Differentiation Of Sec 2 - Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = x2 f (x) = x 2 and g(x). X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div: Sec 2 x is the square of the trigonometric function secant x, generally. The derivative of sec^2x is equal to 2 sec 2 x tanx. The formula for the derivative of sec square x is d(sec 2 x)/dx = 2 sec 2 x tanx; The derivative derivative of sec 2 x is 2sec 2 xtanx.
X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div: The derivative derivative of sec 2 x is 2sec 2 xtanx. The derivative of sec^2x is equal to 2 sec 2 x tanx. The formula for the derivative of sec square x is d(sec 2 x)/dx = 2 sec 2 x tanx; Sec 2 x is the square of the trigonometric function secant x, generally. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = x2 f (x) = x 2 and g(x).
X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div: Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = x2 f (x) = x 2 and g(x). The formula for the derivative of sec square x is d(sec 2 x)/dx = 2 sec 2 x tanx; The derivative derivative of sec 2 x is 2sec 2 xtanx. The derivative of sec^2x is equal to 2 sec 2 x tanx. Sec 2 x is the square of the trigonometric function secant x, generally.
Differentiation of Sec X AbelqoSheppard
Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = x2 f (x) = x 2 and g(x). The formula for the derivative of sec square x is d(sec 2 x)/dx = 2 sec 2 x tanx; The.
Differentiation Formulas
Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = x2 f (x) = x 2 and g(x). The derivative derivative of sec 2 x is 2sec 2 xtanx. The formula for the derivative of sec square x.
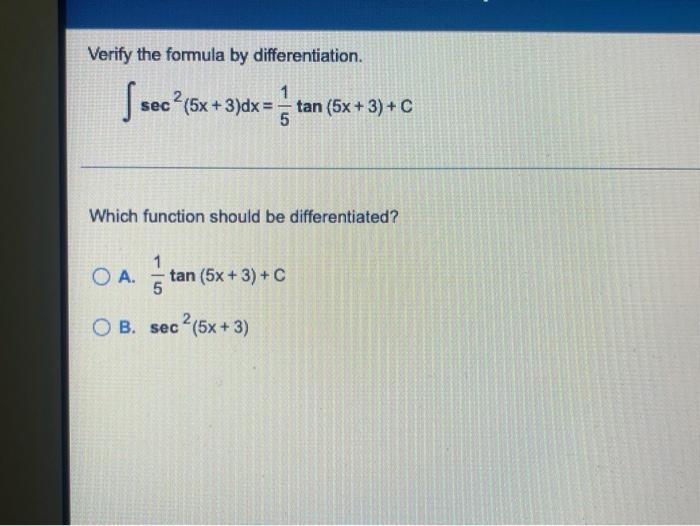
Solved Verify the formula by differentiation. [sec ² sec ²
The formula for the derivative of sec square x is d(sec 2 x)/dx = 2 sec 2 x tanx; X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div: Sec 2 x is the square of the trigonometric function secant x, generally. The derivative of sec^2x is equal to 2 sec 2 x tanx. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states.
Differentiation of Sec X HavenoiRosales
X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div: Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = x2 f (x) = x 2 and g(x). Sec 2 x is the square of the trigonometric function secant.
Sec 2 Math PDF Mathematical Concepts Mathematics
Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = x2 f (x) = x 2 and g(x). The derivative derivative of sec 2 x is 2sec 2 xtanx. The formula for the derivative of sec square x.
Sec.2 Part A 23 PDF
Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = x2 f (x) = x 2 and g(x). The formula for the derivative of sec square x is d(sec 2 x)/dx = 2 sec 2 x tanx; X^{\msquare}.
Sec.2 Part A 13 PDF
The formula for the derivative of sec square x is d(sec 2 x)/dx = 2 sec 2 x tanx; The derivative of sec^2x is equal to 2 sec 2 x tanx. X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div: Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f.
Differentiation of Sec X JesusjoysLeon
X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div: The derivative derivative of sec 2 x is 2sec 2 xtanx. Sec 2 x is the square of the trigonometric function secant x, generally. The formula for the derivative of sec square x is d(sec 2 x)/dx = 2 sec 2 x tanx; Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that.
Solved Verify the formula by differentiation. sec 2
Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = x2 f (x) = x 2 and g(x). X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div: The derivative of sec^2x is equal to 2 sec 2 x.
Differentiation of Sec x, Formula, and Examples
Sec 2 x is the square of the trigonometric function secant x, generally. The formula for the derivative of sec square x is d(sec 2 x)/dx = 2 sec 2 x tanx; The derivative of sec^2x is equal to 2 sec 2 x tanx. Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f.
The Derivative Derivative Of Sec 2 X Is 2Sec 2 Xtanx.
Sec 2 x is the square of the trigonometric function secant x, generally. The derivative of sec^2x is equal to 2 sec 2 x tanx. The formula for the derivative of sec square x is d(sec 2 x)/dx = 2 sec 2 x tanx; Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx [f (g(x))] d d x [f (g (x))] is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ (g (x)) g ′ (x) where f (x) = x2 f (x) = x 2 and g(x).