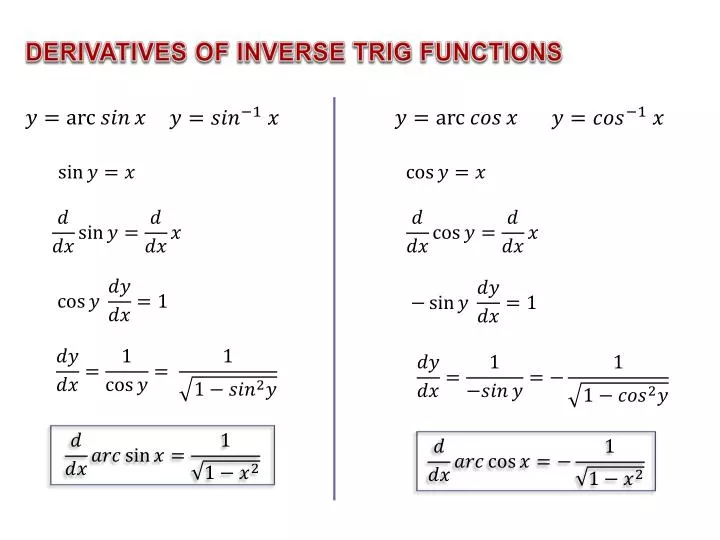
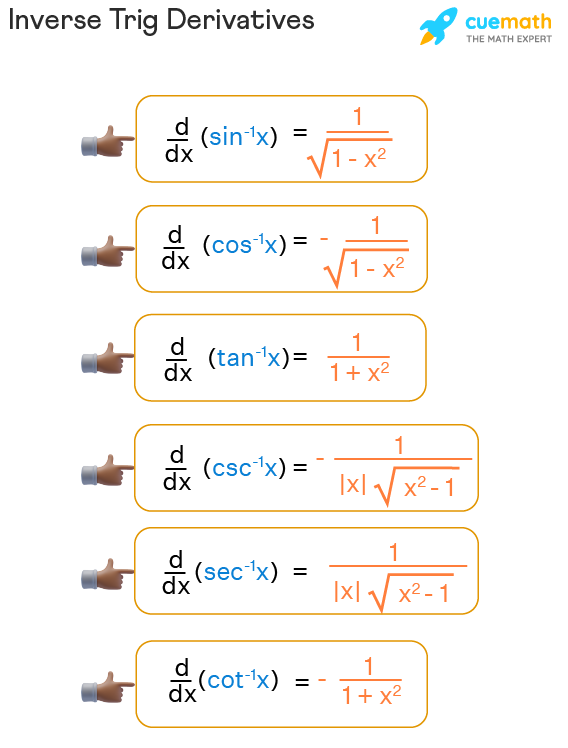
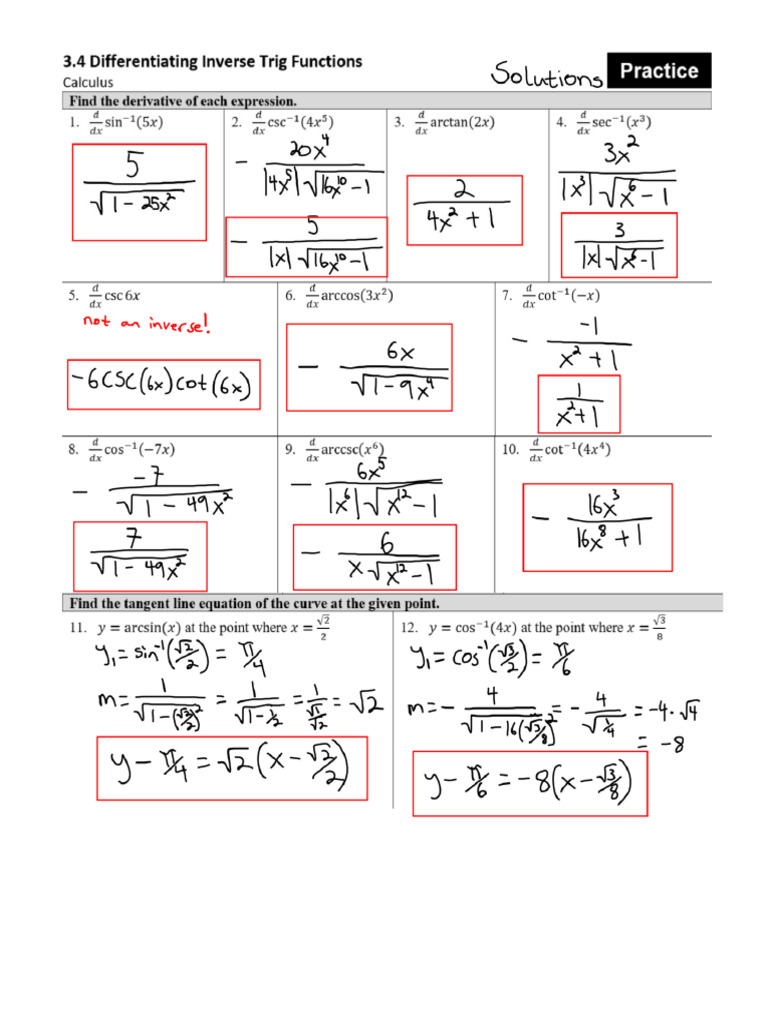
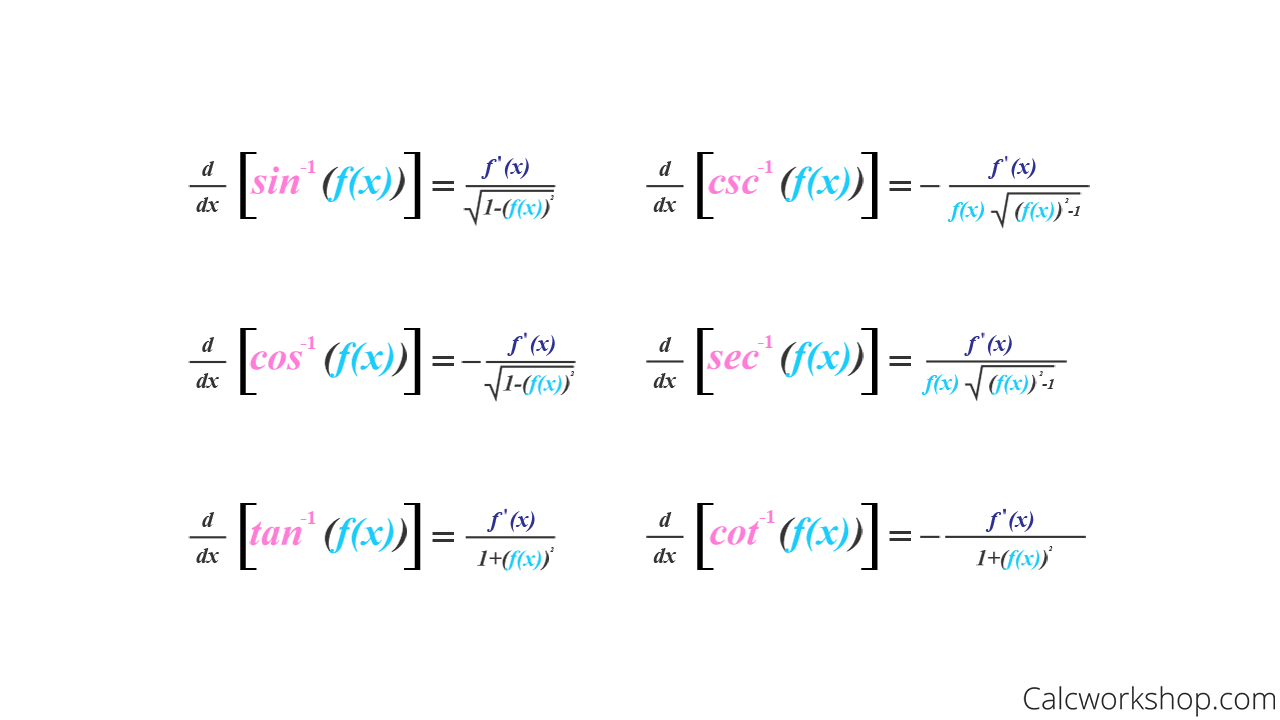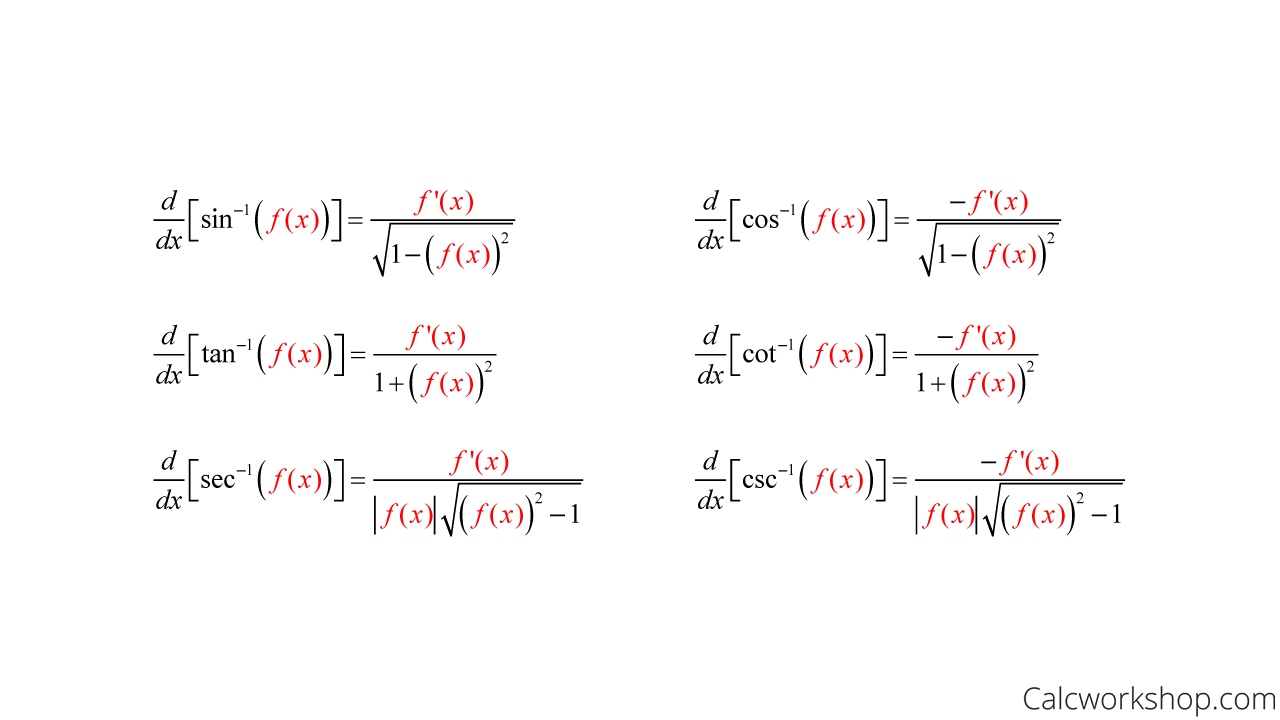Differentiating Inverse Trig Functions - Then for all x such that f ′ (f − 1 (x)) ≠ 0, (f − 1) ′ (x) =. Here is a set of practice problems to accompany the. Suppose f (x) is a function which has an inverse, f − 1 (x), and both f and f − 1 are differentiable. For each of the following problems differentiate the given function. Derivative of inverse trigonometric functions the inverse trigonometric functions are also called as arcus functions, cyclometric functions or anti.
Then for all x such that f ′ (f − 1 (x)) ≠ 0, (f − 1) ′ (x) =. Derivative of inverse trigonometric functions the inverse trigonometric functions are also called as arcus functions, cyclometric functions or anti. Suppose f (x) is a function which has an inverse, f − 1 (x), and both f and f − 1 are differentiable. Here is a set of practice problems to accompany the. For each of the following problems differentiate the given function.
For each of the following problems differentiate the given function. Then for all x such that f ′ (f − 1 (x)) ≠ 0, (f − 1) ′ (x) =. Here is a set of practice problems to accompany the. Derivative of inverse trigonometric functions the inverse trigonometric functions are also called as arcus functions, cyclometric functions or anti. Suppose f (x) is a function which has an inverse, f − 1 (x), and both f and f − 1 are differentiable.
PPT DERIVATIVES OF INVERSE TRIG FUNCTIONS PowerPoint Presentation
Suppose f (x) is a function which has an inverse, f − 1 (x), and both f and f − 1 are differentiable. For each of the following problems differentiate the given function. Then for all x such that f ′ (f − 1 (x)) ≠ 0, (f − 1) ′ (x) =. Here is a set of practice problems.
12X1 T05 04 differentiating inverse trig (2010)
Then for all x such that f ′ (f − 1 (x)) ≠ 0, (f − 1) ′ (x) =. For each of the following problems differentiate the given function. Derivative of inverse trigonometric functions the inverse trigonometric functions are also called as arcus functions, cyclometric functions or anti. Suppose f (x) is a function which has an inverse, f.
Inverse Trig Derivatives
Here is a set of practice problems to accompany the. Then for all x such that f ′ (f − 1 (x)) ≠ 0, (f − 1) ′ (x) =. Suppose f (x) is a function which has an inverse, f − 1 (x), and both f and f − 1 are differentiable. Derivative of inverse trigonometric functions the inverse.
Differentiating inverse trig r/alevelmaths
Derivative of inverse trigonometric functions the inverse trigonometric functions are also called as arcus functions, cyclometric functions or anti. Here is a set of practice problems to accompany the. Suppose f (x) is a function which has an inverse, f − 1 (x), and both f and f − 1 are differentiable. For each of the following problems differentiate the.
Trig And Inverse Trig
Suppose f (x) is a function which has an inverse, f − 1 (x), and both f and f − 1 are differentiable. For each of the following problems differentiate the given function. Derivative of inverse trigonometric functions the inverse trigonometric functions are also called as arcus functions, cyclometric functions or anti. Then for all x such that f ′.
Differentiating Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Here is a set of practice problems to accompany the. Suppose f (x) is a function which has an inverse, f − 1 (x), and both f and f − 1 are differentiable. Then for all x such that f ′ (f − 1 (x)) ≠ 0, (f − 1) ′ (x) =. Derivative of inverse trigonometric functions the inverse.
Inverse Trig Derivatives (Derivatives of Inverse Trig Functions)
Here is a set of practice problems to accompany the. Suppose f (x) is a function which has an inverse, f − 1 (x), and both f and f − 1 are differentiable. Derivative of inverse trigonometric functions the inverse trigonometric functions are also called as arcus functions, cyclometric functions or anti. For each of the following problems differentiate the.
Differentiating Inverse Trig Functions Notes ANSWER PDF
For each of the following problems differentiate the given function. Derivative of inverse trigonometric functions the inverse trigonometric functions are also called as arcus functions, cyclometric functions or anti. Here is a set of practice problems to accompany the. Suppose f (x) is a function which has an inverse, f − 1 (x), and both f and f − 1.
SOLUTION Differentiating inverse trig functions Studypool
Derivative of inverse trigonometric functions the inverse trigonometric functions are also called as arcus functions, cyclometric functions or anti. Then for all x such that f ′ (f − 1 (x)) ≠ 0, (f − 1) ′ (x) =. Here is a set of practice problems to accompany the. For each of the following problems differentiate the given function. Suppose.
Inverse Trig Derivatives (w/ 7 StepbyStep Examples!)
Derivative of inverse trigonometric functions the inverse trigonometric functions are also called as arcus functions, cyclometric functions or anti. Then for all x such that f ′ (f − 1 (x)) ≠ 0, (f − 1) ′ (x) =. For each of the following problems differentiate the given function. Here is a set of practice problems to accompany the. Suppose.
Then For All X Such That F ′ (F − 1 (X)) ≠ 0, (F − 1) ′ (X) =.
For each of the following problems differentiate the given function. Derivative of inverse trigonometric functions the inverse trigonometric functions are also called as arcus functions, cyclometric functions or anti. Here is a set of practice problems to accompany the. Suppose f (x) is a function which has an inverse, f − 1 (x), and both f and f − 1 are differentiable.