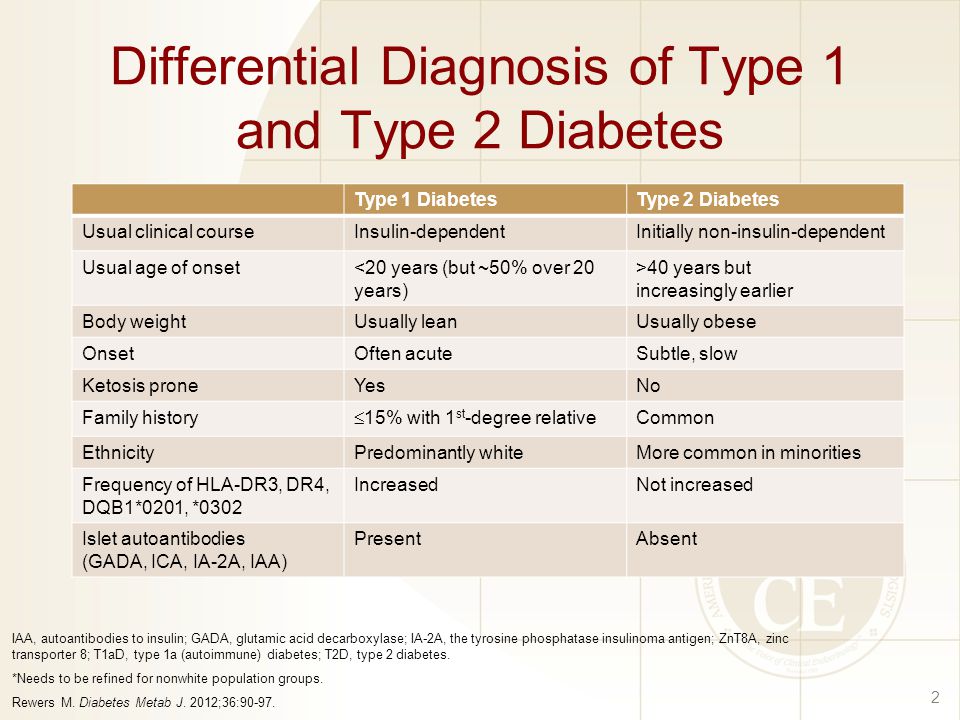
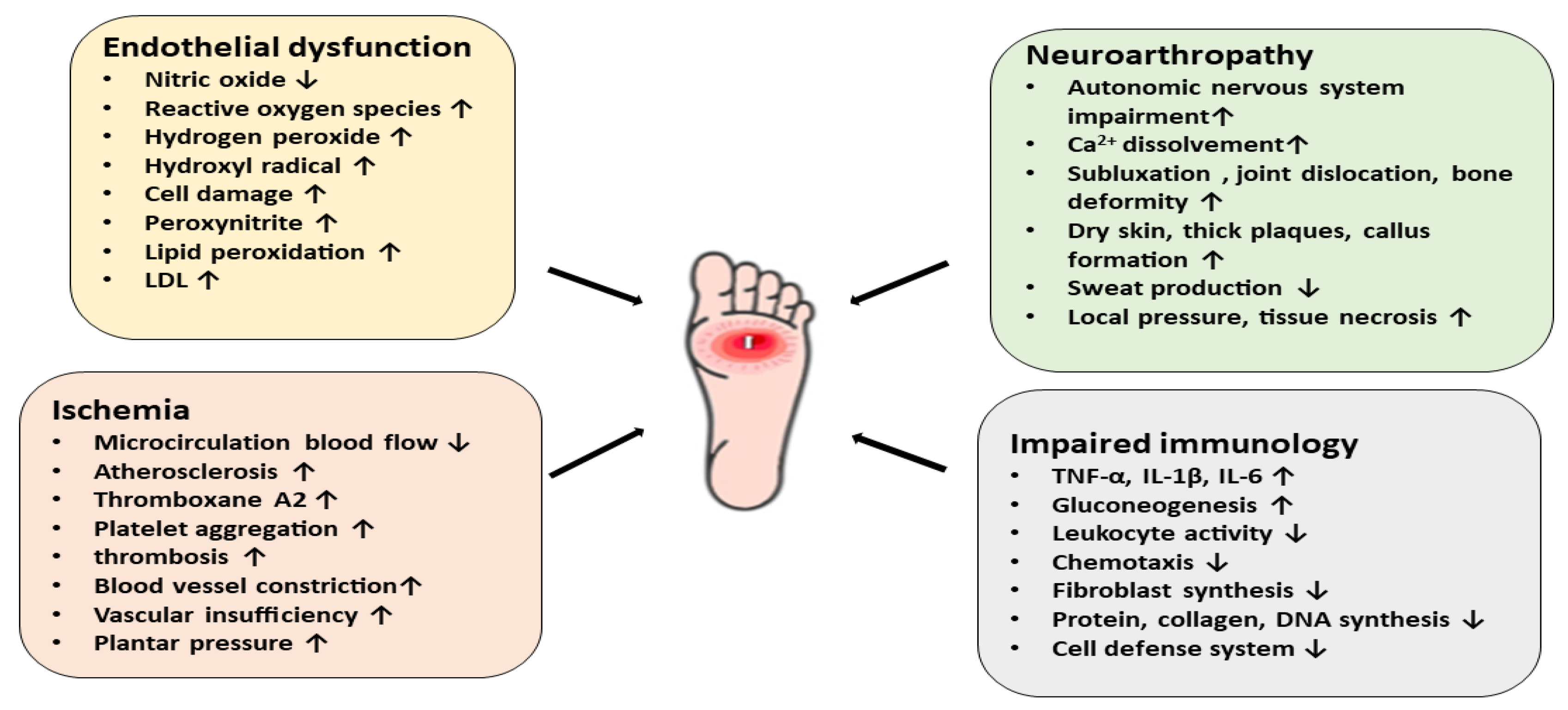
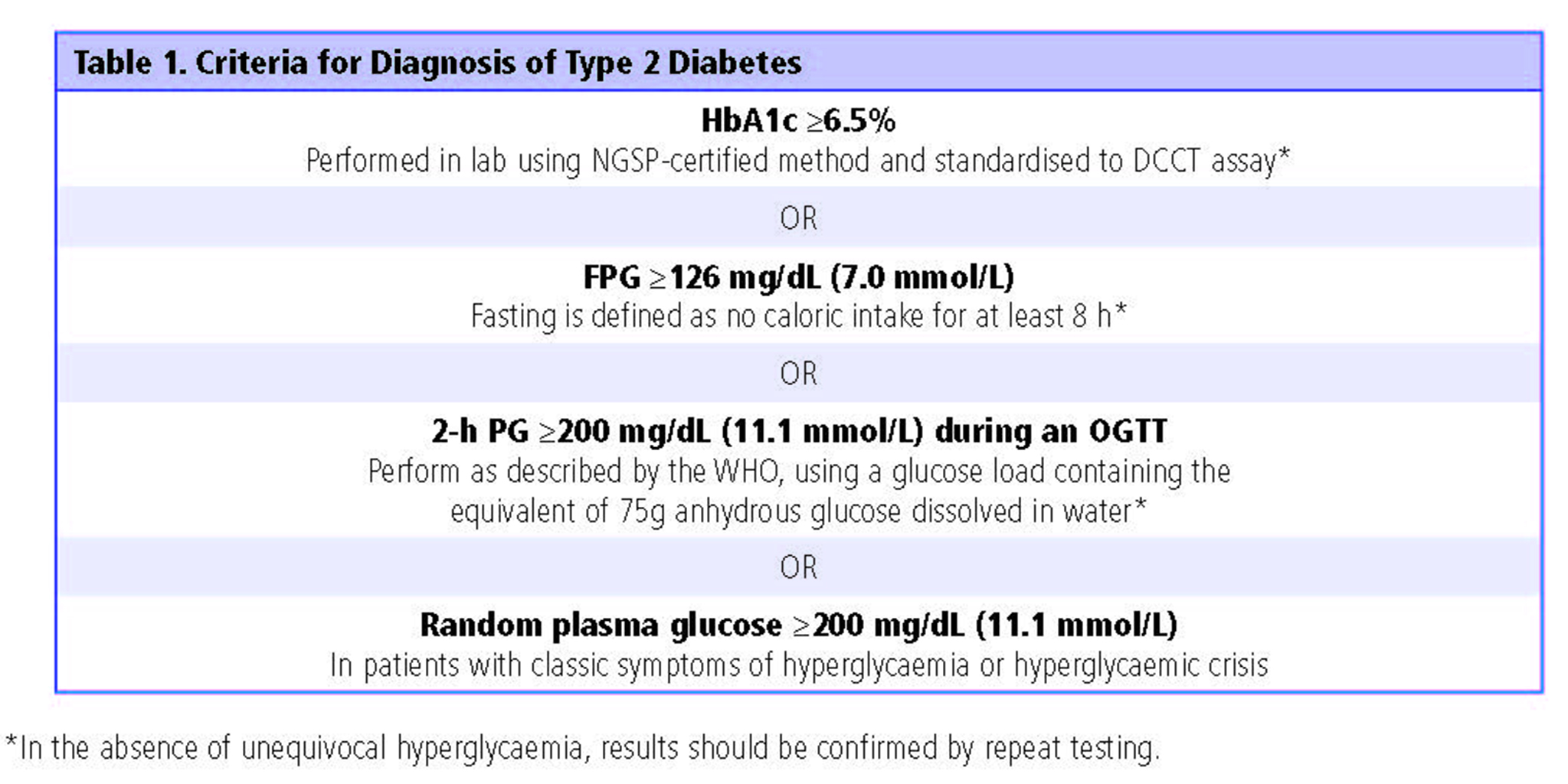
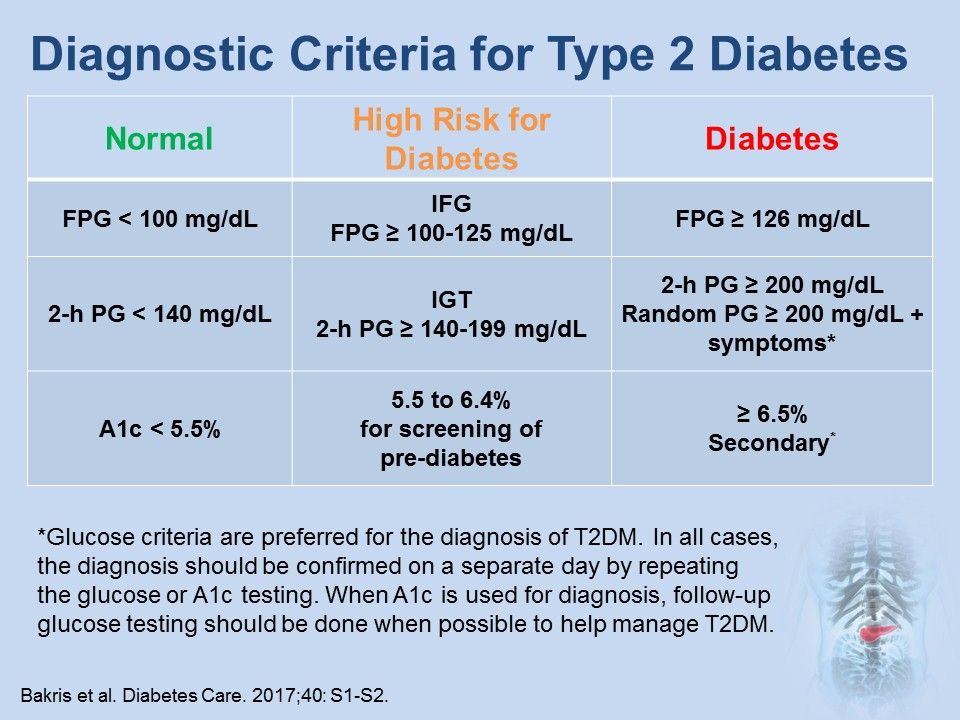
Differential Diagnosis Diabetes Type 2 - As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Diabetes mellitus (dm) is a disease of inadequate control of blood levels of glucose. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific gravity (<1.010), low.
As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific gravity (<1.010), low. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Diabetes mellitus (dm) is a disease of inadequate control of blood levels of glucose.
Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific gravity (<1.010), low. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: Diabetes mellitus (dm) is a disease of inadequate control of blood levels of glucose. As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be.
Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosis
Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: Diabetes mellitus (dm) is a disease of inadequate control of blood levels of glucose. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific gravity (<1.010), low. As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be.
Differential Diagnosis For Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 DiabetesWalls
Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific gravity (<1.010), low. As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be.
6 Quick and Accurate Test for Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosis Drlogy
As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Diabetes mellitus (dm) is a disease of inadequate control of blood levels of glucose. Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific gravity (<1.010), low.
Diagnosis Diagnosis Type 2 Diabetes
As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: Diabetes mellitus (dm) is a disease of inadequate control of blood levels of glucose. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific gravity (<1.010), low.
Diabetes Mellitus Differential Diagnosis Hot Sex Picture
Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific gravity (<1.010), low.
Diagnostic Form With Diagnosis Diabetes Type 2. Stock Photo Image of
Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Diabetes mellitus (dm) is a disease of inadequate control of blood levels of glucose. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific gravity (<1.010), low.
Differential Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus PDF Diabetes Autoimmunity
Diabetes mellitus (dm) is a disease of inadequate control of blood levels of glucose. Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific gravity (<1.010), low. As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%];
Diabetes Type 2 Diagnosis iLearn
As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific gravity (<1.010), low. Diabetes mellitus (dm) is a disease of inadequate control of blood levels of glucose. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%];
Diagnosis Diagnosis Type 2 Diabetes
Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific gravity (<1.010), low. Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Diabetes mellitus (dm) is a disease of inadequate control of blood levels of glucose. As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be.
Type 2 Diabetes Clinical Suspicion and Diagnosis Patient Care Online
As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Diabetes mellitus (dm) is a disease of inadequate control of blood levels of glucose. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: Ndh is defined as raised blood glucose levels (hba1c 42 to 47 mmol/mol [6.0% to 6.4%]; Polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific gravity (<1.010), low.
Ndh Is Defined As Raised Blood Glucose Levels (Hba1C 42 To 47 Mmol/Mol [6.0% To 6.4%];
Diabetes mellitus (dm) is a disease of inadequate control of blood levels of glucose. Review [preventing type 2 diabetes complications: As previously stated, patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus can usually be. Basic criteria for diagnosis of di include: