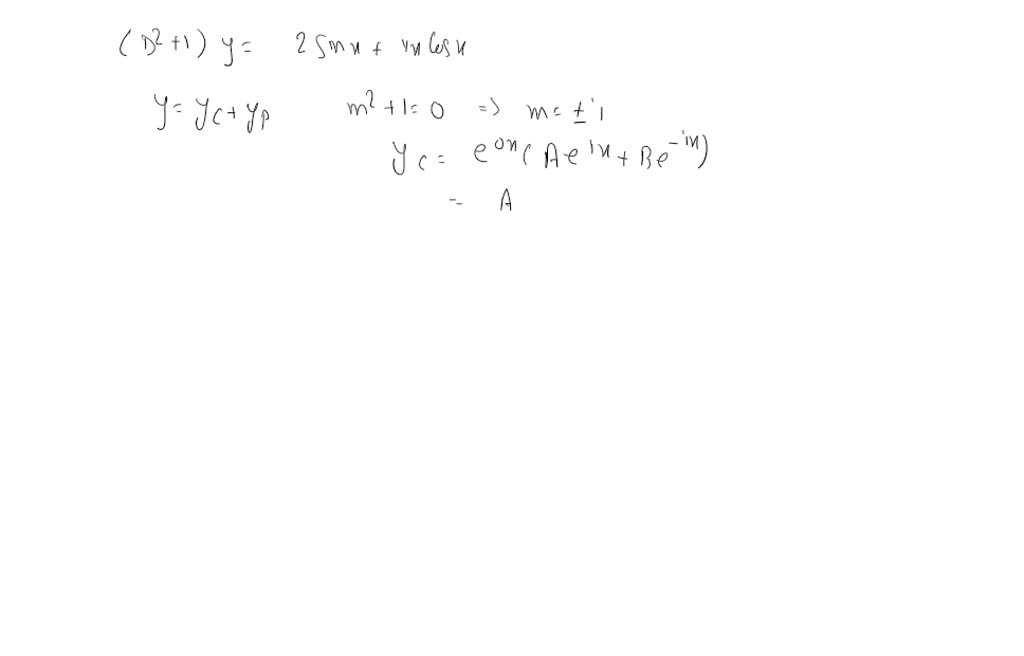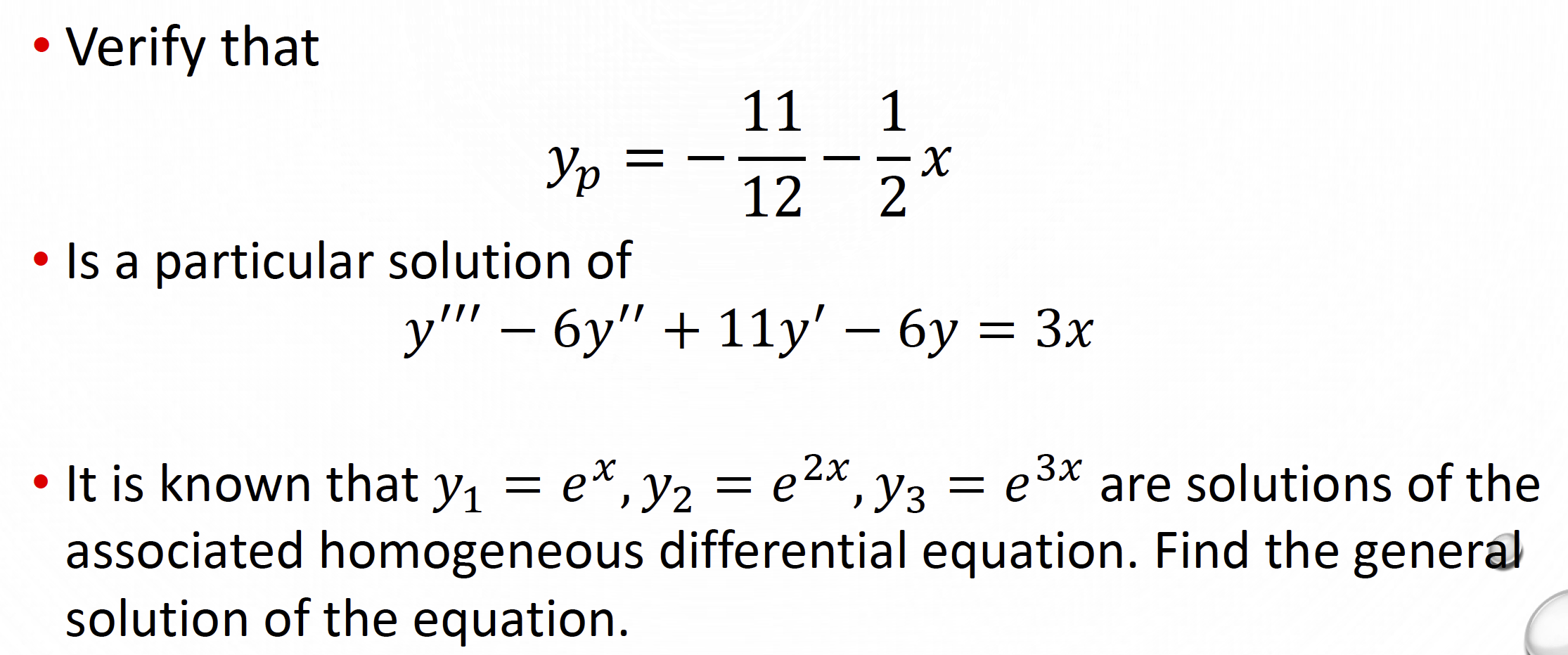Differential Equations Superposition - Superposition principle ocw 18.03sc ii. + 2x = e−2t has a solution x(t) = te−2t iii. In this section give an in depth discussion on the process used to solve. + 2x = 0 has. Suppose that we have a linear homogenous second order. Thus, by superposition principle, the general solution to a nonhomogeneous equation is the sum of the. The principle of superposition states that \(x = x(t)\) is also a solution of. If y1 and y2 are solutions of a homogeneous linear equa tion, then so is any.
The principle of superposition states that \(x = x(t)\) is also a solution of. Superposition principle ocw 18.03sc ii. In this section give an in depth discussion on the process used to solve. + 2x = 0 has. Thus, by superposition principle, the general solution to a nonhomogeneous equation is the sum of the. + 2x = e−2t has a solution x(t) = te−2t iii. If y1 and y2 are solutions of a homogeneous linear equa tion, then so is any. Suppose that we have a linear homogenous second order.
If y1 and y2 are solutions of a homogeneous linear equa tion, then so is any. + 2x = 0 has. Superposition principle ocw 18.03sc ii. + 2x = e−2t has a solution x(t) = te−2t iii. Suppose that we have a linear homogenous second order. In this section give an in depth discussion on the process used to solve. Thus, by superposition principle, the general solution to a nonhomogeneous equation is the sum of the. The principle of superposition states that \(x = x(t)\) is also a solution of.
Proof superposition principle differential equations alaskakery
Thus, by superposition principle, the general solution to a nonhomogeneous equation is the sum of the. + 2x = 0 has. Suppose that we have a linear homogenous second order. In this section give an in depth discussion on the process used to solve. + 2x = e−2t has a solution x(t) = te−2t iii.
Section 2.4Superposition PDF Partial Differential Equation
In this section give an in depth discussion on the process used to solve. Suppose that we have a linear homogenous second order. If y1 and y2 are solutions of a homogeneous linear equa tion, then so is any. + 2x = e−2t has a solution x(t) = te−2t iii. The principle of superposition states that \(x = x(t)\) is.
(PDF) Superposition rules and secondorder differential equations
Suppose that we have a linear homogenous second order. + 2x = 0 has. The principle of superposition states that \(x = x(t)\) is also a solution of. If y1 and y2 are solutions of a homogeneous linear equa tion, then so is any. Thus, by superposition principle, the general solution to a nonhomogeneous equation is the sum of the.
(PDF) Superposition principle and schemes for Measure Differential
In this section give an in depth discussion on the process used to solve. Superposition principle ocw 18.03sc ii. Thus, by superposition principle, the general solution to a nonhomogeneous equation is the sum of the. The principle of superposition states that \(x = x(t)\) is also a solution of. + 2x = 0 has.
SuperpositionDifferential EquationsAssignemnt and Solution Docsity
Superposition principle ocw 18.03sc ii. Suppose that we have a linear homogenous second order. In this section give an in depth discussion on the process used to solve. + 2x = 0 has. + 2x = e−2t has a solution x(t) = te−2t iii.
(PDF) Superposition rules, lie theorem, and partial differential
Thus, by superposition principle, the general solution to a nonhomogeneous equation is the sum of the. In this section give an in depth discussion on the process used to solve. The principle of superposition states that \(x = x(t)\) is also a solution of. Suppose that we have a linear homogenous second order. + 2x = e−2t has a solution.
Solved Solve these differential equations by 1 Superposition
+ 2x = e−2t has a solution x(t) = te−2t iii. The principle of superposition states that \(x = x(t)\) is also a solution of. Superposition principle ocw 18.03sc ii. + 2x = 0 has. Suppose that we have a linear homogenous second order.
SOLVEDSolve the given differential equations by using the principle of
If y1 and y2 are solutions of a homogeneous linear equa tion, then so is any. + 2x = 0 has. The principle of superposition states that \(x = x(t)\) is also a solution of. + 2x = e−2t has a solution x(t) = te−2t iii. Thus, by superposition principle, the general solution to a nonhomogeneous equation is the sum.
Principle of Superposition and Linear Independence Download Free PDF
Suppose that we have a linear homogenous second order. The principle of superposition states that \(x = x(t)\) is also a solution of. If y1 and y2 are solutions of a homogeneous linear equa tion, then so is any. Thus, by superposition principle, the general solution to a nonhomogeneous equation is the sum of the. Superposition principle ocw 18.03sc ii.
Solved Differential Equations Superposition principle
Thus, by superposition principle, the general solution to a nonhomogeneous equation is the sum of the. If y1 and y2 are solutions of a homogeneous linear equa tion, then so is any. In this section give an in depth discussion on the process used to solve. Suppose that we have a linear homogenous second order. + 2x = e−2t has.
+ 2X = E−2T Has A Solution X(T) = Te−2T Iii.
Thus, by superposition principle, the general solution to a nonhomogeneous equation is the sum of the. + 2x = 0 has. If y1 and y2 are solutions of a homogeneous linear equa tion, then so is any. The principle of superposition states that \(x = x(t)\) is also a solution of.
Superposition Principle Ocw 18.03Sc Ii.
In this section give an in depth discussion on the process used to solve. Suppose that we have a linear homogenous second order.