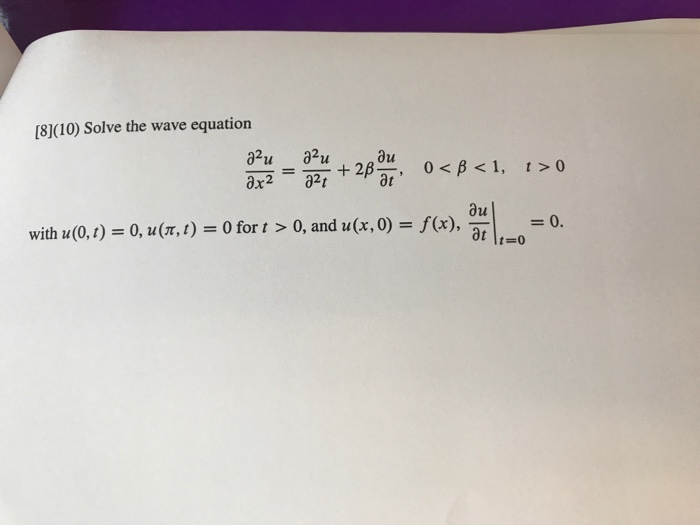Differential Wave Equation - 7.4 wave equation the wave equation models the propagation of waves, such as sound waves, light. The governing equation for \(u(x, t)\), the position of the string from its equilibrium. The principle of “superposition” holds. The wave equation shows how waves move along the x axis, starting. A wave equation is a differential equation involving partial derivatives, representing some medium. The wave equation is linear: In this section we do a partial derivation of the wave equation which can be.
The principle of “superposition” holds. A wave equation is a differential equation involving partial derivatives, representing some medium. The wave equation shows how waves move along the x axis, starting. The governing equation for \(u(x, t)\), the position of the string from its equilibrium. The wave equation is linear: 7.4 wave equation the wave equation models the propagation of waves, such as sound waves, light. In this section we do a partial derivation of the wave equation which can be.
The wave equation is linear: A wave equation is a differential equation involving partial derivatives, representing some medium. In this section we do a partial derivation of the wave equation which can be. The wave equation shows how waves move along the x axis, starting. The governing equation for \(u(x, t)\), the position of the string from its equilibrium. The principle of “superposition” holds. 7.4 wave equation the wave equation models the propagation of waves, such as sound waves, light.
Solved Solve the wave equation partial differential ^2
The governing equation for \(u(x, t)\), the position of the string from its equilibrium. A wave equation is a differential equation involving partial derivatives, representing some medium. In this section we do a partial derivation of the wave equation which can be. The wave equation shows how waves move along the x axis, starting. The wave equation is linear:
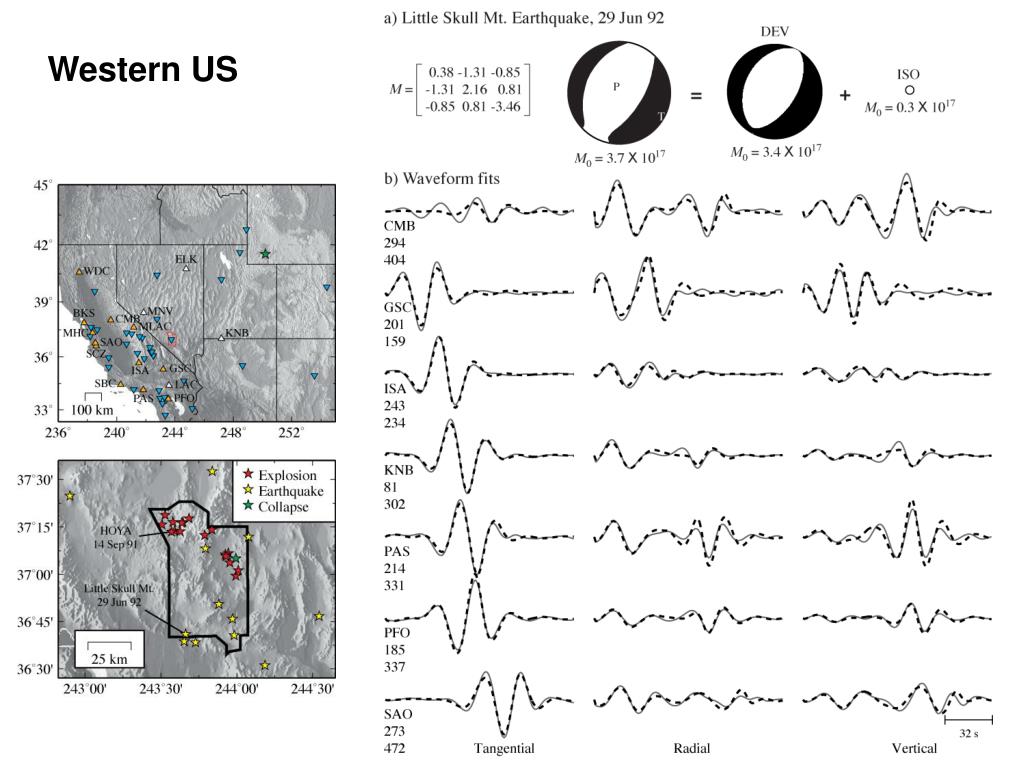
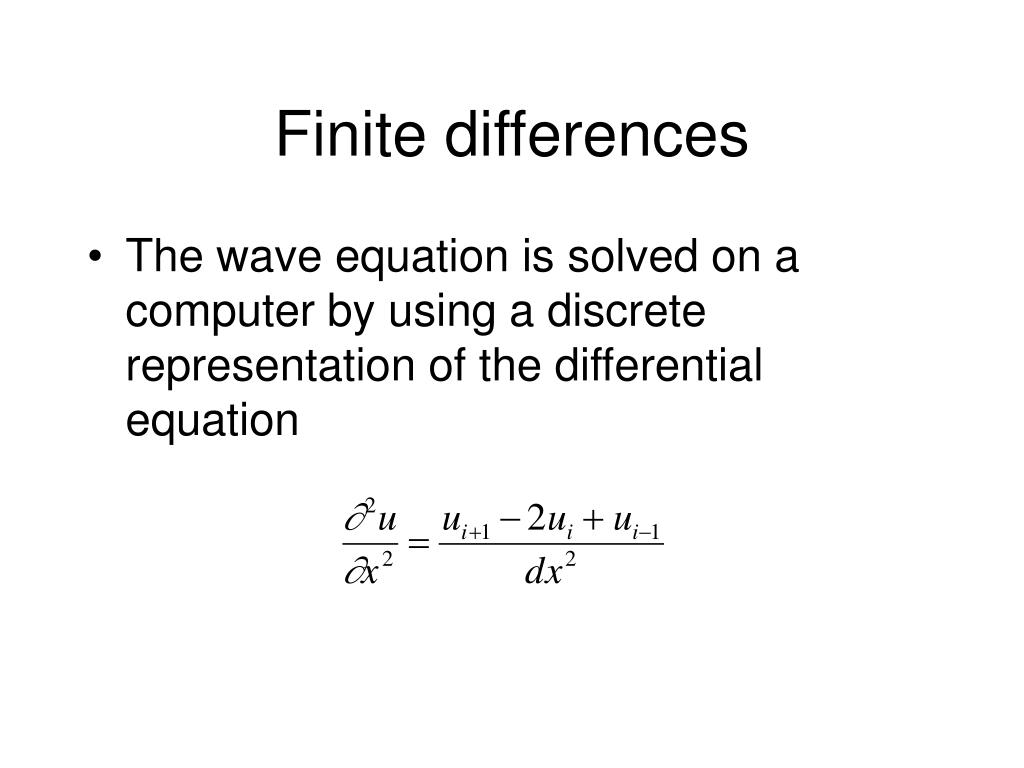
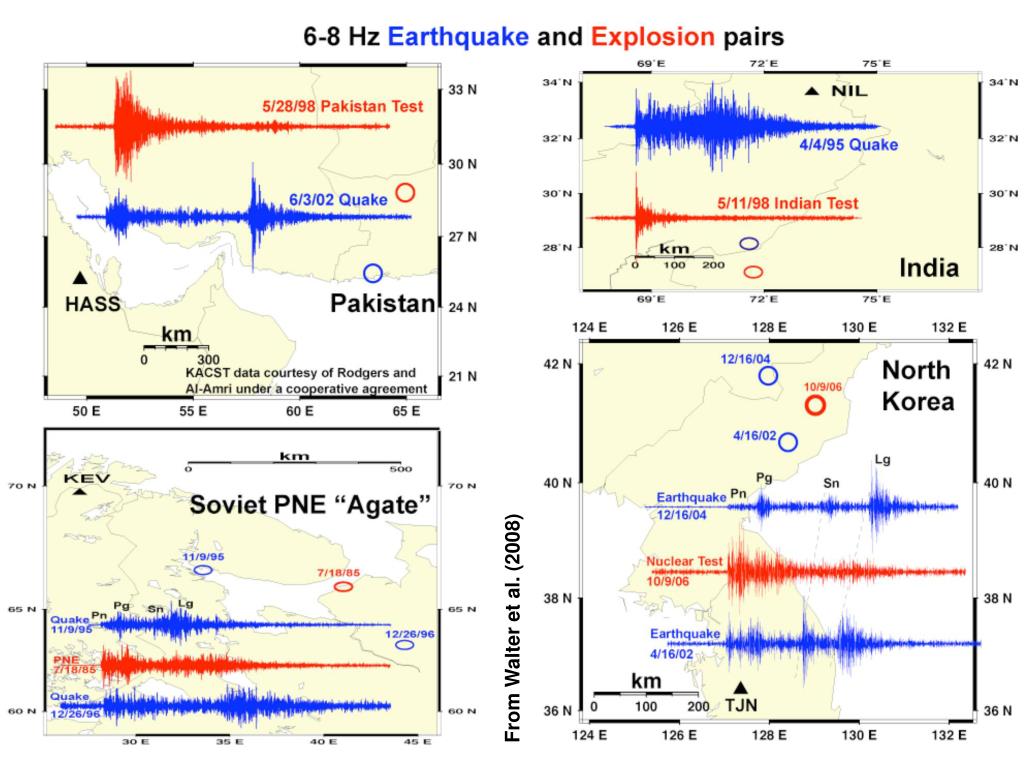
PPT Differential wave equation and seismic events PowerPoint
The wave equation shows how waves move along the x axis, starting. The wave equation is linear: A wave equation is a differential equation involving partial derivatives, representing some medium. The governing equation for \(u(x, t)\), the position of the string from its equilibrium. 7.4 wave equation the wave equation models the propagation of waves, such as sound waves, light.
proof verification Application of differential equation (wave
The wave equation is linear: The governing equation for \(u(x, t)\), the position of the string from its equilibrium. A wave equation is a differential equation involving partial derivatives, representing some medium. 7.4 wave equation the wave equation models the propagation of waves, such as sound waves, light. In this section we do a partial derivation of the wave equation.
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION OF WAVE FUNCTIONConsider a wave function of a wav..
7.4 wave equation the wave equation models the propagation of waves, such as sound waves, light. In this section we do a partial derivation of the wave equation which can be. A wave equation is a differential equation involving partial derivatives, representing some medium. The principle of “superposition” holds. The wave equation shows how waves move along the x axis,.
PPT Differential wave equation and seismic events PowerPoint
A wave equation is a differential equation involving partial derivatives, representing some medium. The principle of “superposition” holds. The wave equation is linear: The governing equation for \(u(x, t)\), the position of the string from its equilibrium. In this section we do a partial derivation of the wave equation which can be.
PPT Differential wave equation and seismic events PowerPoint
A wave equation is a differential equation involving partial derivatives, representing some medium. The principle of “superposition” holds. In this section we do a partial derivation of the wave equation which can be. The wave equation is linear: 7.4 wave equation the wave equation models the propagation of waves, such as sound waves, light.
PPT Differential wave equation and seismic events PowerPoint
The wave equation shows how waves move along the x axis, starting. The principle of “superposition” holds. A wave equation is a differential equation involving partial derivatives, representing some medium. The wave equation is linear: In this section we do a partial derivation of the wave equation which can be.
PPT Differential wave equation and seismic events PowerPoint
The wave equation shows how waves move along the x axis, starting. In this section we do a partial derivation of the wave equation which can be. A wave equation is a differential equation involving partial derivatives, representing some medium. The governing equation for \(u(x, t)\), the position of the string from its equilibrium. The wave equation is linear:
Field Wave Equation Derivation Tessshebaylo
The wave equation is linear: The wave equation shows how waves move along the x axis, starting. 7.4 wave equation the wave equation models the propagation of waves, such as sound waves, light. A wave equation is a differential equation involving partial derivatives, representing some medium. In this section we do a partial derivation of the wave equation which can.
PPT Differential wave equation and seismic events PowerPoint
The principle of “superposition” holds. The governing equation for \(u(x, t)\), the position of the string from its equilibrium. In this section we do a partial derivation of the wave equation which can be. The wave equation shows how waves move along the x axis, starting. A wave equation is a differential equation involving partial derivatives, representing some medium.
7.4 Wave Equation The Wave Equation Models The Propagation Of Waves, Such As Sound Waves, Light.
In this section we do a partial derivation of the wave equation which can be. The wave equation shows how waves move along the x axis, starting. The principle of “superposition” holds. A wave equation is a differential equation involving partial derivatives, representing some medium.
The Governing Equation For \(U(X, T)\), The Position Of The String From Its Equilibrium.
The wave equation is linear: