Differential Rate Law - Rate = k[a]m[b]n[c]p… in which [a], [b], and [c] represent the molar concentrations of. Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in the concentration of reactants (d [r]) over a small interval of time (dt). A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or more reactants (δ[r]) over a specific time interval (δt). The differential rate law can be. In other words, if we have a reaction of the type: Differential rate laws express the rate of reaction as a function of a change in the concentration of one or more reactants over a particular period of time; In general, a rate law (or differential rate law, as it is sometimes called) takes this form: They are used to describe what is.
In general, a rate law (or differential rate law, as it is sometimes called) takes this form: In other words, if we have a reaction of the type: Differential rate laws express the rate of reaction as a function of a change in the concentration of one or more reactants over a particular period of time; Rate = k[a]m[b]n[c]p… in which [a], [b], and [c] represent the molar concentrations of. Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in the concentration of reactants (d [r]) over a small interval of time (dt). The differential rate law can be. They are used to describe what is. A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or more reactants (δ[r]) over a specific time interval (δt).
They are used to describe what is. Rate = k[a]m[b]n[c]p… in which [a], [b], and [c] represent the molar concentrations of. Differential rate laws express the rate of reaction as a function of a change in the concentration of one or more reactants over a particular period of time; In general, a rate law (or differential rate law, as it is sometimes called) takes this form: Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in the concentration of reactants (d [r]) over a small interval of time (dt). In other words, if we have a reaction of the type: The differential rate law can be. A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or more reactants (δ[r]) over a specific time interval (δt).
Solved From the differential rate law for a secondorder
A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or more reactants (δ[r]) over a specific time interval (δt). In general, a rate law (or differential rate law, as it is sometimes called) takes this form: In other words, if we have a reaction of the type: They are used to describe.
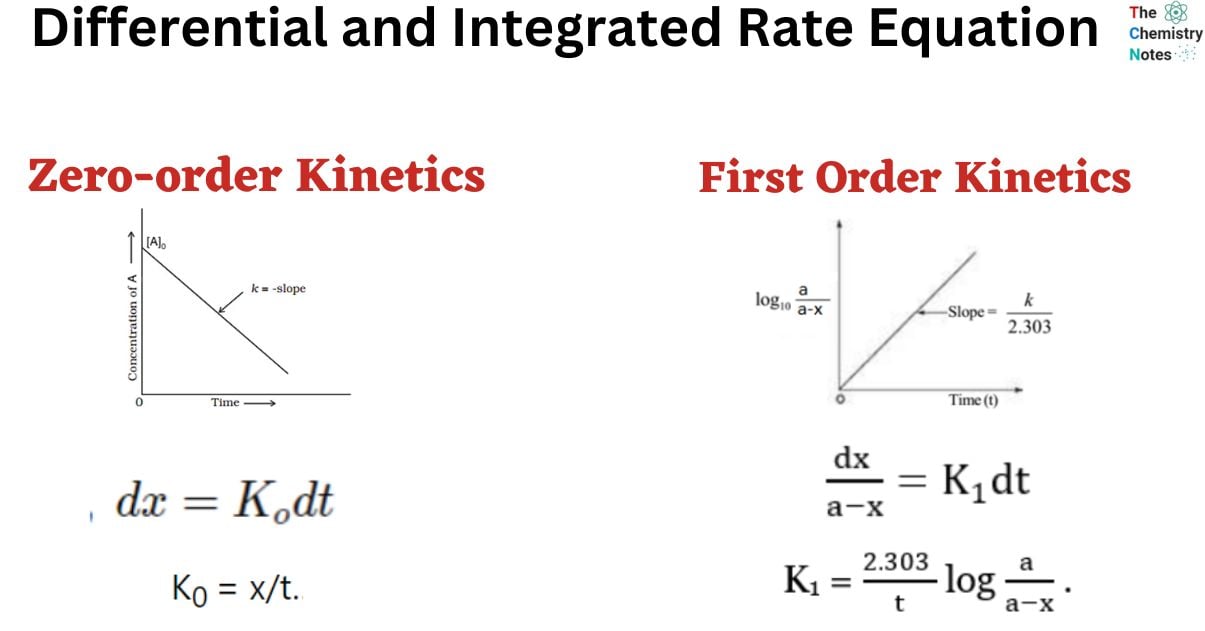
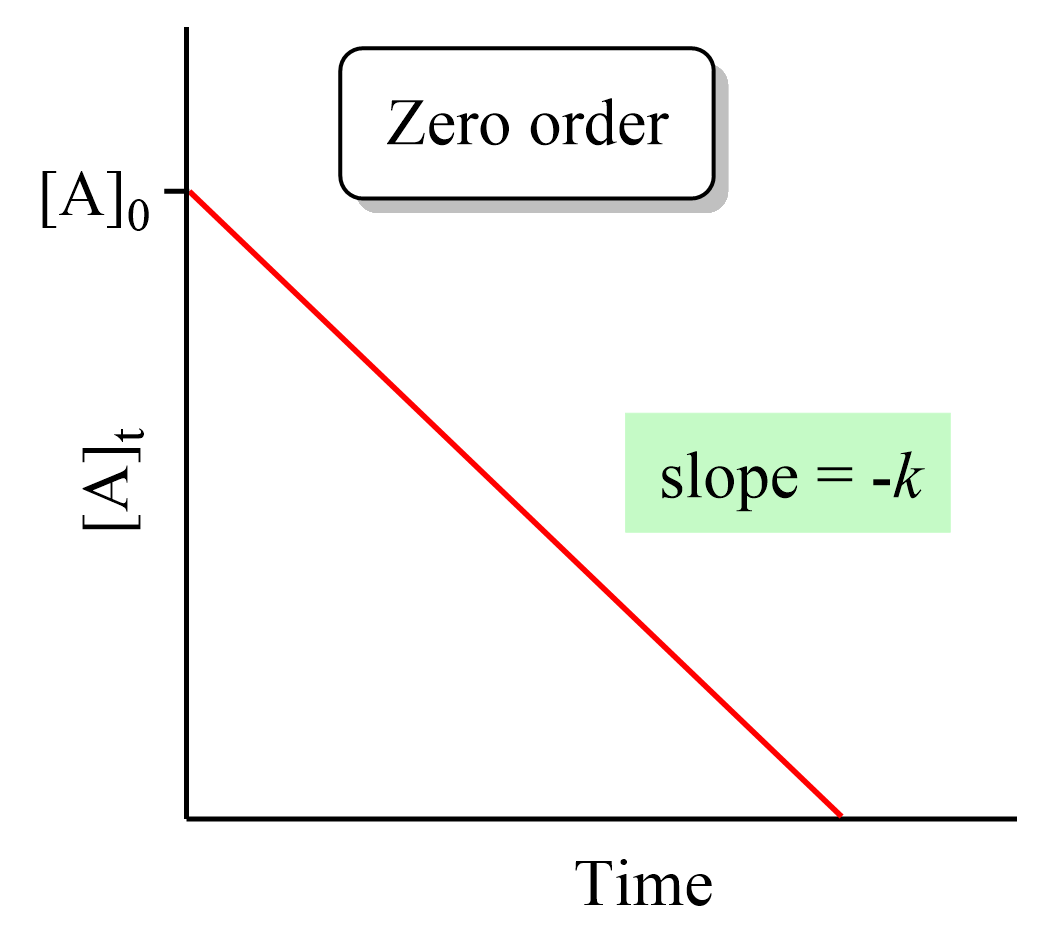
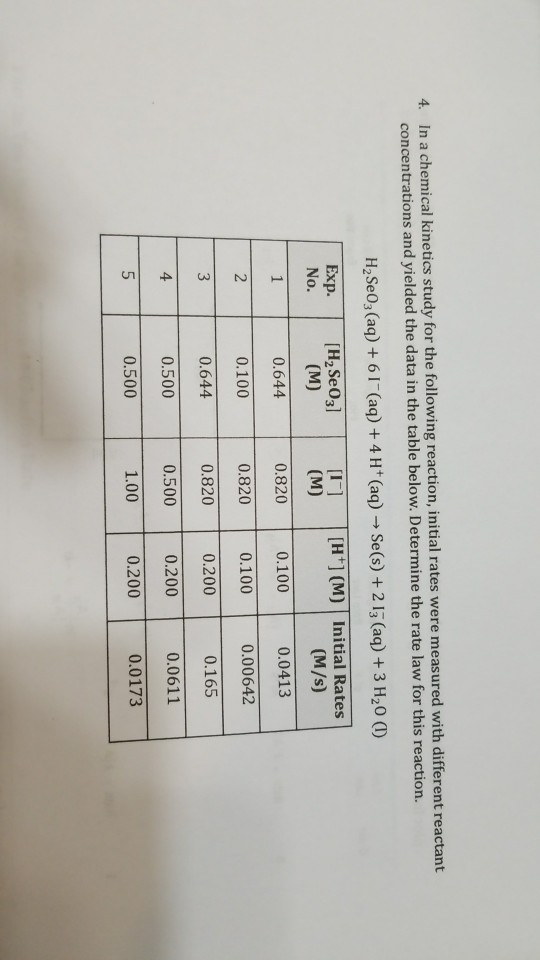
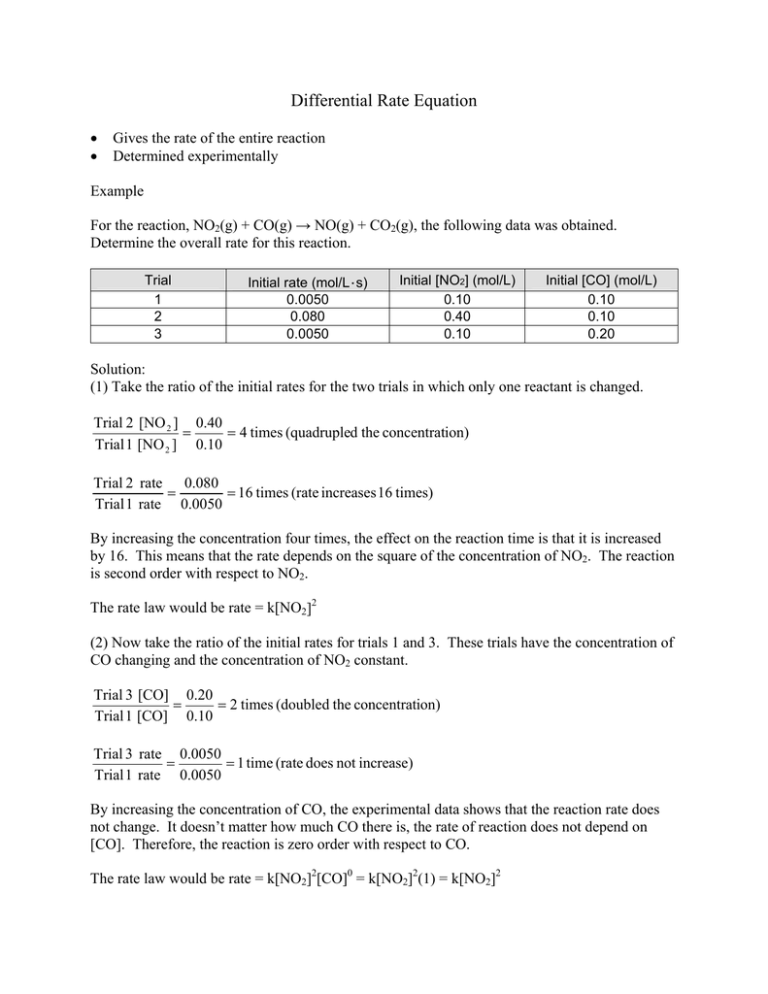
Differential and Integrated Rate Equation
In general, a rate law (or differential rate law, as it is sometimes called) takes this form: Differential rate laws express the rate of reaction as a function of a change in the concentration of one or more reactants over a particular period of time; A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration.
The type of rate law for a reaction, either the d…
In general, a rate law (or differential rate law, as it is sometimes called) takes this form: In other words, if we have a reaction of the type: The differential rate law can be. Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in the concentration of reactants (d [r]) over a small.
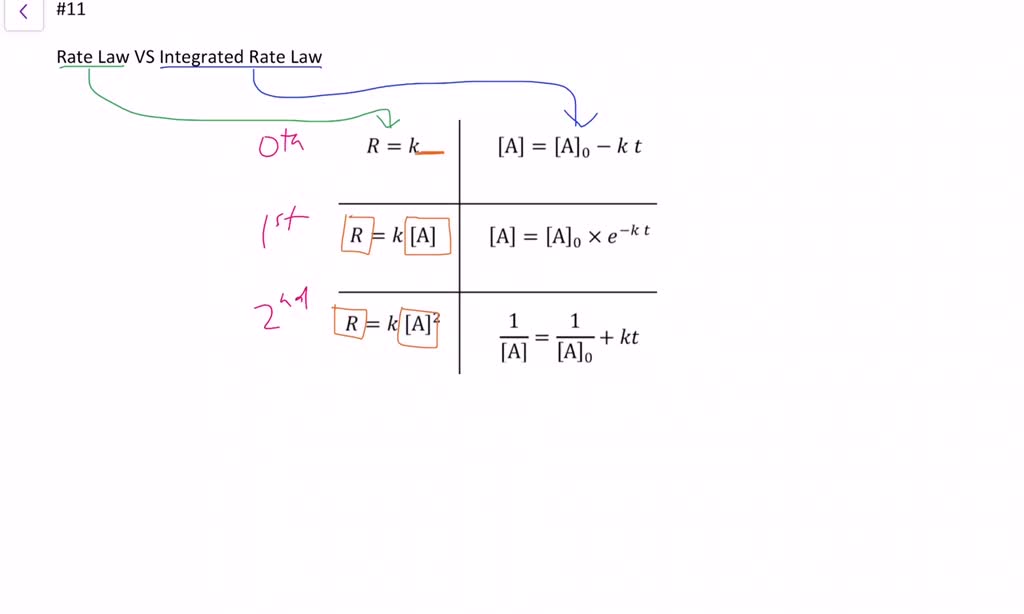
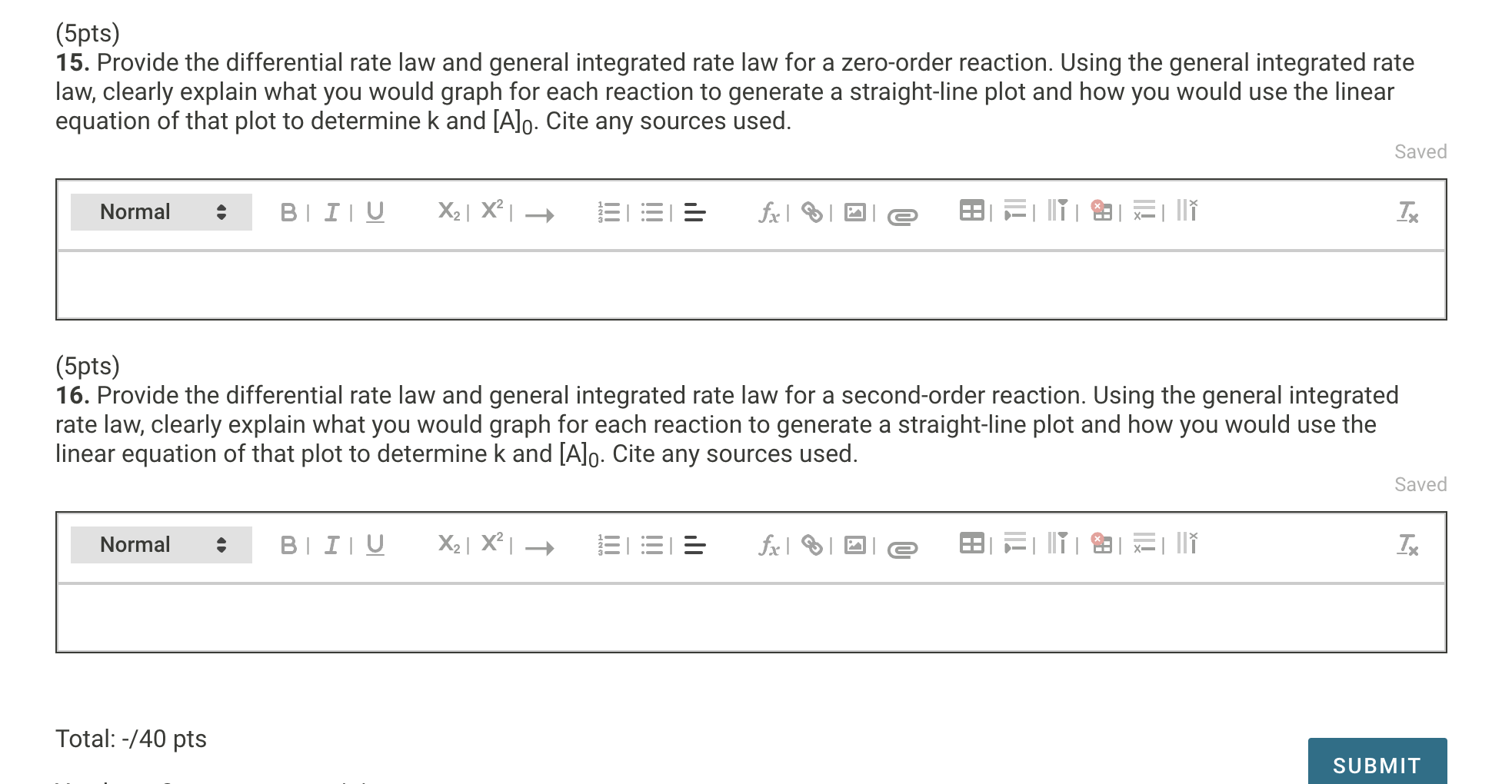
Solved (5pts) 15. Provide the differential rate law and
A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or more reactants (δ[r]) over a specific time interval (δt). Rate = k[a]m[b]n[c]p… in which [a], [b], and [c] represent the molar concentrations of. The differential rate law can be. In other words, if we have a reaction of the type: In general,.
Integrated Rate Law Chemistry Steps
They are used to describe what is. A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or more reactants (δ[r]) over a specific time interval (δt). In general, a rate law (or differential rate law, as it is sometimes called) takes this form: The differential rate law can be. Differential rate laws.
Integrated Rate Law Chemistry Steps
Rate = k[a]m[b]n[c]p… in which [a], [b], and [c] represent the molar concentrations of. They are used to describe what is. A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or more reactants (δ[r]) over a specific time interval (δt). In general, a rate law (or differential rate law, as it is.
Solved 2. Differential rate law relates instantaneous
The differential rate law can be. Rate = k[a]m[b]n[c]p… in which [a], [b], and [c] represent the molar concentrations of. Differential rate laws are used to express the rate of a reaction in terms of change in the concentration of reactants (d [r]) over a small interval of time (dt). In other words, if we have a reaction of the.
Differential Rate Equation
Rate = k[a]m[b]n[c]p… in which [a], [b], and [c] represent the molar concentrations of. The differential rate law can be. They are used to describe what is. In other words, if we have a reaction of the type: Differential rate laws express the rate of reaction as a function of a change in the concentration of one or more reactants.
Rate Law and Integrated Rate Law Diagram Quizlet
A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or more reactants (δ[r]) over a specific time interval (δt). Rate = k[a]m[b]n[c]p… in which [a], [b], and [c] represent the molar concentrations of. In general, a rate law (or differential rate law, as it is sometimes called) takes this form: The differential.
Differential Rate Law Equation Method… Chemistry in Hindi
A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or more reactants (δ[r]) over a specific time interval (δt). The differential rate law can be. In other words, if we have a reaction of the type: They are used to describe what is. In general, a rate law (or differential rate law,.
Differential Rate Laws Express The Rate Of Reaction As A Function Of A Change In The Concentration Of One Or More Reactants Over A Particular Period Of Time;
In other words, if we have a reaction of the type: Rate = k[a]m[b]n[c]p… in which [a], [b], and [c] represent the molar concentrations of. A differential rate law expresses the reaction rate in terms of changes in the concentration of one or more reactants (δ[r]) over a specific time interval (δt). They are used to describe what is.
Differential Rate Laws Are Used To Express The Rate Of A Reaction In Terms Of Change In The Concentration Of Reactants (D [R]) Over A Small Interval Of Time (Dt).
The differential rate law can be. In general, a rate law (or differential rate law, as it is sometimes called) takes this form: