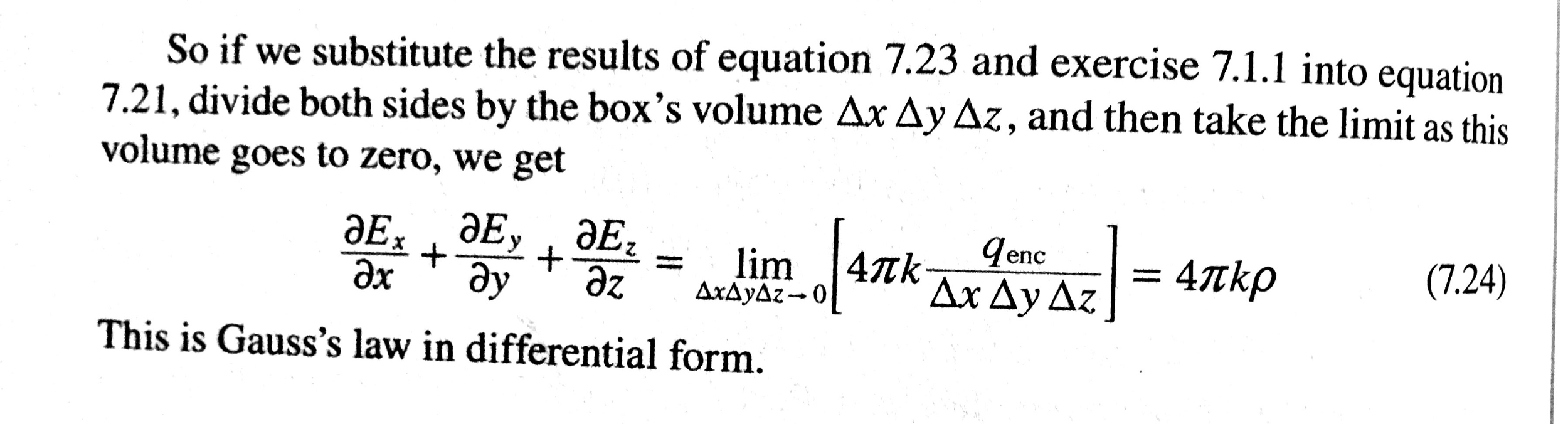Differential Form Of Gauss's Law - The differential (“point”) form of gauss’ law for magnetic fields (equation \ref{m0047_eglmd}). Gauss’ law in differential form (equation 5.7.3) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating. (1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and differential. Gauss’ law in differential form (equation \ref{m0045_egldf}) says that the electric flux per. This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. We therefore refer to it as the differential form of gauss' law, as opposed to φ =.
Gauss’ law in differential form (equation 5.7.3) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating. The differential (“point”) form of gauss’ law for magnetic fields (equation \ref{m0047_eglmd}). We therefore refer to it as the differential form of gauss' law, as opposed to φ =. (1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and differential. This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. Gauss’ law in differential form (equation \ref{m0045_egldf}) says that the electric flux per.
The differential (“point”) form of gauss’ law for magnetic fields (equation \ref{m0047_eglmd}). (1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and differential. Gauss’ law in differential form (equation \ref{m0045_egldf}) says that the electric flux per. We therefore refer to it as the differential form of gauss' law, as opposed to φ =. This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. Gauss’ law in differential form (equation 5.7.3) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating.
gauss's law in differential form r/PhysicsStepByStep
(1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and differential. The differential (“point”) form of gauss’ law for magnetic fields (equation \ref{m0047_eglmd}). Gauss’ law in differential form (equation 5.7.3) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating. Gauss’ law in differential form (equation \ref{m0045_egldf}) says that the electric flux per. This conclusion is the.
Gauss's Law Integral & Differential Electricity
Gauss’ law in differential form (equation 5.7.3) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating. (1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and differential. This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. Gauss’ law in differential form (equation \ref{m0045_egldf}) says that the electric flux per. The.
Solved BOX 7.1 Gauss's Law in Integral and Differential Form
This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. The differential (“point”) form of gauss’ law for magnetic fields (equation \ref{m0047_eglmd}). Gauss’ law in differential form (equation 5.7.3) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating. We therefore refer to it as the differential form of gauss' law, as opposed to φ =..
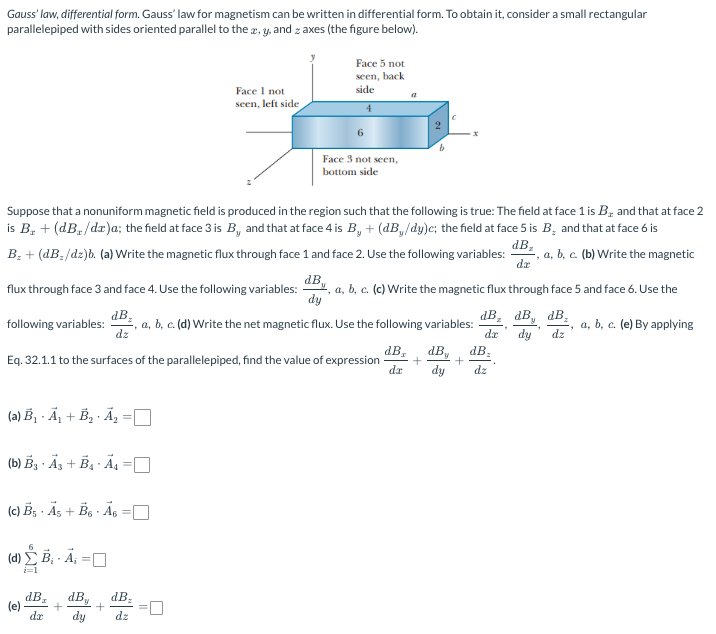
Solved Gauss' law, differential form. Gauss' law for
We therefore refer to it as the differential form of gauss' law, as opposed to φ =. (1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and differential. The differential (“point”) form of gauss’ law for magnetic fields (equation \ref{m0047_eglmd}). This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. Gauss’.
Solved Gauss's law in differential form relates the electric
This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. Gauss’ law in differential form (equation 5.7.3) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating. We therefore refer to it as the differential form of gauss' law, as opposed to φ =. (1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the.
Solved Using the differential form of Gauss's law, determine
This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. We therefore refer to it as the differential form of gauss' law, as opposed to φ =. (1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and differential. Gauss’ law in differential form (equation \ref{m0045_egldf}) says that the electric flux per..
electrostatics Problem in understanding Differential form of Gauss's
We therefore refer to it as the differential form of gauss' law, as opposed to φ =. Gauss’ law in differential form (equation 5.7.3) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating. (1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and differential. The differential (“point”) form of gauss’ law for magnetic fields (equation \ref{m0047_eglmd})..
Gauss's Law And Its Application Unifyphysics
(1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and differential. This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. We therefore refer to it as the differential form of gauss' law, as opposed to φ =. Gauss’ law in differential form (equation 5.7.3) says that the electric flux per.
Differential Integral Form Gauss Law Stock Vector (Royalty
This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. Gauss’ law in differential form (equation \ref{m0045_egldf}) says that the electric flux per. The differential (“point”) form of gauss’ law for magnetic fields (equation \ref{m0047_eglmd}). We therefore refer to it as the differential form of gauss' law, as opposed to φ =. Gauss’ law in.
Gauss's Law And Its Application Unifyphysics
We therefore refer to it as the differential form of gauss' law, as opposed to φ =. Gauss’ law in differential form (equation 5.7.3) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating. This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. (1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the.
This Conclusion Is The Differential Form Of Gauss' Law, And Is One Of Maxwell's Equations.
Gauss’ law in differential form (equation 5.7.3) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating. (1) in the following part, we will discuss the difference between the integral and differential. We therefore refer to it as the differential form of gauss' law, as opposed to φ =. The differential (“point”) form of gauss’ law for magnetic fields (equation \ref{m0047_eglmd}).