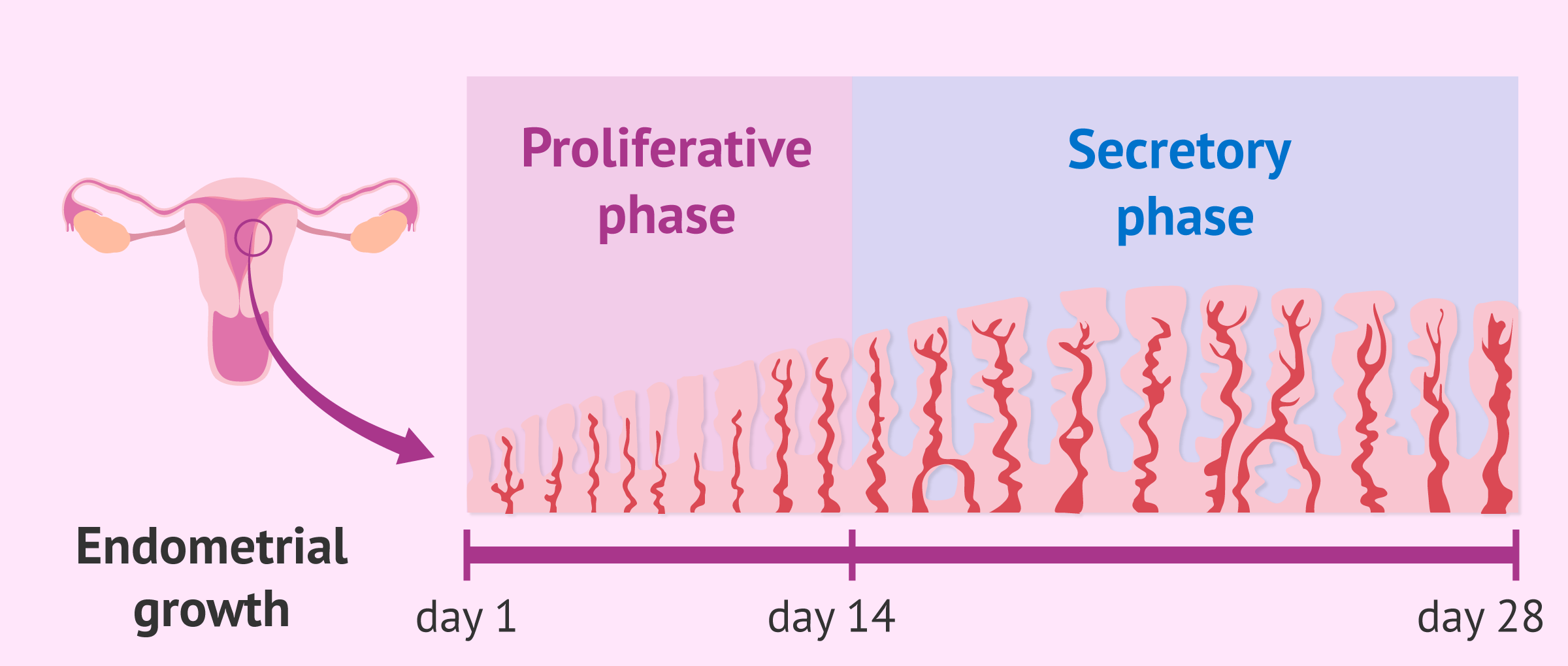
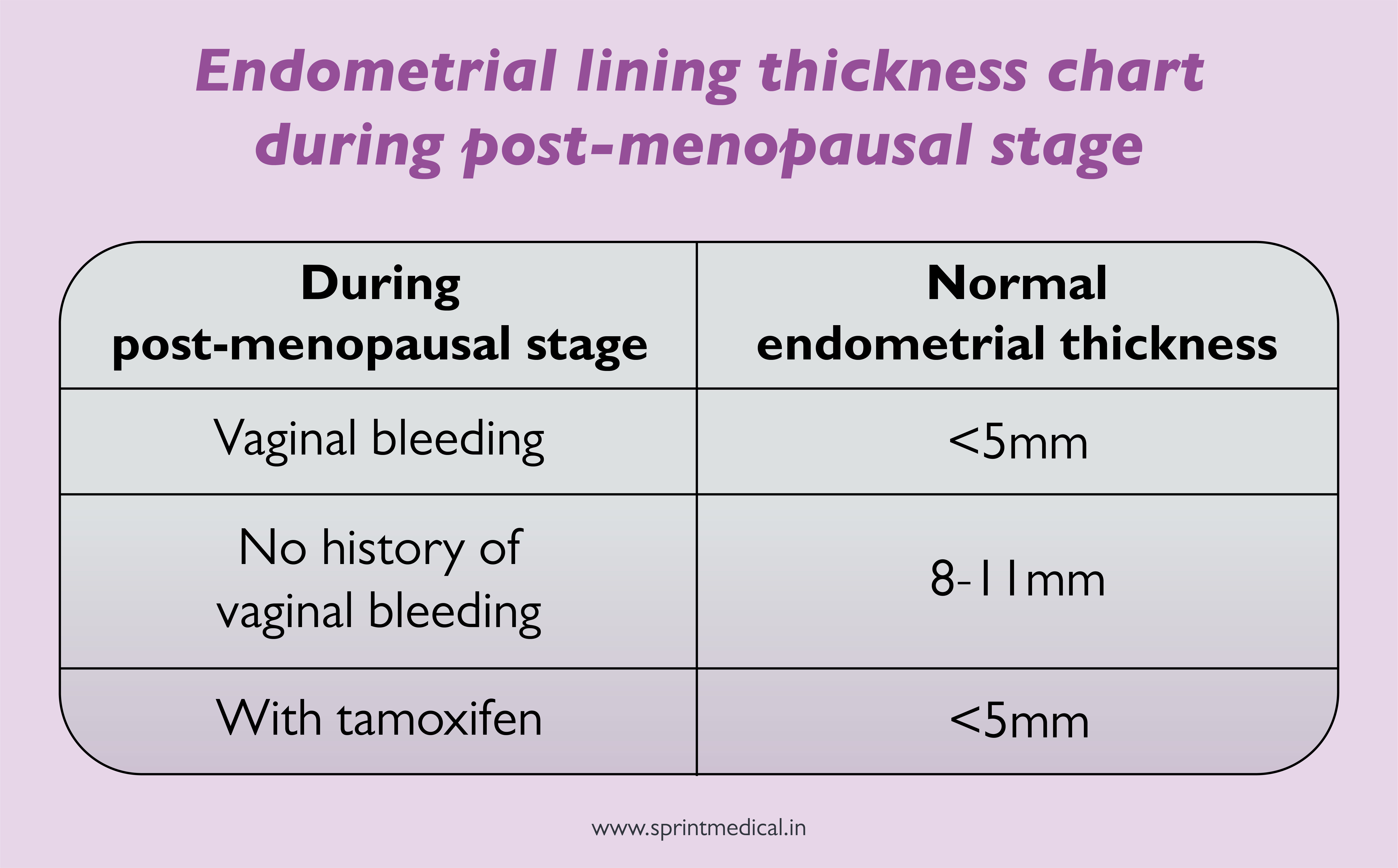
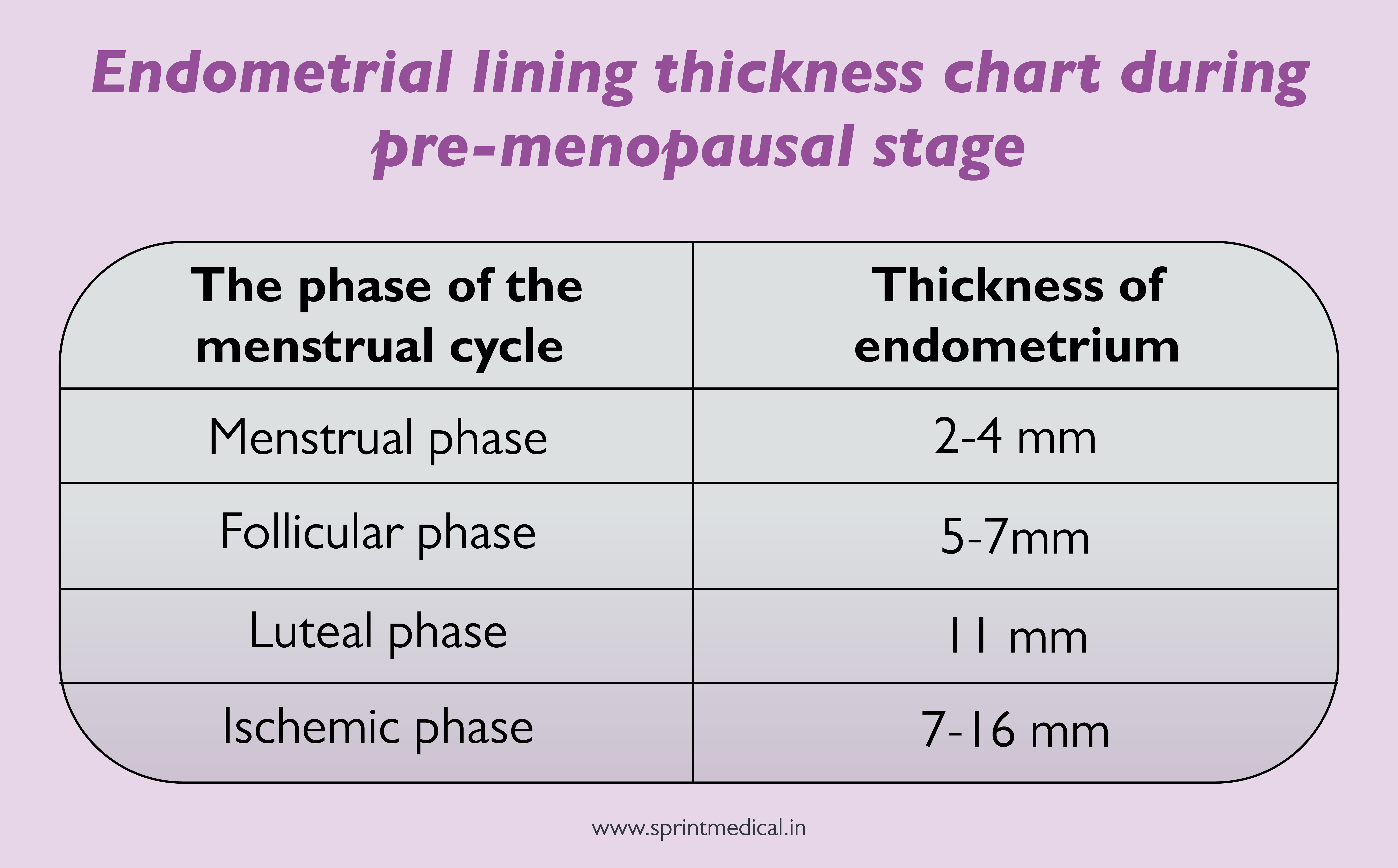
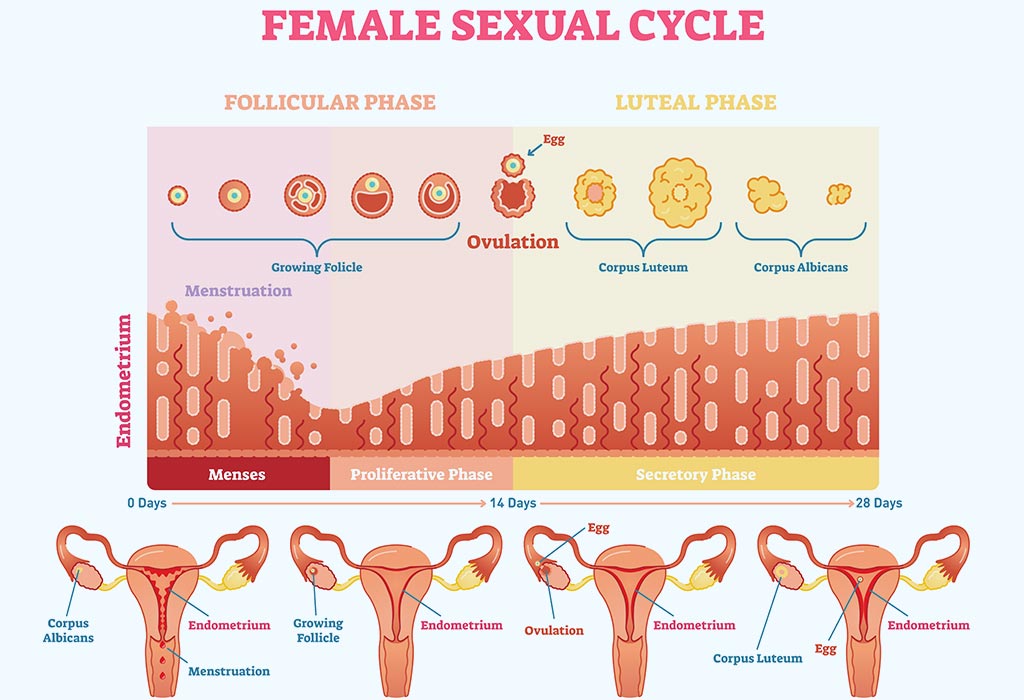
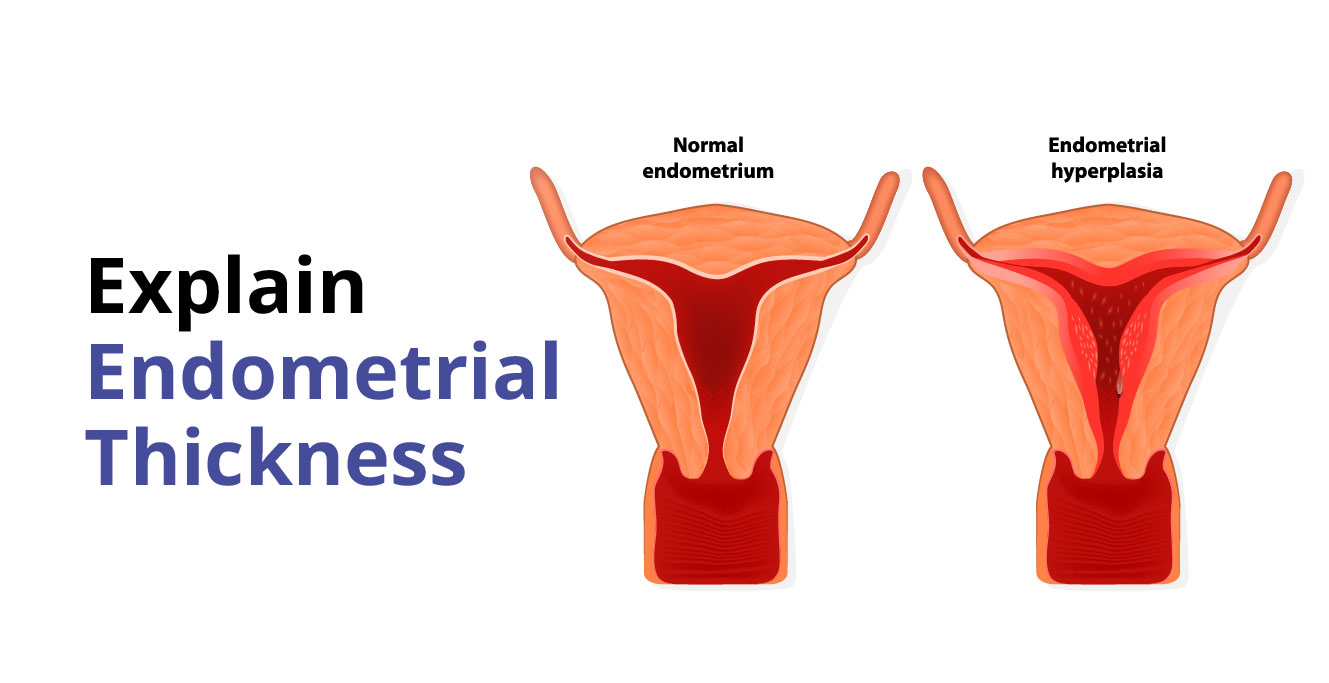
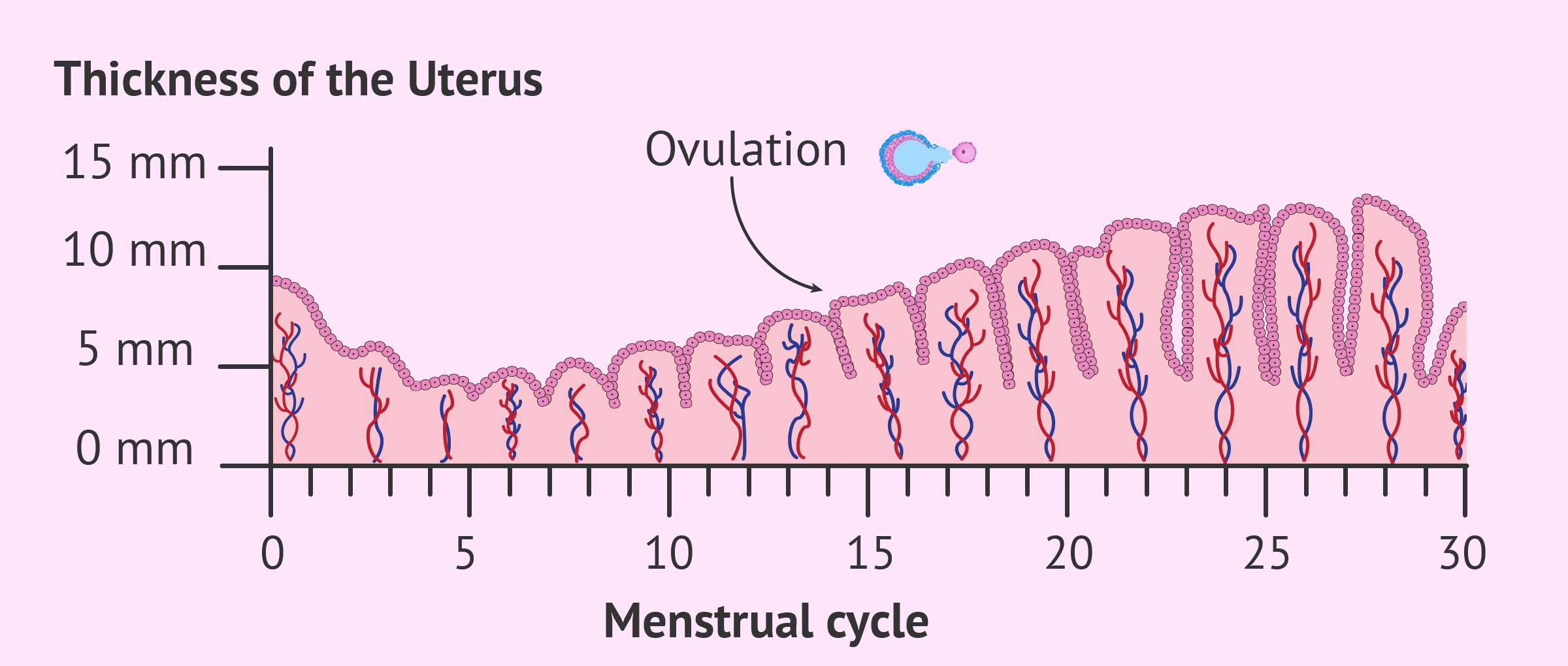
Endometrial Thickness Ovulation - An endometrial thickness of less than 14 mm is typically considered normal at any stage of the menstrual cycle. During ovulation, the endometrial thickness plays a crucial role in successful conception. Following ovulation, another hormone (progesterone) begins to increase to. As the cycle continues, the endometrium grows thicker up to 11 mm before ovulation and up to 16mm during ovulation.
An endometrial thickness of less than 14 mm is typically considered normal at any stage of the menstrual cycle. During ovulation, the endometrial thickness plays a crucial role in successful conception. As the cycle continues, the endometrium grows thicker up to 11 mm before ovulation and up to 16mm during ovulation. Following ovulation, another hormone (progesterone) begins to increase to.
As the cycle continues, the endometrium grows thicker up to 11 mm before ovulation and up to 16mm during ovulation. Following ovulation, another hormone (progesterone) begins to increase to. An endometrial thickness of less than 14 mm is typically considered normal at any stage of the menstrual cycle. During ovulation, the endometrial thickness plays a crucial role in successful conception.
The Endometrial Cycle The Female Reproductive System The
An endometrial thickness of less than 14 mm is typically considered normal at any stage of the menstrual cycle. Following ovulation, another hormone (progesterone) begins to increase to. As the cycle continues, the endometrium grows thicker up to 11 mm before ovulation and up to 16mm during ovulation. During ovulation, the endometrial thickness plays a crucial role in successful conception.
What is the endometrium? Thickening, types and pathologies
As the cycle continues, the endometrium grows thicker up to 11 mm before ovulation and up to 16mm during ovulation. During ovulation, the endometrial thickness plays a crucial role in successful conception. Following ovulation, another hormone (progesterone) begins to increase to. An endometrial thickness of less than 14 mm is typically considered normal at any stage of the menstrual cycle.
Endometrial Thickness
As the cycle continues, the endometrium grows thicker up to 11 mm before ovulation and up to 16mm during ovulation. During ovulation, the endometrial thickness plays a crucial role in successful conception. An endometrial thickness of less than 14 mm is typically considered normal at any stage of the menstrual cycle. Following ovulation, another hormone (progesterone) begins to increase to.
Endometrial Stripe Thickness Chart
As the cycle continues, the endometrium grows thicker up to 11 mm before ovulation and up to 16mm during ovulation. Following ovulation, another hormone (progesterone) begins to increase to. During ovulation, the endometrial thickness plays a crucial role in successful conception. An endometrial thickness of less than 14 mm is typically considered normal at any stage of the menstrual cycle.
Endometrium Size During Ovulation
As the cycle continues, the endometrium grows thicker up to 11 mm before ovulation and up to 16mm during ovulation. An endometrial thickness of less than 14 mm is typically considered normal at any stage of the menstrual cycle. During ovulation, the endometrial thickness plays a crucial role in successful conception. Following ovulation, another hormone (progesterone) begins to increase to.
Endometrial Thickness Ultrasound Image Appearances Endometrium
During ovulation, the endometrial thickness plays a crucial role in successful conception. Following ovulation, another hormone (progesterone) begins to increase to. An endometrial thickness of less than 14 mm is typically considered normal at any stage of the menstrual cycle. As the cycle continues, the endometrium grows thicker up to 11 mm before ovulation and up to 16mm during ovulation.
Endometrial Thickness What Is The Normal Range?
During ovulation, the endometrial thickness plays a crucial role in successful conception. Following ovulation, another hormone (progesterone) begins to increase to. An endometrial thickness of less than 14 mm is typically considered normal at any stage of the menstrual cycle. As the cycle continues, the endometrium grows thicker up to 11 mm before ovulation and up to 16mm during ovulation.
Endometrial Thickness What’s the Normal Range for Conceiving?
As the cycle continues, the endometrium grows thicker up to 11 mm before ovulation and up to 16mm during ovulation. During ovulation, the endometrial thickness plays a crucial role in successful conception. An endometrial thickness of less than 14 mm is typically considered normal at any stage of the menstrual cycle. Following ovulation, another hormone (progesterone) begins to increase to.
Endometrial Thickness Causes ,Symptoms & Treatment Birla Fertility & IVF
During ovulation, the endometrial thickness plays a crucial role in successful conception. As the cycle continues, the endometrium grows thicker up to 11 mm before ovulation and up to 16mm during ovulation. An endometrial thickness of less than 14 mm is typically considered normal at any stage of the menstrual cycle. Following ovulation, another hormone (progesterone) begins to increase to.
Uterine lining thickness chart
An endometrial thickness of less than 14 mm is typically considered normal at any stage of the menstrual cycle. As the cycle continues, the endometrium grows thicker up to 11 mm before ovulation and up to 16mm during ovulation. During ovulation, the endometrial thickness plays a crucial role in successful conception. Following ovulation, another hormone (progesterone) begins to increase to.
As The Cycle Continues, The Endometrium Grows Thicker Up To 11 Mm Before Ovulation And Up To 16Mm During Ovulation.
During ovulation, the endometrial thickness plays a crucial role in successful conception. An endometrial thickness of less than 14 mm is typically considered normal at any stage of the menstrual cycle. Following ovulation, another hormone (progesterone) begins to increase to.