Calf Pain Differential Diagnosis - Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion. A duplex ultrasound (us) scan of the leg was performed and did not show any evidence of a. The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular. At the middle third of the left achilles tendon. Findings to narrow the imaging differential diagnosis. (a) longitudinal and (b) transverse images of the calf: Neoplastic causes of calf swelling include.
Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion. Findings to narrow the imaging differential diagnosis. The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular. A duplex ultrasound (us) scan of the leg was performed and did not show any evidence of a. At the middle third of the left achilles tendon. (a) longitudinal and (b) transverse images of the calf: Neoplastic causes of calf swelling include.
At the middle third of the left achilles tendon. Neoplastic causes of calf swelling include. Findings to narrow the imaging differential diagnosis. The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular. Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion. A duplex ultrasound (us) scan of the leg was performed and did not show any evidence of a. (a) longitudinal and (b) transverse images of the calf:
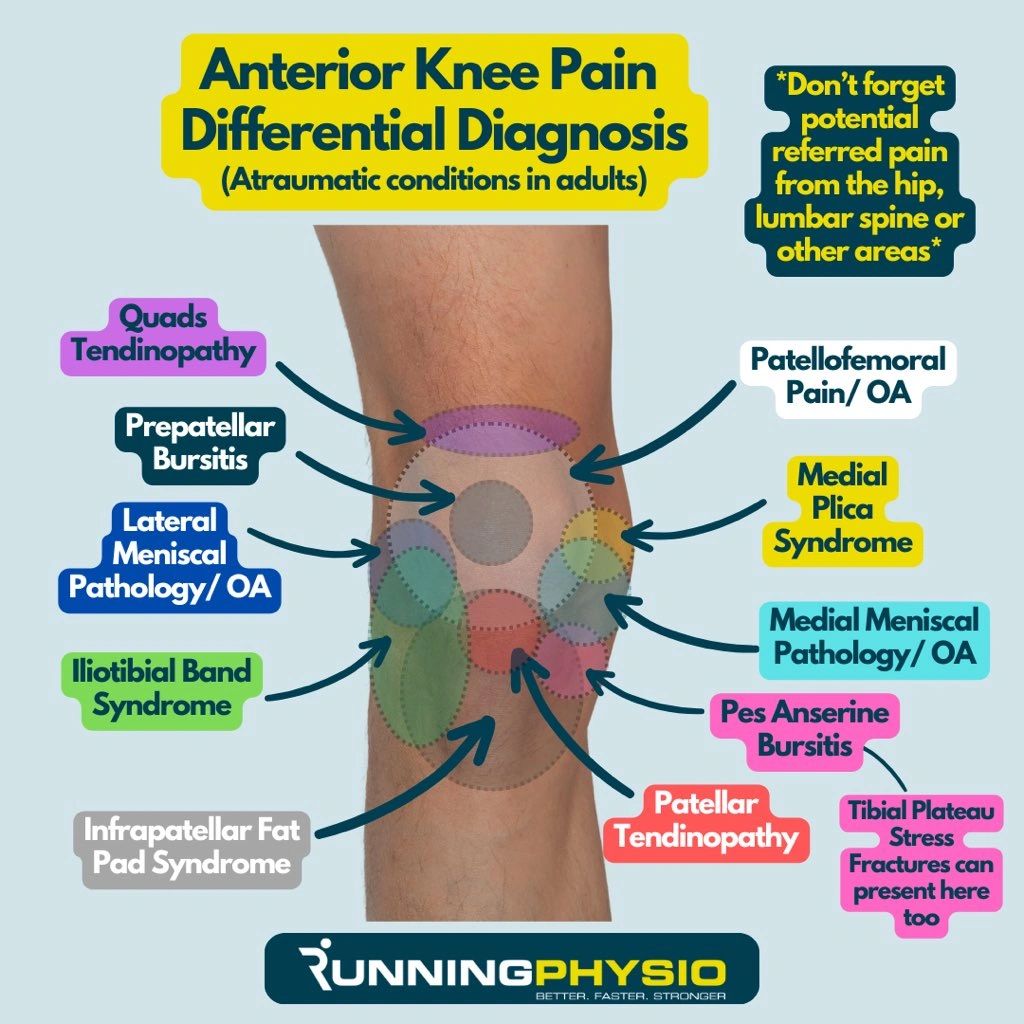
Knee Pain Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular. Neoplastic causes of calf swelling include. (a) longitudinal and (b) transverse images of the calf: A duplex ultrasound (us) scan of the leg was performed and did not show any evidence of a. Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion.
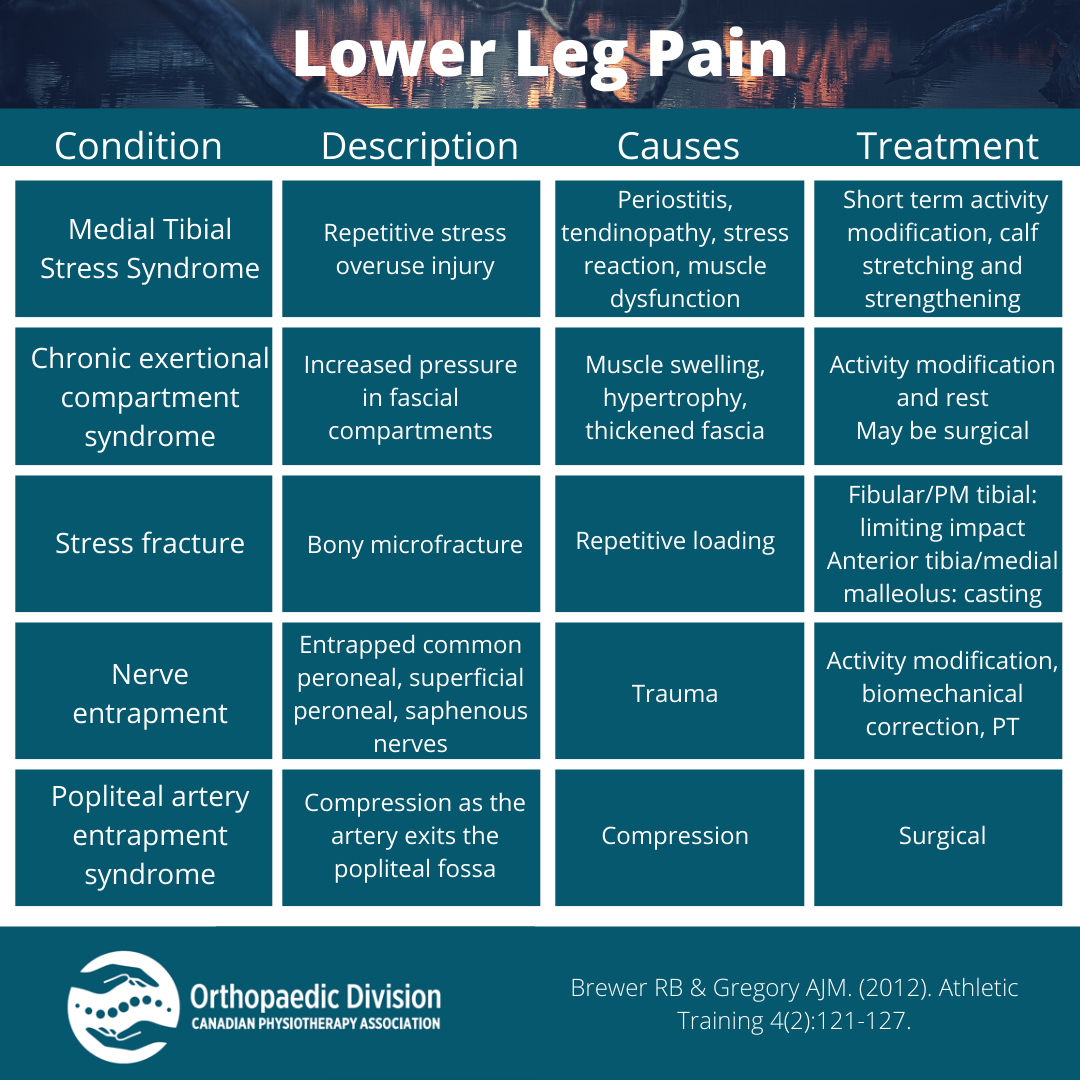
Lower Leg Pain Differential Diagnosis for Clinicians Therapy Insights
(a) longitudinal and (b) transverse images of the calf: A duplex ultrasound (us) scan of the leg was performed and did not show any evidence of a. At the middle third of the left achilles tendon. Findings to narrow the imaging differential diagnosis. Neoplastic causes of calf swelling include.
Differential Diagnosis of Lower Leg Pain National Orthopaedic
(a) longitudinal and (b) transverse images of the calf: Neoplastic causes of calf swelling include. A duplex ultrasound (us) scan of the leg was performed and did not show any evidence of a. Findings to narrow the imaging differential diagnosis. The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular.
Ankle Pain Differential Diagnosis Newman Feet
Neoplastic causes of calf swelling include. Findings to narrow the imaging differential diagnosis. Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion. At the middle third of the left achilles tendon. A duplex ultrasound (us) scan of the leg was performed and did not show any evidence of a.
Figure 1 from Differential Diagnosis of Acute Calf Pain and Swelling
At the middle third of the left achilles tendon. Findings to narrow the imaging differential diagnosis. Neoplastic causes of calf swelling include. A duplex ultrasound (us) scan of the leg was performed and did not show any evidence of a. (a) longitudinal and (b) transverse images of the calf:
Stream Physio Edge 065 Differential diagnosis of calf pain in runners
Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion. Neoplastic causes of calf swelling include. The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular. At the middle third of the left achilles tendon. (a) longitudinal and (b) transverse images of the calf:
Clinical Edge Infographic Differential diagnosis of calf pain with
Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion. (a) longitudinal and (b) transverse images of the calf: Findings to narrow the imaging differential diagnosis. At the middle third of the left achilles tendon. The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular.
Adaptació / Adaptation Differential Diagnosis of Calf pain in athletes
A duplex ultrasound (us) scan of the leg was performed and did not show any evidence of a. (a) longitudinal and (b) transverse images of the calf: Neoplastic causes of calf swelling include. Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion. At the middle third of the left achilles tendon.
Calf Pain Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment The Healthy
A duplex ultrasound (us) scan of the leg was performed and did not show any evidence of a. Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion. The differential diagnosis of calf pain and swelling includes dvt, cellulitis, baker’s cyst, muscular. At the middle third of the left achilles tendon. Findings to narrow the imaging differential diagnosis.
(PDF) Differential diagnosis of calf pain by ultrasonography Marcelo
Muscle strain (gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris) or contusion. A duplex ultrasound (us) scan of the leg was performed and did not show any evidence of a. (a) longitudinal and (b) transverse images of the calf: At the middle third of the left achilles tendon. Neoplastic causes of calf swelling include.
Muscle Strain (Gastrocnemius, Soleus, Plantaris) Or Contusion.
Findings to narrow the imaging differential diagnosis. A duplex ultrasound (us) scan of the leg was performed and did not show any evidence of a. (a) longitudinal and (b) transverse images of the calf: Neoplastic causes of calf swelling include.
The Differential Diagnosis Of Calf Pain And Swelling Includes Dvt, Cellulitis, Baker’s Cyst, Muscular.
At the middle third of the left achilles tendon.