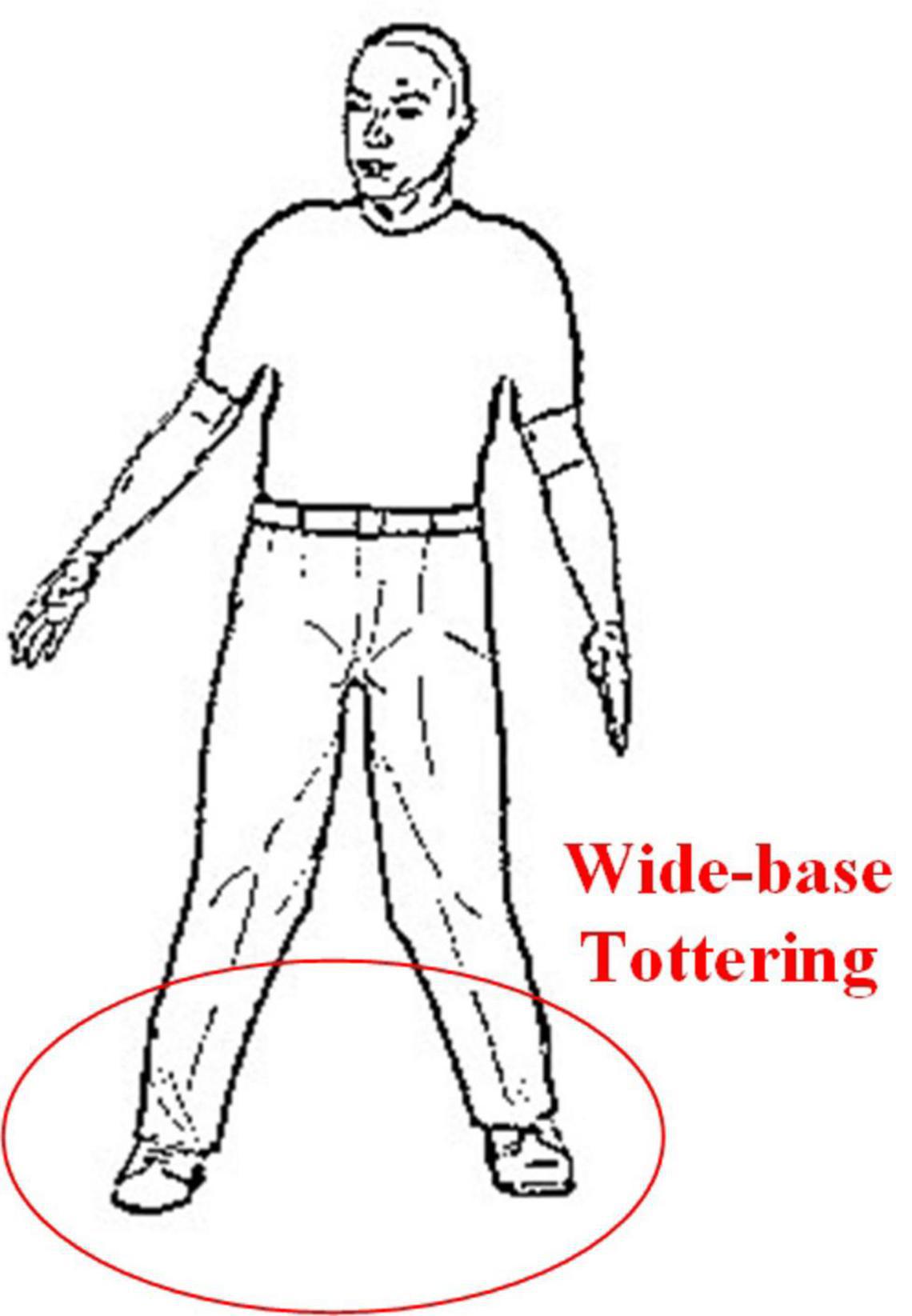
Ataxic Gait Pattern - Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range. Ataxia describes poor muscle control that causes clumsy movements. Although a few studies investigated fgd by instrumented gait analysis, it has been. In this chapter, we will focus on ataxic gait due to cerebellar circuitry. Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range of motion,. There are eight basic pathological gaits that can be attributed to neurological conditions:.
Although a few studies investigated fgd by instrumented gait analysis, it has been. In this chapter, we will focus on ataxic gait due to cerebellar circuitry. Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range. Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range of motion,. Ataxia describes poor muscle control that causes clumsy movements. There are eight basic pathological gaits that can be attributed to neurological conditions:.
Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range. Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range of motion,. Ataxia describes poor muscle control that causes clumsy movements. In this chapter, we will focus on ataxic gait due to cerebellar circuitry. There are eight basic pathological gaits that can be attributed to neurological conditions:. Although a few studies investigated fgd by instrumented gait analysis, it has been.
Although a few studies investigated fgd by instrumented gait analysis, it has been. There are eight basic pathological gaits that can be attributed to neurological conditions:. Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range of motion,. Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range. In this chapter, we will focus on ataxic.
Ataxic Gait
In this chapter, we will focus on ataxic gait due to cerebellar circuitry. There are eight basic pathological gaits that can be attributed to neurological conditions:. Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range of motion,. Ataxia describes poor muscle control that causes clumsy movements. Although a few studies investigated fgd by instrumented gait analysis, it.
Consensus Paper Ataxic Gait Request PDF
Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range. In this chapter, we will focus on ataxic gait due to cerebellar circuitry. There are eight basic pathological gaits that can be attributed to neurological conditions:. Although a few studies investigated fgd by instrumented gait analysis, it has been. Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced.
Ataxic Gait
Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range of motion,. In this chapter, we will focus on ataxic gait due to cerebellar circuitry. Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range. There are eight basic pathological gaits that can be attributed to neurological conditions:. Ataxia describes poor muscle control that causes clumsy.
Ataxic Gait
Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range. In this chapter, we will focus on ataxic gait due to cerebellar circuitry. There are eight basic pathological gaits that can be attributed to neurological conditions:. Ataxia describes poor muscle control that causes clumsy movements. Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range of.
Ataxic Gait Over 3 RoyaltyFree Licensable Stock Illustrations
Ataxia describes poor muscle control that causes clumsy movements. Although a few studies investigated fgd by instrumented gait analysis, it has been. Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range of motion,. Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range. In this chapter, we will focus on ataxic gait due to cerebellar.
Ataxic Gait Causes, Symptoms, and Management Boundless Home Health
There are eight basic pathological gaits that can be attributed to neurological conditions:. Although a few studies investigated fgd by instrumented gait analysis, it has been. Ataxia describes poor muscle control that causes clumsy movements. In this chapter, we will focus on ataxic gait due to cerebellar circuitry. Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range.
Analysis of ataxic gait in the taiep rat. Stepping pattern and limb
In this chapter, we will focus on ataxic gait due to cerebellar circuitry. Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range. Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range of motion,. Ataxia describes poor muscle control that causes clumsy movements. Although a few studies investigated fgd by instrumented gait analysis, it has.
(PDF) Change of Gait Pattern of Patients with Ataxic Gait by Cerebellar
Although a few studies investigated fgd by instrumented gait analysis, it has been. Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range. Ataxia describes poor muscle control that causes clumsy movements. Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range of motion,. There are eight basic pathological gaits that can be attributed to neurological.
Ataxic Gait
In this chapter, we will focus on ataxic gait due to cerebellar circuitry. Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range of motion,. Ataxia describes poor muscle control that causes clumsy movements. Ataxic gait is characterized by increased step width, reduced ankle joint range. Although a few studies investigated fgd by instrumented gait analysis, it has.
Ataxic Gait Is Characterized By Increased Step Width, Reduced Ankle Joint Range.
Although a few studies investigated fgd by instrumented gait analysis, it has been. There are eight basic pathological gaits that can be attributed to neurological conditions:. Ataxia describes poor muscle control that causes clumsy movements. In this chapter, we will focus on ataxic gait due to cerebellar circuitry.