Dsc Differential - In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum. Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization.
Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by. In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum.
Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Covalent Metrology
Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by. In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization.
Dsc Tga Pdf Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc And Hot Sex Picture
Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by. In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization.
Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC) Differential, 51 OFF
Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum. Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by.
DSC 1 Differential Scanning Calorimeter CSI Malaysia
Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum.
Interpretation Of Dsc Curve Differential Scanning Calorimetry Hot Sex
Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by. In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) As An Analytical, 49 OFF
In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by.
Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC) / Differential Thermal Analyzer
In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum. Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Surface Science Western
Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by. In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization.
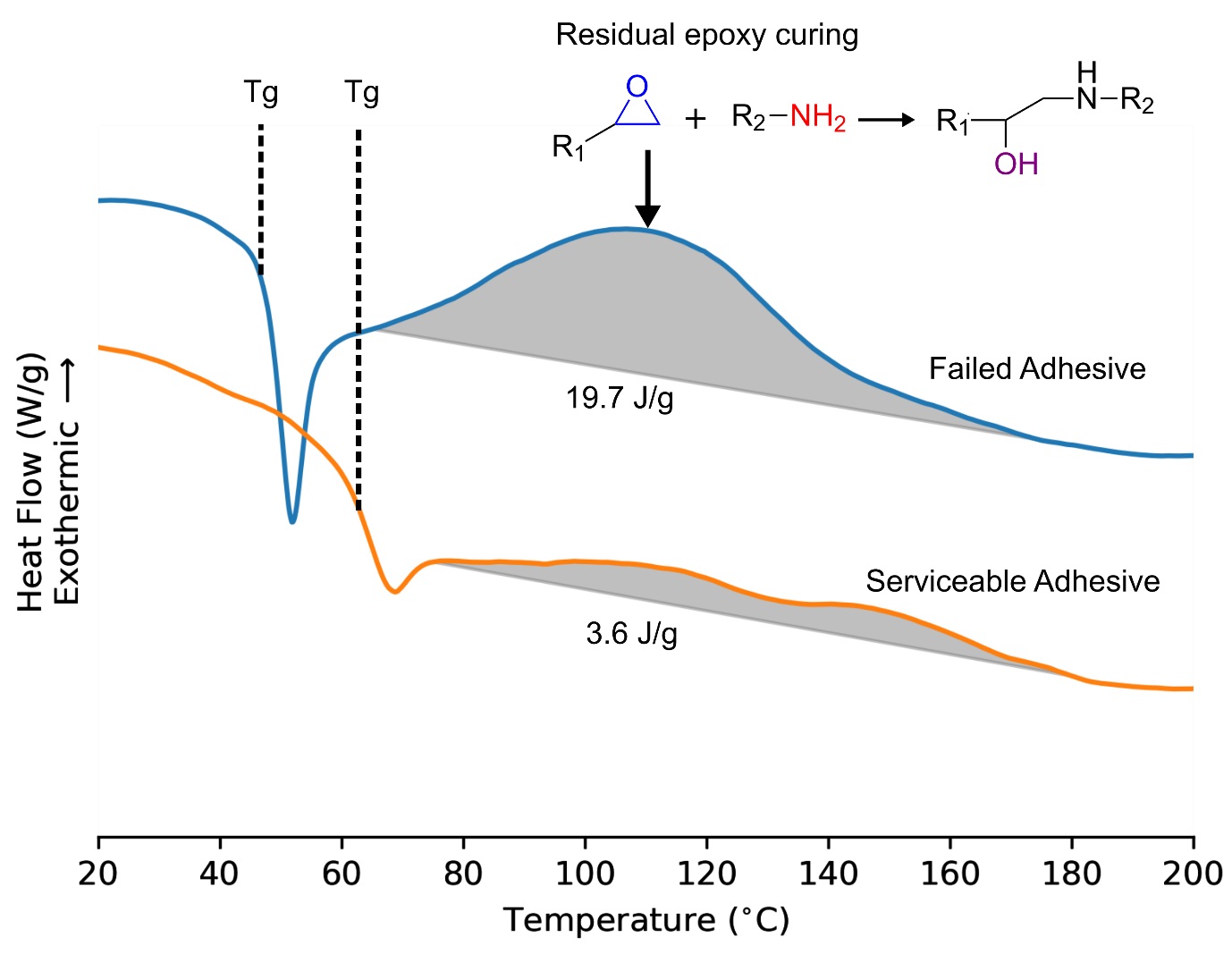
Adhesive Cure Troubleshooting with Differential Scanning Calorimetry
Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum. Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by.
BEST CHEMISTRY NOTES DSCDifferential Scanning Calorimeter
In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by.
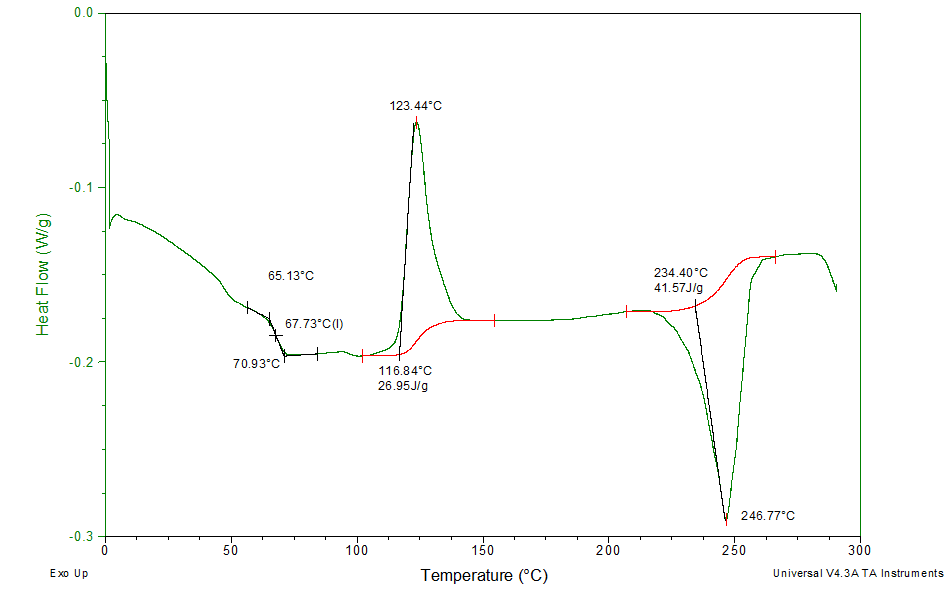
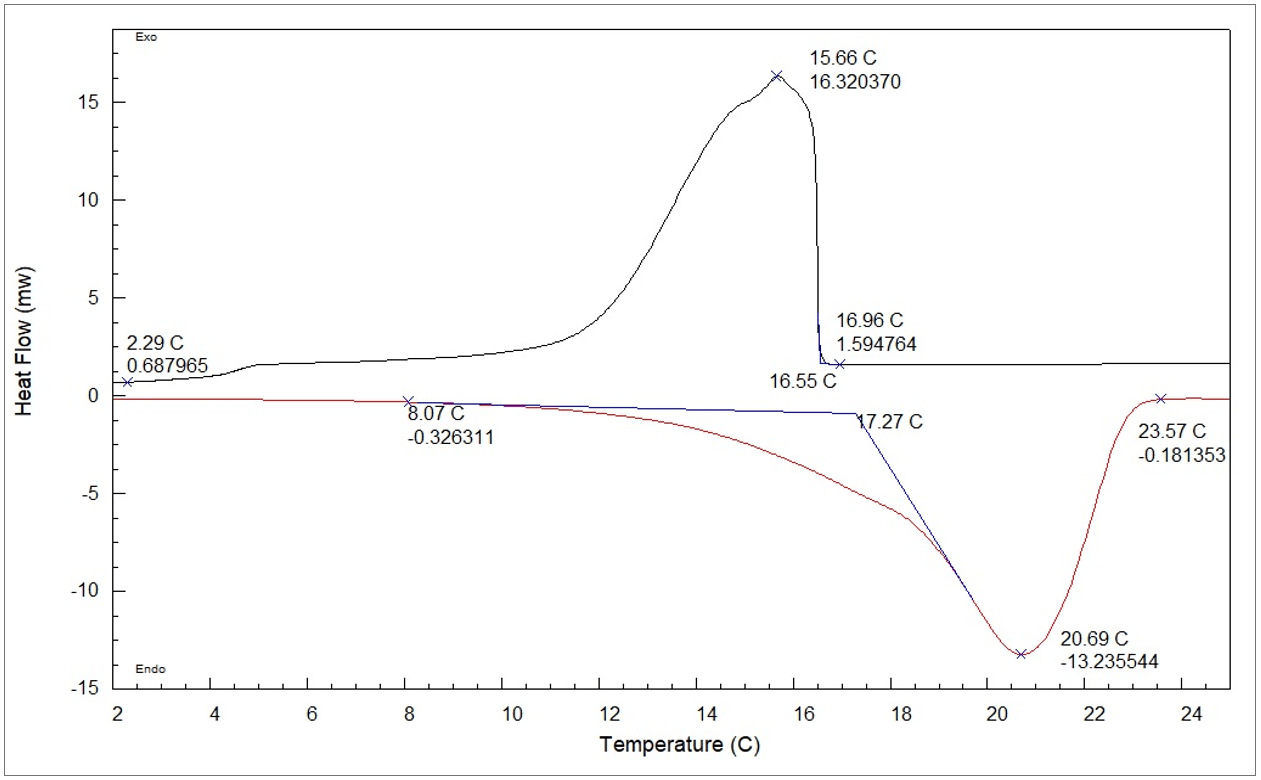
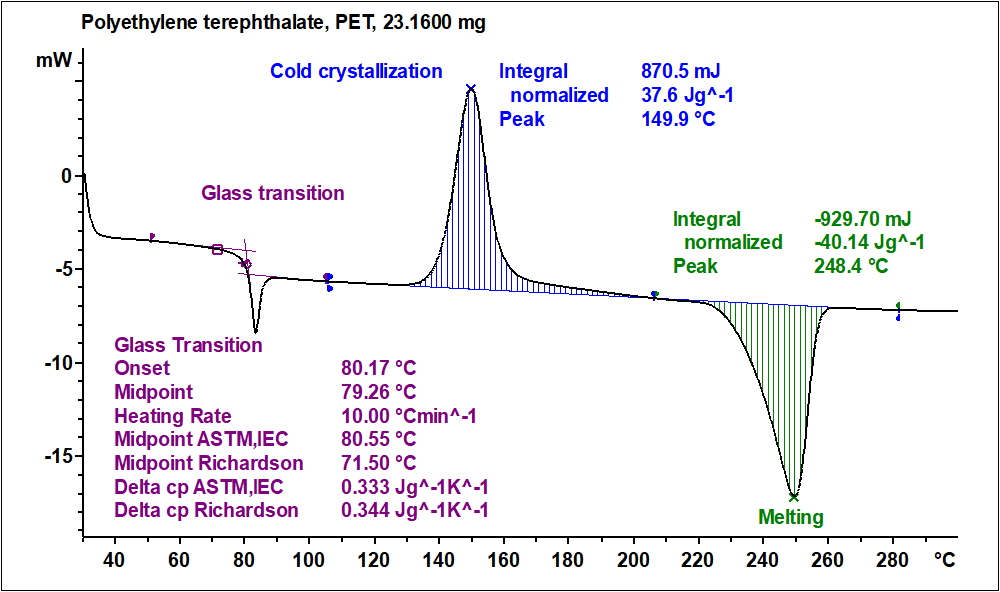
Dsc Enables The Measurements Of The Transition Such As The Glass Transition, Melting, And Crystallization.
In a differential scanning calorimeter (dsc) a sample and a reference (often a piece of indium metal) are contained in small aluminum. Differential scanning calorimetry, or dsc, is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a material’s heat capacity (cp) is changed by.