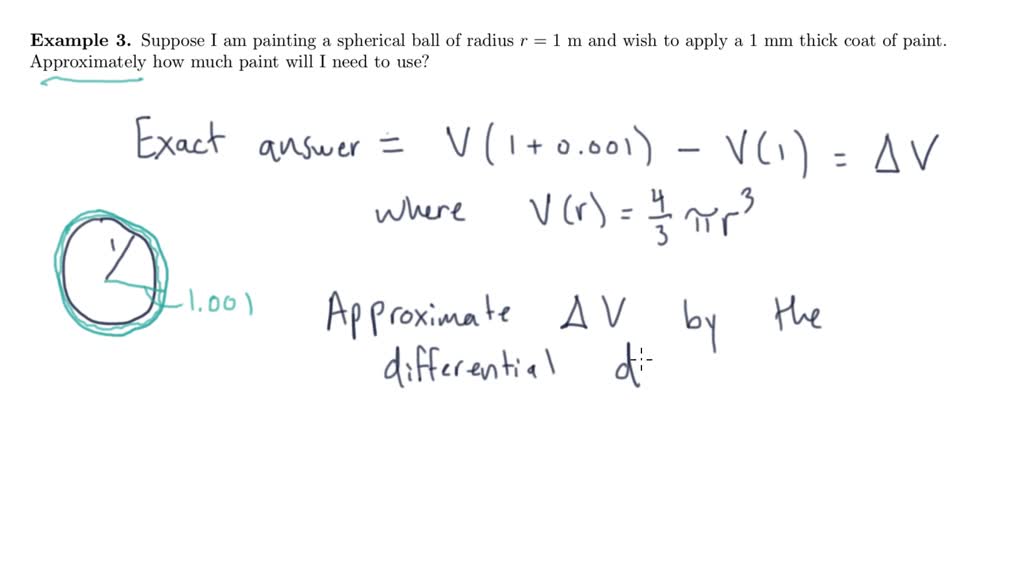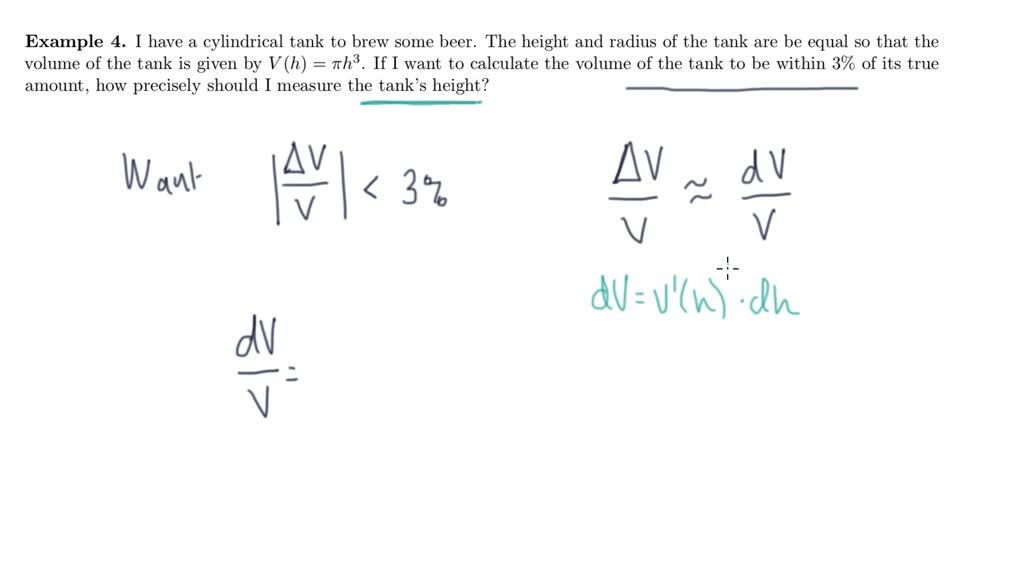Differentials And Linearization - This calculus video tutorial provides a basic introduction into differentials and. In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function y = ƒ(x) with. We can compare actual changes in a function and the. 3.11 linearization and differentials 4 definition. Example 1 find the linearization l(x) of the function f(x) = sinxat π/6. What does it mean for a function of two variables to be locally linear at a point? We have seen that linear approximations can be used to estimate function.
Example 1 find the linearization l(x) of the function f(x) = sinxat π/6. This calculus video tutorial provides a basic introduction into differentials and. 3.11 linearization and differentials 4 definition. In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function y = ƒ(x) with. We can compare actual changes in a function and the. We have seen that linear approximations can be used to estimate function. What does it mean for a function of two variables to be locally linear at a point?
What does it mean for a function of two variables to be locally linear at a point? In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function y = ƒ(x) with. 3.11 linearization and differentials 4 definition. We can compare actual changes in a function and the. Example 1 find the linearization l(x) of the function f(x) = sinxat π/6. We have seen that linear approximations can be used to estimate function. This calculus video tutorial provides a basic introduction into differentials and.
Linearization and differentials overview Numerade
We can compare actual changes in a function and the. We have seen that linear approximations can be used to estimate function. Example 1 find the linearization l(x) of the function f(x) = sinxat π/6. In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function y = ƒ(x) with. This calculus video tutorial provides a basic.
(PDF) SECTION 3.5 DIFFERENTIALS and LINEARIZATION OF FUNCTIONSkkuniyuk
We can compare actual changes in a function and the. We have seen that linear approximations can be used to estimate function. Example 1 find the linearization l(x) of the function f(x) = sinxat π/6. What does it mean for a function of two variables to be locally linear at a point? In calculus, the differential represents the principal part.
3.9 Linearization and Differentials
What does it mean for a function of two variables to be locally linear at a point? In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function y = ƒ(x) with. We have seen that linear approximations can be used to estimate function. 3.11 linearization and differentials 4 definition. We can compare actual changes in a.
3.9 Linearization and Differentials
3.11 linearization and differentials 4 definition. What does it mean for a function of two variables to be locally linear at a point? We can compare actual changes in a function and the. Example 1 find the linearization l(x) of the function f(x) = sinxat π/6. This calculus video tutorial provides a basic introduction into differentials and.
(PDF) SECTION 3.5 DIFFERENTIALS and LINEARIZATION OF FUNCTIONSkkuniyuk
Example 1 find the linearization l(x) of the function f(x) = sinxat π/6. 3.11 linearization and differentials 4 definition. In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function y = ƒ(x) with. This calculus video tutorial provides a basic introduction into differentials and. We can compare actual changes in a function and the.
Linearization and differentials overview Numerade
What does it mean for a function of two variables to be locally linear at a point? We can compare actual changes in a function and the. Example 1 find the linearization l(x) of the function f(x) = sinxat π/6. This calculus video tutorial provides a basic introduction into differentials and. 3.11 linearization and differentials 4 definition.
Linearization and differentials example 1 Numerade
We have seen that linear approximations can be used to estimate function. We can compare actual changes in a function and the. This calculus video tutorial provides a basic introduction into differentials and. In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function y = ƒ(x) with. Example 1 find the linearization l(x) of the function.
Linearization and differentials overview Numerade
We can compare actual changes in a function and the. What does it mean for a function of two variables to be locally linear at a point? We have seen that linear approximations can be used to estimate function. This calculus video tutorial provides a basic introduction into differentials and. 3.11 linearization and differentials 4 definition.
WS 03.7 Linearization & Differentials KEY PDF
What does it mean for a function of two variables to be locally linear at a point? We have seen that linear approximations can be used to estimate function. Example 1 find the linearization l(x) of the function f(x) = sinxat π/6. We can compare actual changes in a function and the. In calculus, the differential represents the principal part.
Linearization and Differentials
What does it mean for a function of two variables to be locally linear at a point? 3.11 linearization and differentials 4 definition. This calculus video tutorial provides a basic introduction into differentials and. We can compare actual changes in a function and the. In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function y =.
We Can Compare Actual Changes In A Function And The.
In calculus, the differential represents the principal part of the change in a function y = ƒ(x) with. This calculus video tutorial provides a basic introduction into differentials and. We have seen that linear approximations can be used to estimate function. What does it mean for a function of two variables to be locally linear at a point?
Example 1 Find The Linearization L(X) Of The Function F(X) = Sinxat Π/6.
3.11 linearization and differentials 4 definition.