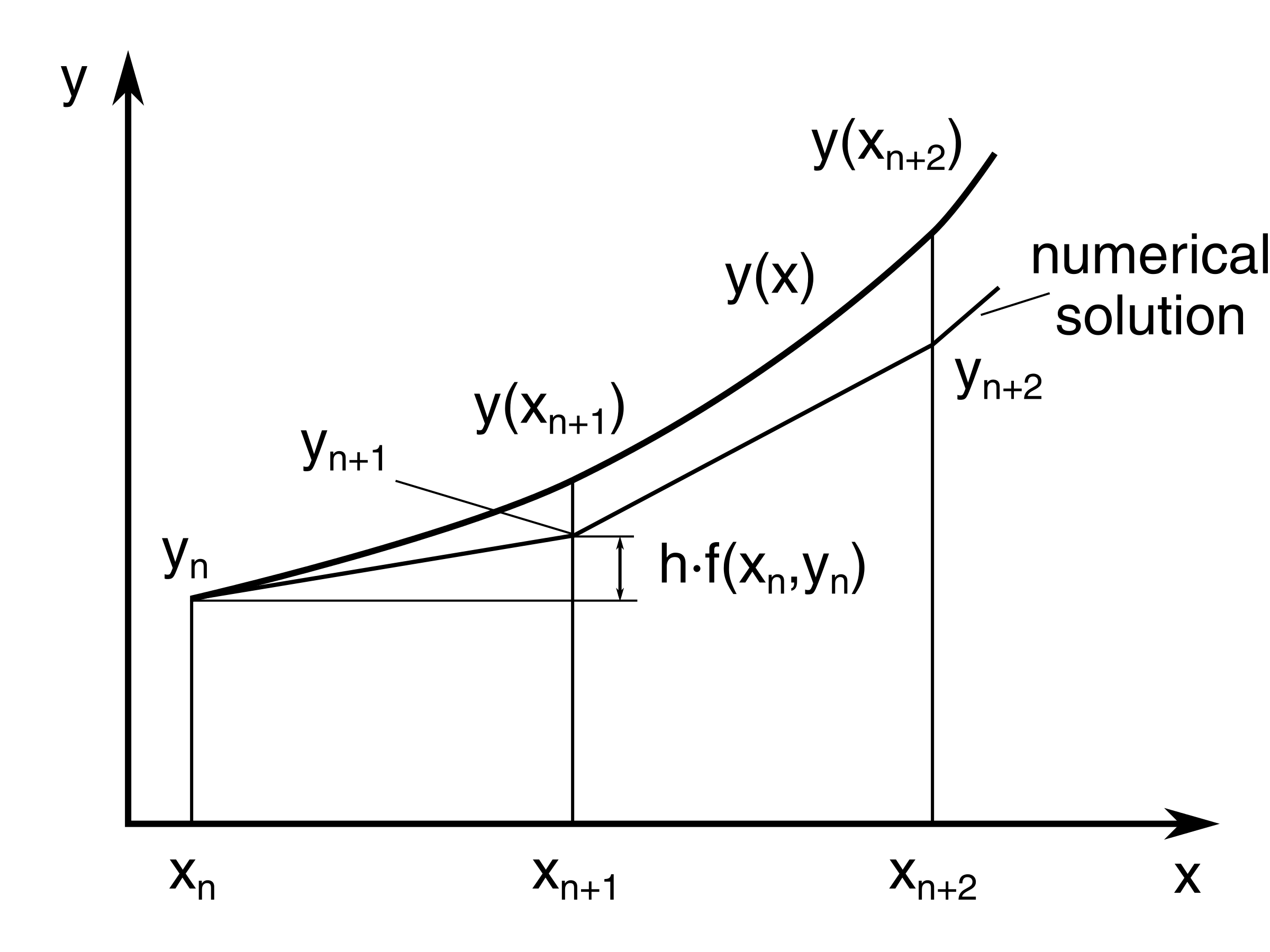
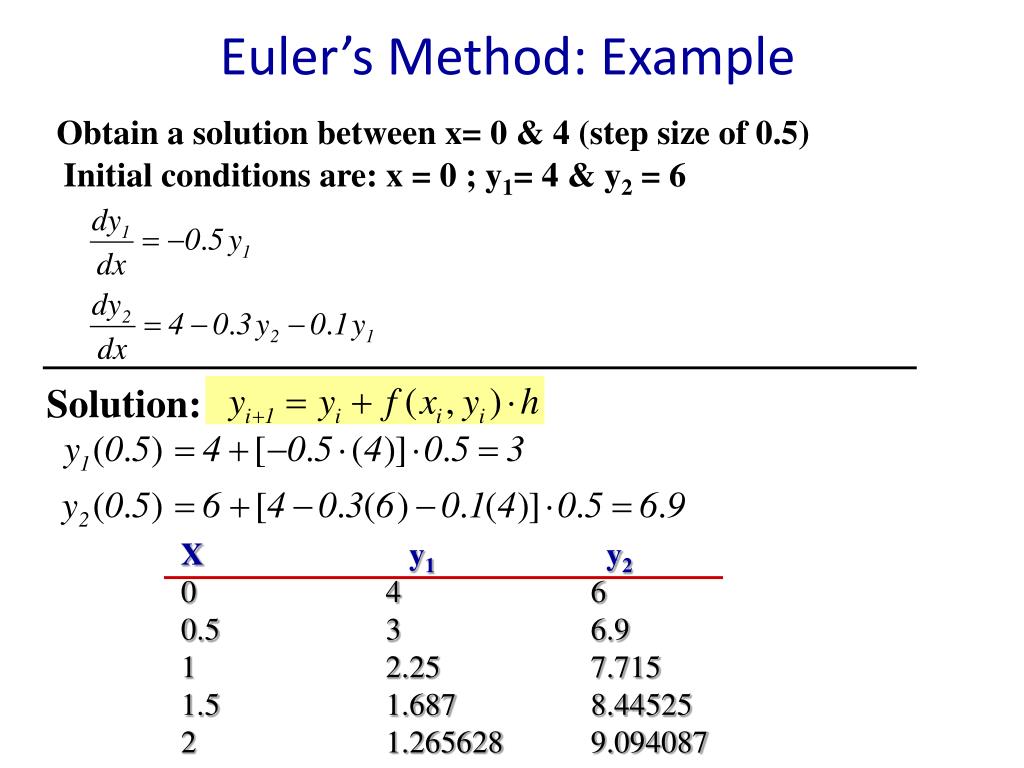
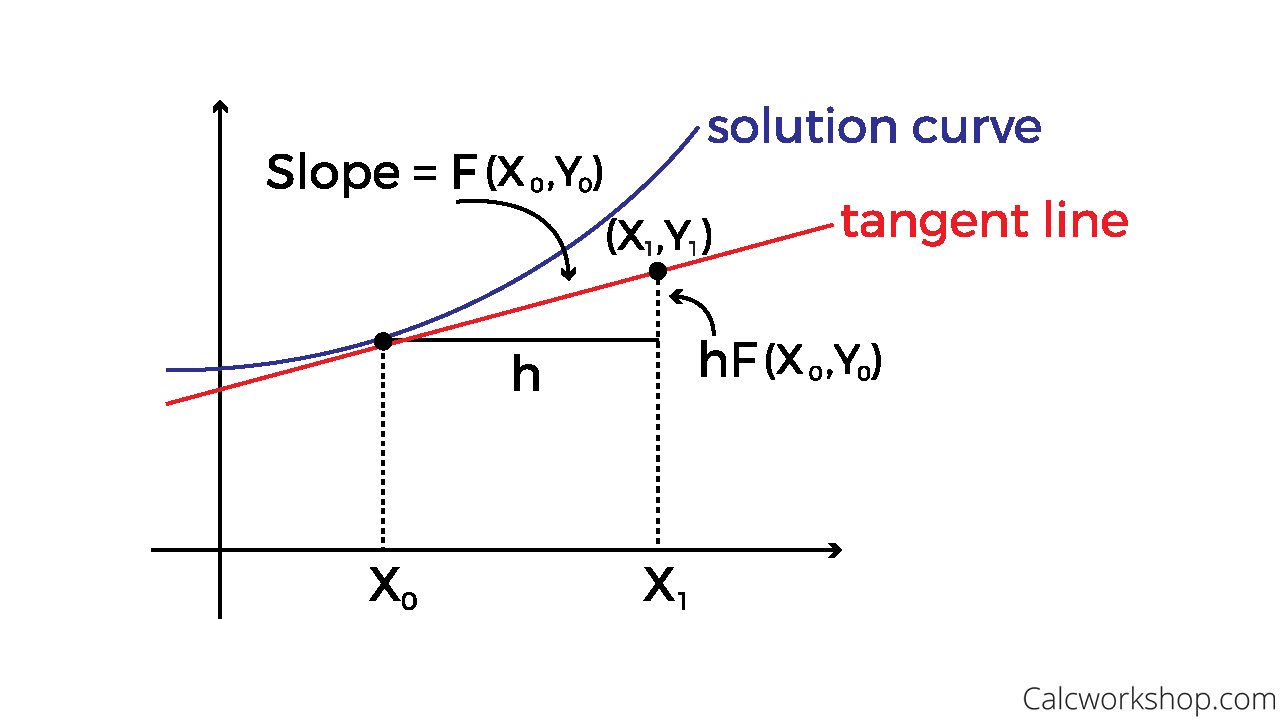
Eulers Method Differential Equations - In this section we’ll take a brief look at a fairly simple method for approximating solutions to differential equations. The simplest numerical method for solving equation \ref{eq:3.1.1} is euler’s method. This method is so crude that it is seldom used.
In this section we’ll take a brief look at a fairly simple method for approximating solutions to differential equations. The simplest numerical method for solving equation \ref{eq:3.1.1} is euler’s method. This method is so crude that it is seldom used.
In this section we’ll take a brief look at a fairly simple method for approximating solutions to differential equations. The simplest numerical method for solving equation \ref{eq:3.1.1} is euler’s method. This method is so crude that it is seldom used.
GitHub aprilivette/DifferentialEquations Numerical differential
This method is so crude that it is seldom used. The simplest numerical method for solving equation \ref{eq:3.1.1} is euler’s method. In this section we’ll take a brief look at a fairly simple method for approximating solutions to differential equations.
Answered Use Euler's method to solve the… bartleby
This method is so crude that it is seldom used. In this section we’ll take a brief look at a fairly simple method for approximating solutions to differential equations. The simplest numerical method for solving equation \ref{eq:3.1.1} is euler’s method.
How to do Euler's Method? (Simply Explained in 4 Powerful Examples)
In this section we’ll take a brief look at a fairly simple method for approximating solutions to differential equations. The simplest numerical method for solving equation \ref{eq:3.1.1} is euler’s method. This method is so crude that it is seldom used.
Euler's Method Explained with Examples
The simplest numerical method for solving equation \ref{eq:3.1.1} is euler’s method. This method is so crude that it is seldom used. In this section we’ll take a brief look at a fairly simple method for approximating solutions to differential equations.
Differential Equations
The simplest numerical method for solving equation \ref{eq:3.1.1} is euler’s method. In this section we’ll take a brief look at a fairly simple method for approximating solutions to differential equations. This method is so crude that it is seldom used.
How to do Euler's Method? (Simply Explained in 4 Powerful Examples)
The simplest numerical method for solving equation \ref{eq:3.1.1} is euler’s method. This method is so crude that it is seldom used. In this section we’ll take a brief look at a fairly simple method for approximating solutions to differential equations.
M8. Eulers Method For ODE PDF Differential Equations Ordinary
This method is so crude that it is seldom used. The simplest numerical method for solving equation \ref{eq:3.1.1} is euler’s method. In this section we’ll take a brief look at a fairly simple method for approximating solutions to differential equations.
61. [Differential Equations Eulers Method] Calculus AB
In this section we’ll take a brief look at a fairly simple method for approximating solutions to differential equations. The simplest numerical method for solving equation \ref{eq:3.1.1} is euler’s method. This method is so crude that it is seldom used.
(Solved) Euler S Method Numerical Integration Important Solving
This method is so crude that it is seldom used. In this section we’ll take a brief look at a fairly simple method for approximating solutions to differential equations. The simplest numerical method for solving equation \ref{eq:3.1.1} is euler’s method.
Lec 11 (Eulers Method) PDF PDF Differential Equations Equations
The simplest numerical method for solving equation \ref{eq:3.1.1} is euler’s method. In this section we’ll take a brief look at a fairly simple method for approximating solutions to differential equations. This method is so crude that it is seldom used.
This Method Is So Crude That It Is Seldom Used.
The simplest numerical method for solving equation \ref{eq:3.1.1} is euler’s method. In this section we’ll take a brief look at a fairly simple method for approximating solutions to differential equations.

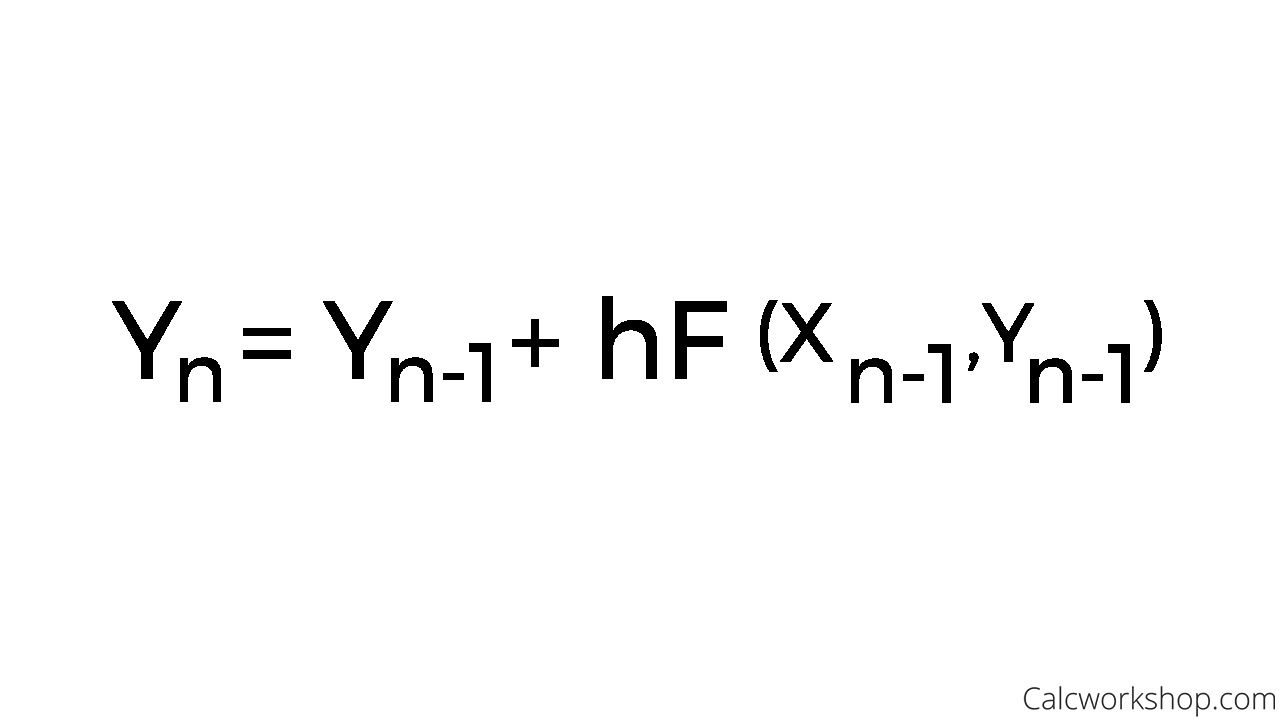

![61. [Differential Equations Eulers Method] Calculus AB](https://www.educator.com/media/lesson/poster/calculus-ab-zhu/differential-equations-eulers-method.jpg)

