Differentiation Of 0 - The derivative calculator supports solving first, second., fourth derivatives, as well as implicit differentiation and finding the zeros/roots. Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph. This makes sense because it is a. The derivative of a constant is always zero, regardless of the value of the constant. How do you find the derivative of 0 using the limit definition? In particular, one should learn that differentiation is a linear operator, and applying any linear operator to zero always returns zero. The derivative of zero is zero. So, the derivative of 0 (which is a constant) is also 0.
Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph. The derivative calculator supports solving first, second., fourth derivatives, as well as implicit differentiation and finding the zeros/roots. How do you find the derivative of 0 using the limit definition? So, the derivative of 0 (which is a constant) is also 0. The derivative of a constant is always zero, regardless of the value of the constant. This makes sense because it is a. In particular, one should learn that differentiation is a linear operator, and applying any linear operator to zero always returns zero. The derivative of zero is zero.
So, the derivative of 0 (which is a constant) is also 0. This makes sense because it is a. How do you find the derivative of 0 using the limit definition? In particular, one should learn that differentiation is a linear operator, and applying any linear operator to zero always returns zero. The derivative of a constant is always zero, regardless of the value of the constant. Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph. The derivative of zero is zero. The derivative calculator supports solving first, second., fourth derivatives, as well as implicit differentiation and finding the zeros/roots.
Differentiation Rules
This makes sense because it is a. The derivative calculator supports solving first, second., fourth derivatives, as well as implicit differentiation and finding the zeros/roots. Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph. The derivative of a constant is always zero, regardless of the value of the constant. How do you find the derivative of 0.
Differentiation Formulas
The derivative of a constant is always zero, regardless of the value of the constant. This makes sense because it is a. How do you find the derivative of 0 using the limit definition? In particular, one should learn that differentiation is a linear operator, and applying any linear operator to zero always returns zero. The derivative of zero is.
(PDF) Differentiation Formulas
How do you find the derivative of 0 using the limit definition? This makes sense because it is a. In particular, one should learn that differentiation is a linear operator, and applying any linear operator to zero always returns zero. The derivative of a constant is always zero, regardless of the value of the constant. So, the derivative of 0.
Differentiation icon Generic gradient outline
The derivative of zero is zero. This makes sense because it is a. So, the derivative of 0 (which is a constant) is also 0. The derivative calculator supports solving first, second., fourth derivatives, as well as implicit differentiation and finding the zeros/roots. How do you find the derivative of 0 using the limit definition?
Differentiation free icon
The derivative of zero is zero. The derivative of a constant is always zero, regardless of the value of the constant. So, the derivative of 0 (which is a constant) is also 0. How do you find the derivative of 0 using the limit definition? In particular, one should learn that differentiation is a linear operator, and applying any linear.
Differentiation Generic Flat icon
The derivative of a constant is always zero, regardless of the value of the constant. Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph. So, the derivative of 0 (which is a constant) is also 0. In particular, one should learn that differentiation is a linear operator, and applying any linear operator to zero always returns zero..
Product Differentiation Examples And Strategies Glossary, 58 OFF
In particular, one should learn that differentiation is a linear operator, and applying any linear operator to zero always returns zero. The derivative of a constant is always zero, regardless of the value of the constant. This makes sense because it is a. So, the derivative of 0 (which is a constant) is also 0. The derivative calculator supports solving.
Differentiation Generic Flat icon
The derivative calculator supports solving first, second., fourth derivatives, as well as implicit differentiation and finding the zeros/roots. In particular, one should learn that differentiation is a linear operator, and applying any linear operator to zero always returns zero. The derivative of zero is zero. The derivative of a constant is always zero, regardless of the value of the constant..
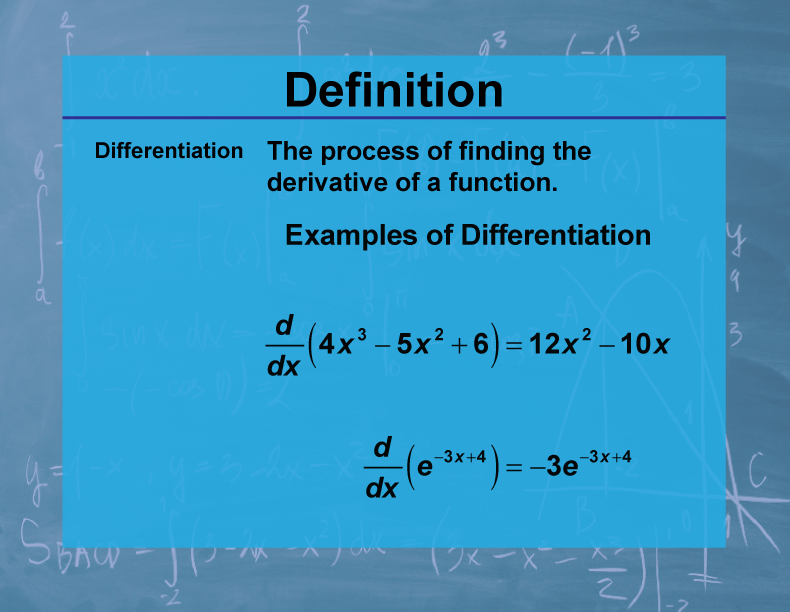
Differentiation
This makes sense because it is a. Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph. The derivative calculator supports solving first, second., fourth derivatives, as well as implicit differentiation and finding the zeros/roots. The derivative of zero is zero. The derivative of a constant is always zero, regardless of the value of the constant.
Master Template
The derivative of a constant is always zero, regardless of the value of the constant. The derivative calculator supports solving first, second., fourth derivatives, as well as implicit differentiation and finding the zeros/roots. So, the derivative of 0 (which is a constant) is also 0. In particular, one should learn that differentiation is a linear operator, and applying any linear.
In Particular, One Should Learn That Differentiation Is A Linear Operator, And Applying Any Linear Operator To Zero Always Returns Zero.
Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph. The derivative calculator supports solving first, second., fourth derivatives, as well as implicit differentiation and finding the zeros/roots. This makes sense because it is a. The derivative of a constant is always zero, regardless of the value of the constant.
The Derivative Of Zero Is Zero.
How do you find the derivative of 0 using the limit definition? So, the derivative of 0 (which is a constant) is also 0.