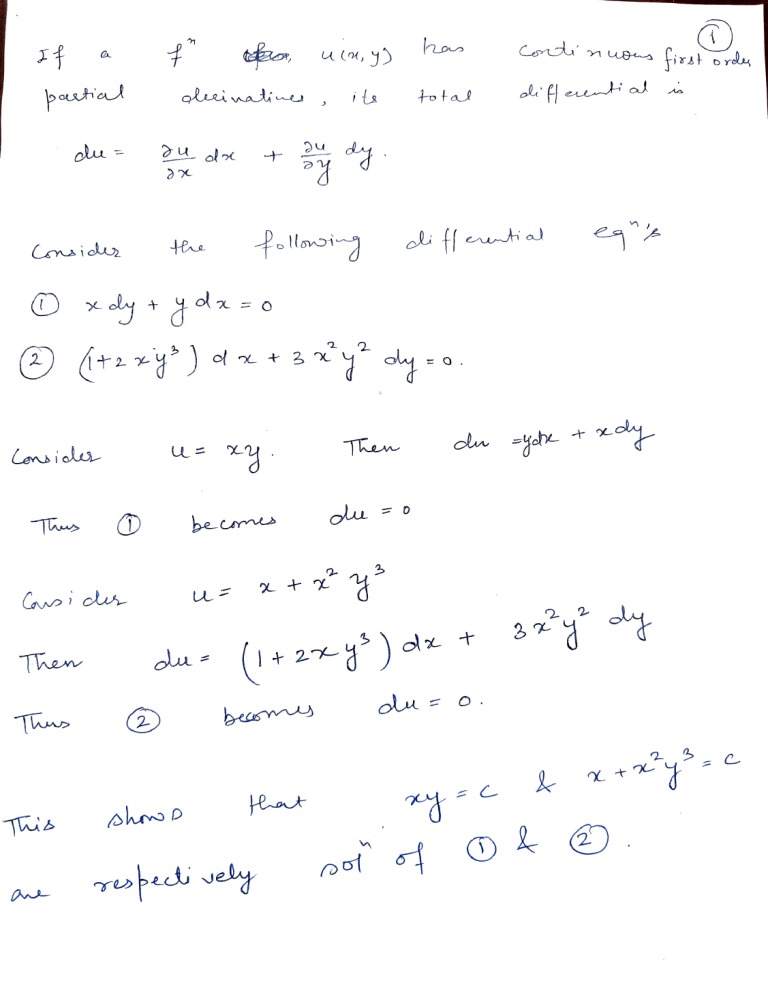Differential Equation Exact Equation - If you have had vector calculus , this. M(x, y)dx + n(x, y)dy = 0 has. A differential equation with a potential function is called exact. Geometrically, theorem 1.9.3 says that the solution curves of an exact differential equation are the.
A differential equation with a potential function is called exact. M(x, y)dx + n(x, y)dy = 0 has. Geometrically, theorem 1.9.3 says that the solution curves of an exact differential equation are the. If you have had vector calculus , this.
Geometrically, theorem 1.9.3 says that the solution curves of an exact differential equation are the. If you have had vector calculus , this. A differential equation with a potential function is called exact. M(x, y)dx + n(x, y)dy = 0 has.
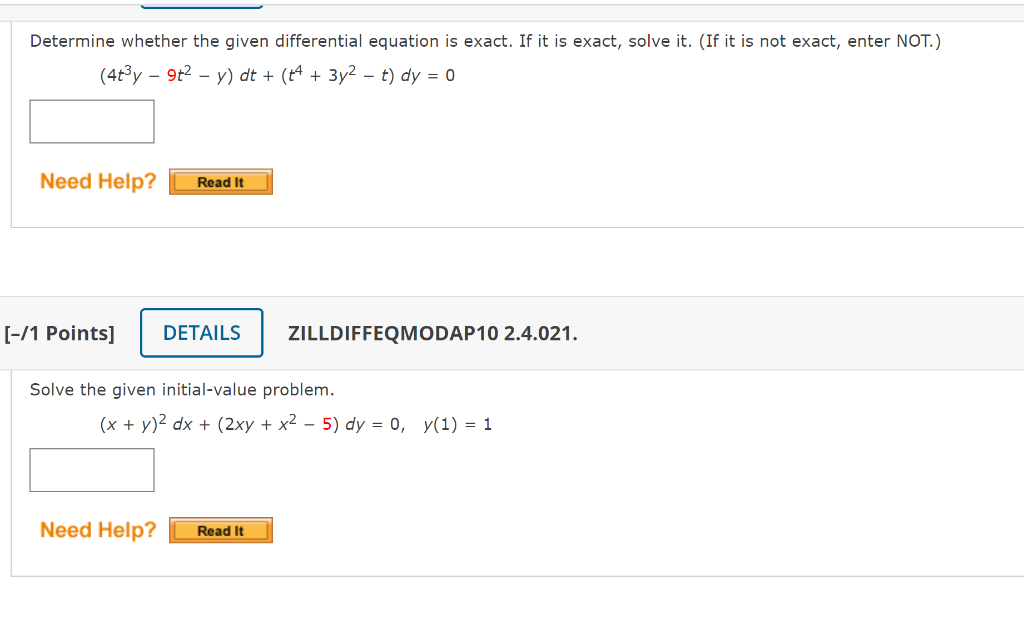
[Solved] . Determine whether the given differential equation is exact
M(x, y)dx + n(x, y)dy = 0 has. If you have had vector calculus , this. Geometrically, theorem 1.9.3 says that the solution curves of an exact differential equation are the. A differential equation with a potential function is called exact.
Engineering Mathematics Reducible to Exact Differential equation
A differential equation with a potential function is called exact. If you have had vector calculus , this. Geometrically, theorem 1.9.3 says that the solution curves of an exact differential equation are the. M(x, y)dx + n(x, y)dy = 0 has.
Solved Determine whether the given differential equation is
A differential equation with a potential function is called exact. M(x, y)dx + n(x, y)dy = 0 has. If you have had vector calculus , this. Geometrically, theorem 1.9.3 says that the solution curves of an exact differential equation are the.
exact differential equation
If you have had vector calculus , this. A differential equation with a potential function is called exact. M(x, y)dx + n(x, y)dy = 0 has. Geometrically, theorem 1.9.3 says that the solution curves of an exact differential equation are the.
Exact Differential Equation Definition, Condition with Examples
Geometrically, theorem 1.9.3 says that the solution curves of an exact differential equation are the. M(x, y)dx + n(x, y)dy = 0 has. If you have had vector calculus , this. A differential equation with a potential function is called exact.
SOLUTION Differential equation exact equation method 1 example 2
Geometrically, theorem 1.9.3 says that the solution curves of an exact differential equation are the. M(x, y)dx + n(x, y)dy = 0 has. If you have had vector calculus , this. A differential equation with a potential function is called exact.
Exact differential equation Alchetron, the free social encyclopedia
M(x, y)dx + n(x, y)dy = 0 has. If you have had vector calculus , this. A differential equation with a potential function is called exact. Geometrically, theorem 1.9.3 says that the solution curves of an exact differential equation are the.
Solved Exact Differential Equations Verify that the given
Geometrically, theorem 1.9.3 says that the solution curves of an exact differential equation are the. M(x, y)dx + n(x, y)dy = 0 has. If you have had vector calculus , this. A differential equation with a potential function is called exact.
Solved Determine whether the given differential equation is
A differential equation with a potential function is called exact. Geometrically, theorem 1.9.3 says that the solution curves of an exact differential equation are the. M(x, y)dx + n(x, y)dy = 0 has. If you have had vector calculus , this.
A Differential Equation With A Potential Function Is Called Exact.
Geometrically, theorem 1.9.3 says that the solution curves of an exact differential equation are the. If you have had vector calculus , this. M(x, y)dx + n(x, y)dy = 0 has.