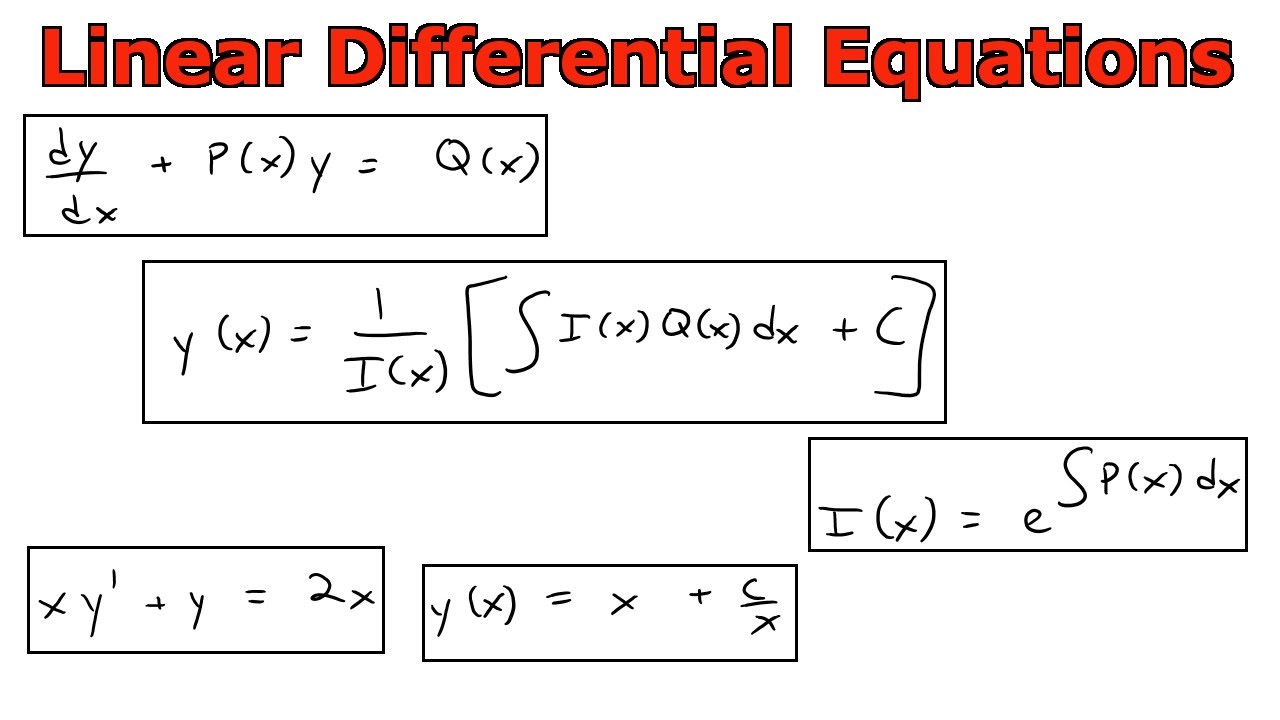
Formula Of Linear Differential Equation - Linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in x. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). It consists of a y and a. State the definition of a linear differential equation. Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y =. Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations. In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e.
State the definition of a linear differential equation. Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y =. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). It consists of a y and a. Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations. In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. Linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in x.
In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). It consists of a y and a. State the definition of a linear differential equation. Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations. Linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in x. Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y =.
06 Linear Differential Equations With Constants & Variable Coefficients
Linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in x. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). It consists of a y and a. In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y =.
SOLUTION Chapter 3 linear differential equation updated 8 Studypool
Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y =. Linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in x. Explain the law of mass action, and.
SOLUTION Chapter 4 linear differential equation of order n Studypool
Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y =. It consists of a y and a. Linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in x. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). State the definition of a linear differential equation.
Linear Equation Examples Tessshebaylo
Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y =. Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations. State the definition of a linear differential equation. Linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in.
Ordinary differential equation PPT
Linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in x. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y =. It consists of a y and a. State the definition of a linear differential equation.
Ordinary differential equation PPT
Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y =. Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations. It consists of a y and a. In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t).
Chapter 3 Linear Differential Equation PDF Equations Differential
In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations. Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y =. State the definition of a linear differential equation. Linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in.
Ex 9.6, 18 The integrating factor of differential equation
Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations. Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y =. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). Linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in x. In this section we solve linear first.
[Differential Equation] Linear Equation Problem Set and Examples Give
In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e. Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y =. Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations. It consists of a y and a. Linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in x.
Differential Equation Calculator
Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t). Linear differential equation is of the form dy/dx + py = q, where p and q are numeric constants or functions in x. Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y =. State the definition of a linear differential equation. Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential.
It Consists Of A Y And A.
Differential equations in the form y′ +p(t)y =. State the definition of a linear differential equation. Explain the law of mass action, and derive simple differential equations. Differential equations in the form y' + p(t) y = g(t).
Linear Differential Equation Is Of The Form Dy/Dx + Py = Q, Where P And Q Are Numeric Constants Or Functions In X.
In this section we solve linear first order differential equations, i.e.



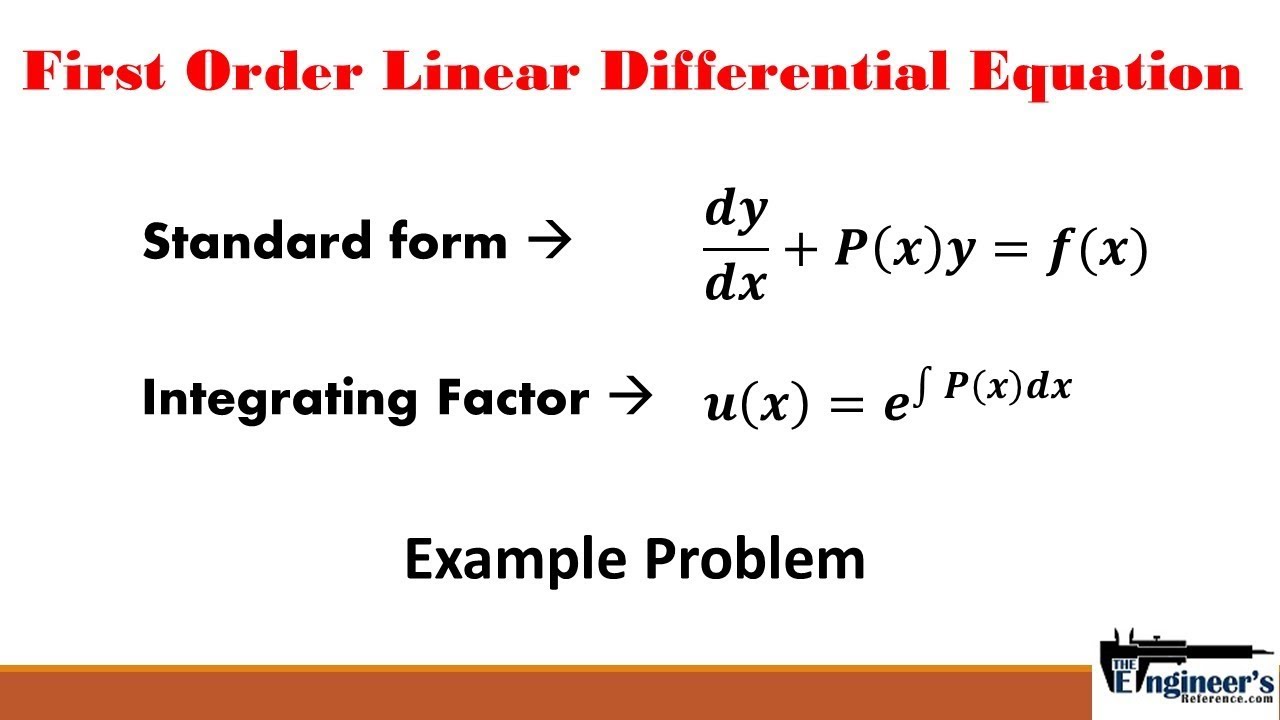




![[Differential Equation] Linear Equation Problem Set and Examples Give](https://d20ohkaloyme4g.cloudfront.net/img/document_thumbnails/c2a24732849b5093a4413f767de10a7e/thumb_1200_1553.png)