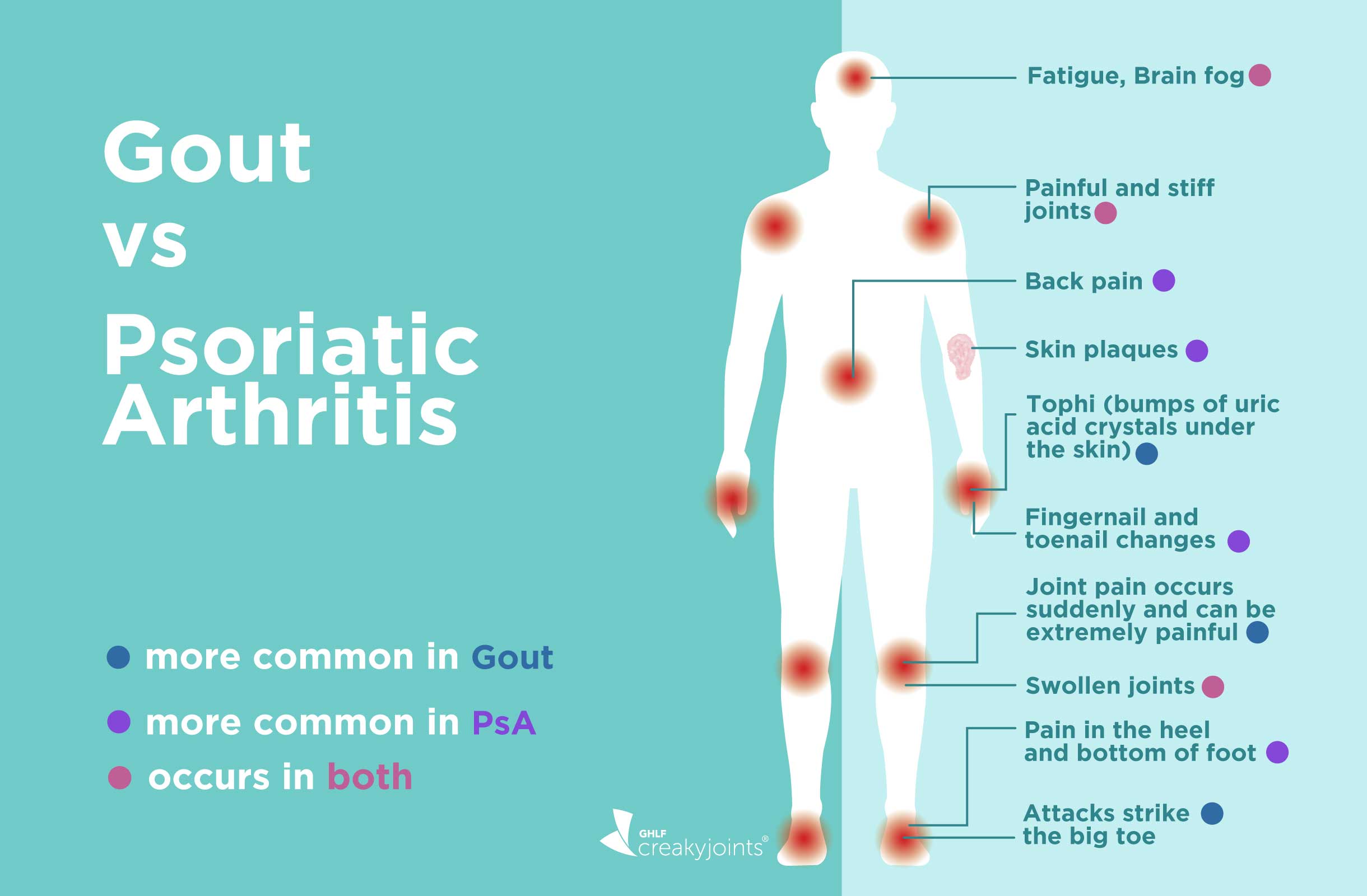
Gout Differential Diagnosis - Gout (monosodium urate [msu] crystal deposition disease) is characterized biochemically by extracellular fluid urate. However, in those with involvement of other joints, joint aspiration is. Gout can be diagnosed on clinical grounds in those with typical podagra. Gout is caused by monosodium urate monohydrate. Learn how to diagnose gout based on clinical manifestations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
However, in those with involvement of other joints, joint aspiration is. Learn how to diagnose gout based on clinical manifestations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Gout can be diagnosed on clinical grounds in those with typical podagra. Gout is caused by monosodium urate monohydrate. Gout (monosodium urate [msu] crystal deposition disease) is characterized biochemically by extracellular fluid urate.
Gout can be diagnosed on clinical grounds in those with typical podagra. However, in those with involvement of other joints, joint aspiration is. Gout (monosodium urate [msu] crystal deposition disease) is characterized biochemically by extracellular fluid urate. Learn how to diagnose gout based on clinical manifestations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Gout is caused by monosodium urate monohydrate.
PPT Diagnosis of gout PowerPoint Presentation ID6371400
However, in those with involvement of other joints, joint aspiration is. Gout can be diagnosed on clinical grounds in those with typical podagra. Learn how to diagnose gout based on clinical manifestations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Gout is caused by monosodium urate monohydrate. Gout (monosodium urate [msu] crystal deposition disease) is characterized biochemically by extracellular fluid urate.
(PDF) A Case of Severe Gout A Differential Diagnosis
Gout is caused by monosodium urate monohydrate. Gout can be diagnosed on clinical grounds in those with typical podagra. Gout (monosodium urate [msu] crystal deposition disease) is characterized biochemically by extracellular fluid urate. However, in those with involvement of other joints, joint aspiration is. Learn how to diagnose gout based on clinical manifestations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
(PDF) The gout diagnosis
Gout is caused by monosodium urate monohydrate. However, in those with involvement of other joints, joint aspiration is. Learn how to diagnose gout based on clinical manifestations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Gout can be diagnosed on clinical grounds in those with typical podagra. Gout (monosodium urate [msu] crystal deposition disease) is characterized biochemically by extracellular fluid urate.
Symptoms and Tests Used to Diagnose Gout
Gout is caused by monosodium urate monohydrate. However, in those with involvement of other joints, joint aspiration is. Gout can be diagnosed on clinical grounds in those with typical podagra. Gout (monosodium urate [msu] crystal deposition disease) is characterized biochemically by extracellular fluid urate. Learn how to diagnose gout based on clinical manifestations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
PPT Practical Diagnosis of Gout PowerPoint Presentation, free
Gout (monosodium urate [msu] crystal deposition disease) is characterized biochemically by extracellular fluid urate. Gout can be diagnosed on clinical grounds in those with typical podagra. However, in those with involvement of other joints, joint aspiration is. Gout is caused by monosodium urate monohydrate. Learn how to diagnose gout based on clinical manifestations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
PPT Practical Diagnosis of Gout PowerPoint Presentation ID597824
Gout can be diagnosed on clinical grounds in those with typical podagra. However, in those with involvement of other joints, joint aspiration is. Gout (monosodium urate [msu] crystal deposition disease) is characterized biochemically by extracellular fluid urate. Learn how to diagnose gout based on clinical manifestations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Gout is caused by monosodium urate monohydrate.
How Gout Is Diagnosed
Gout (monosodium urate [msu] crystal deposition disease) is characterized biochemically by extracellular fluid urate. Learn how to diagnose gout based on clinical manifestations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Gout is caused by monosodium urate monohydrate. However, in those with involvement of other joints, joint aspiration is. Gout can be diagnosed on clinical grounds in those with typical podagra.
Gout Differential Diagnosis media GoutPal Gout Forum
Gout (monosodium urate [msu] crystal deposition disease) is characterized biochemically by extracellular fluid urate. Learn how to diagnose gout based on clinical manifestations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Gout can be diagnosed on clinical grounds in those with typical podagra. Gout is caused by monosodium urate monohydrate. However, in those with involvement of other joints, joint aspiration is.
Gout clinical features and diagnosis The Pharmaceutical Journal
However, in those with involvement of other joints, joint aspiration is. Gout (monosodium urate [msu] crystal deposition disease) is characterized biochemically by extracellular fluid urate. Learn how to diagnose gout based on clinical manifestations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Gout is caused by monosodium urate monohydrate. Gout can be diagnosed on clinical grounds in those with typical podagra.
Gout vs. Psoriatic Arthritis Differences in Symptoms and Treatments
Gout is caused by monosodium urate monohydrate. Gout can be diagnosed on clinical grounds in those with typical podagra. However, in those with involvement of other joints, joint aspiration is. Gout (monosodium urate [msu] crystal deposition disease) is characterized biochemically by extracellular fluid urate. Learn how to diagnose gout based on clinical manifestations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
Gout Is Caused By Monosodium Urate Monohydrate.
Learn how to diagnose gout based on clinical manifestations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Gout can be diagnosed on clinical grounds in those with typical podagra. Gout (monosodium urate [msu] crystal deposition disease) is characterized biochemically by extracellular fluid urate. However, in those with involvement of other joints, joint aspiration is.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/gout-diagnosis1-5af9e59aba617700363b93b9.png)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/gout-diagnosis1-5af9e59aba617700363b93b9.png)