Bronchiolitis Differential Diagnosis - Bronchiolitis should be differentiated from asthma, copd, pneumonia, congestive heart failure,. It is characterised by epithelial cell destruction, cellular oedema, and airway. Bronchiolitis is an acute inflammatory injury of the bronchioles that is usually caused by. The differential diagnosis may include bacterial pneumonia, congenital lesions of the lung or heart,. While the majority of wheezing infants who present acutely between november and april most likely.
The differential diagnosis may include bacterial pneumonia, congenital lesions of the lung or heart,. Bronchiolitis should be differentiated from asthma, copd, pneumonia, congestive heart failure,. Bronchiolitis is an acute inflammatory injury of the bronchioles that is usually caused by. While the majority of wheezing infants who present acutely between november and april most likely. It is characterised by epithelial cell destruction, cellular oedema, and airway.
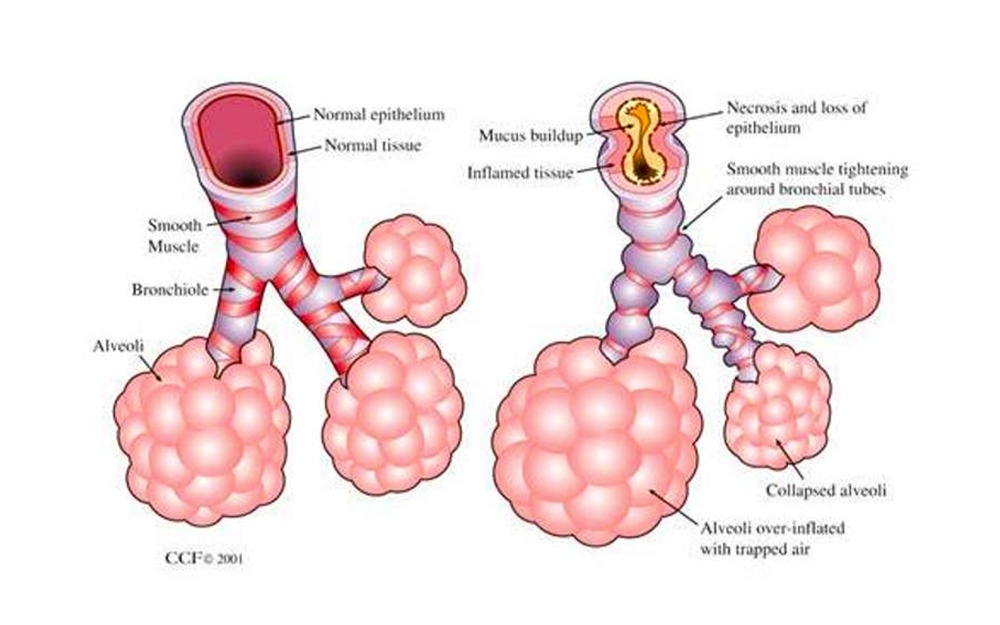
It is characterised by epithelial cell destruction, cellular oedema, and airway. Bronchiolitis is an acute inflammatory injury of the bronchioles that is usually caused by. Bronchiolitis should be differentiated from asthma, copd, pneumonia, congestive heart failure,. The differential diagnosis may include bacterial pneumonia, congenital lesions of the lung or heart,. While the majority of wheezing infants who present acutely between november and april most likely.
Differential diagnosis of acute bronchiolitis Download Table
The differential diagnosis may include bacterial pneumonia, congenital lesions of the lung or heart,. It is characterised by epithelial cell destruction, cellular oedema, and airway. Bronchiolitis is an acute inflammatory injury of the bronchioles that is usually caused by. While the majority of wheezing infants who present acutely between november and april most likely. Bronchiolitis should be differentiated from asthma,.
Bronchiolitis Diagnosis and Management CHOP OPEN
Bronchiolitis should be differentiated from asthma, copd, pneumonia, congestive heart failure,. The differential diagnosis may include bacterial pneumonia, congenital lesions of the lung or heart,. It is characterised by epithelial cell destruction, cellular oedema, and airway. Bronchiolitis is an acute inflammatory injury of the bronchioles that is usually caused by. While the majority of wheezing infants who present acutely between.
Bronchiolitis guidelines Diagnosis, management, and prevention
The differential diagnosis may include bacterial pneumonia, congenital lesions of the lung or heart,. Bronchiolitis is an acute inflammatory injury of the bronchioles that is usually caused by. While the majority of wheezing infants who present acutely between november and april most likely. It is characterised by epithelial cell destruction, cellular oedema, and airway. Bronchiolitis should be differentiated from asthma,.
Bronchitis Diagnosis
While the majority of wheezing infants who present acutely between november and april most likely. It is characterised by epithelial cell destruction, cellular oedema, and airway. Bronchiolitis is an acute inflammatory injury of the bronchioles that is usually caused by. The differential diagnosis may include bacterial pneumonia, congenital lesions of the lung or heart,. Bronchiolitis should be differentiated from asthma,.
Bronchitis Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis may include bacterial pneumonia, congenital lesions of the lung or heart,. Bronchiolitis is an acute inflammatory injury of the bronchioles that is usually caused by. Bronchiolitis should be differentiated from asthma, copd, pneumonia, congestive heart failure,. While the majority of wheezing infants who present acutely between november and april most likely. It is characterised by epithelial cell.
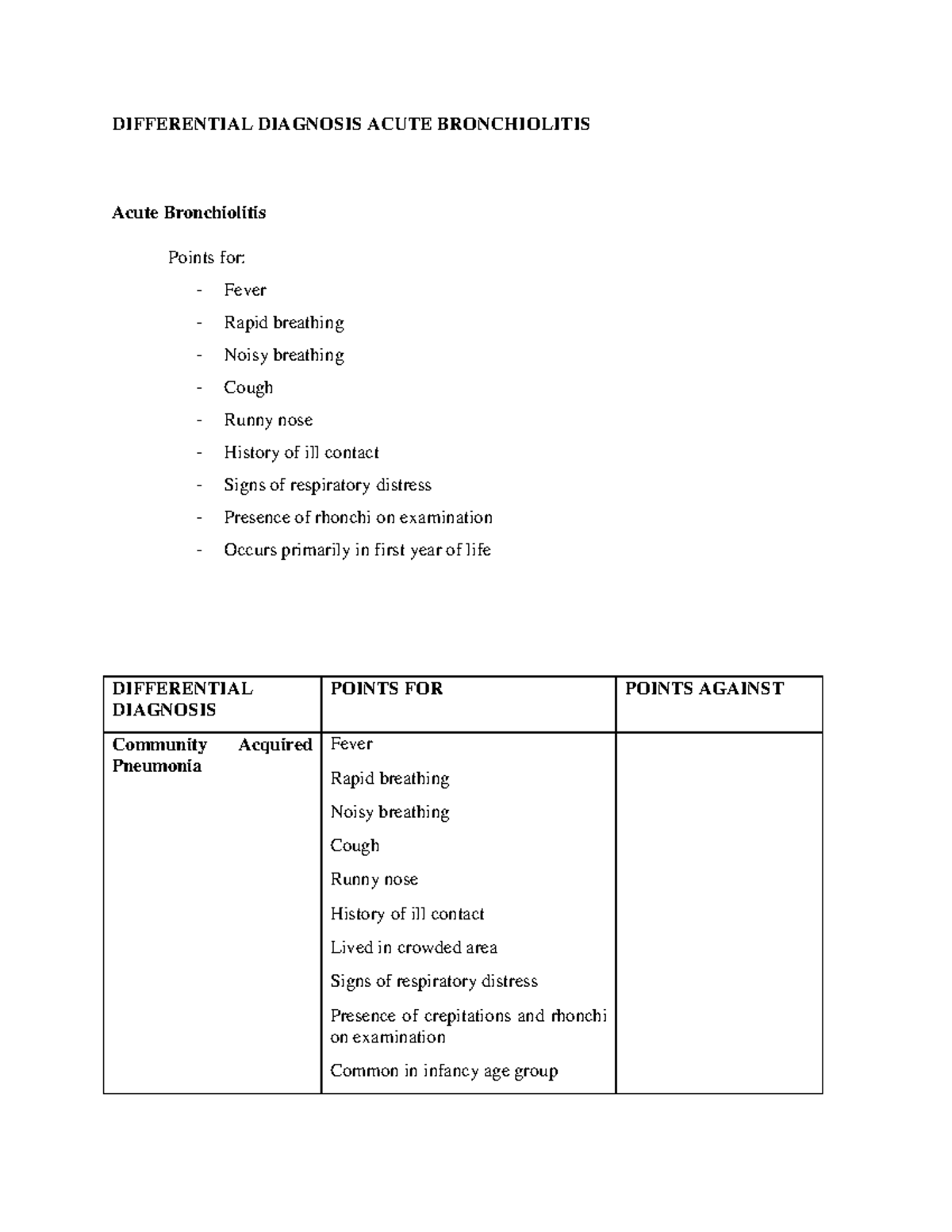
Differential Diagnosis Acute Bronchiolitis DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
While the majority of wheezing infants who present acutely between november and april most likely. Bronchiolitis should be differentiated from asthma, copd, pneumonia, congestive heart failure,. Bronchiolitis is an acute inflammatory injury of the bronchioles that is usually caused by. The differential diagnosis may include bacterial pneumonia, congenital lesions of the lung or heart,. It is characterised by epithelial cell.
Differential diagnosis of bronchial asthma depending of the patient's
The differential diagnosis may include bacterial pneumonia, congenital lesions of the lung or heart,. It is characterised by epithelial cell destruction, cellular oedema, and airway. Bronchiolitis should be differentiated from asthma, copd, pneumonia, congestive heart failure,. While the majority of wheezing infants who present acutely between november and april most likely. Bronchiolitis is an acute inflammatory injury of the bronchioles.
Differential diagnosis of acute bronchiolitis Download Table
It is characterised by epithelial cell destruction, cellular oedema, and airway. While the majority of wheezing infants who present acutely between november and april most likely. The differential diagnosis may include bacterial pneumonia, congenital lesions of the lung or heart,. Bronchiolitis is an acute inflammatory injury of the bronchioles that is usually caused by. Bronchiolitis should be differentiated from asthma,.
Differential Diagnosis of Children with Severe Respiratory Symptoms
Bronchiolitis is an acute inflammatory injury of the bronchioles that is usually caused by. Bronchiolitis should be differentiated from asthma, copd, pneumonia, congestive heart failure,. While the majority of wheezing infants who present acutely between november and april most likely. It is characterised by epithelial cell destruction, cellular oedema, and airway. The differential diagnosis may include bacterial pneumonia, congenital lesions.
PPT COPD Differential Diagnosis PowerPoint Presentation, free
While the majority of wheezing infants who present acutely between november and april most likely. The differential diagnosis may include bacterial pneumonia, congenital lesions of the lung or heart,. It is characterised by epithelial cell destruction, cellular oedema, and airway. Bronchiolitis is an acute inflammatory injury of the bronchioles that is usually caused by. Bronchiolitis should be differentiated from asthma,.
Bronchiolitis Should Be Differentiated From Asthma, Copd, Pneumonia, Congestive Heart Failure,.
The differential diagnosis may include bacterial pneumonia, congenital lesions of the lung or heart,. While the majority of wheezing infants who present acutely between november and april most likely. It is characterised by epithelial cell destruction, cellular oedema, and airway. Bronchiolitis is an acute inflammatory injury of the bronchioles that is usually caused by.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/bronchitis-symptoms-5b4372f3c9e77c00370a4c93.png)